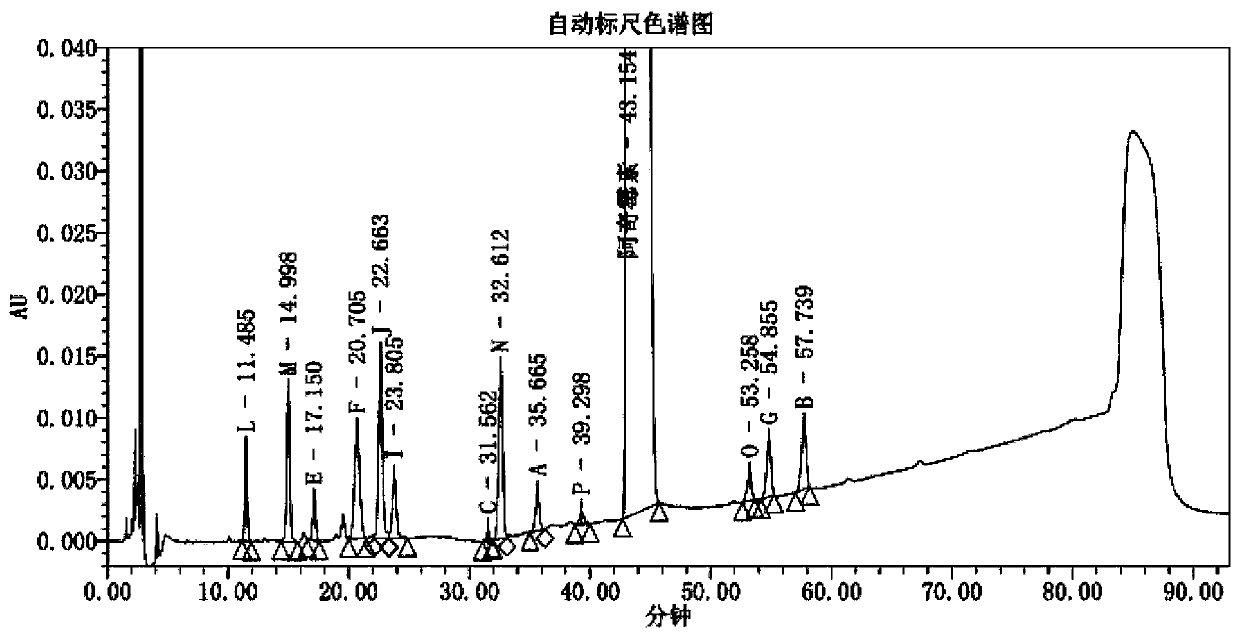
Method for detecting azithromycin capsule related impurities
A technology of azithromycin and detection method, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems such as the increase of the organic phase ratio, the fluctuation of the column pressure and the enlargement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0112] The instrument and chromatographic conditions adopted are as follows:
[0113] High performance liquid chromatography: Waters 2695+2998;
[0114] Chromatographic column: Waters XTerra MS C18 column (4.6mm×250mm, 5μm);
[0115] Mobile phase A: methanol-acetonitrile (1:3);
[0116] Mobile phase B: 1.74g / L (0.01mol / L) anhydrous dipotassium hydrogen phosphate solution (use phosphoric acid with a volume ratio of 10%, or potassium hydroxide solution with a mass volume ratio of 10%, to adjust the pH to 8.9);
[0117] Perform gradient elution as shown in Table 3 of the mobile phase;
[0118] Table 3 Example 2 gradient elution table
[0119]
[0120] Detection wavelength: 210nm;
[0121] Column temperature: 60°C;
[0122] Flow rate: 1.0ml / min;
[0123] Injection volume: 50μL;
[0124] Diluent: ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution (weigh 1.73g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, add water to dissolve and dilute to 1000ml, use ammonia test solution to adjust the pH value...
Embodiment 3
[0134] The instrument and chromatographic conditions adopted are as follows:
[0135] High performance liquid chromatography: Shimadzu LC-16PDA;
[0136] Chromatographic column: Waters XTerra MS C18 column (4.6mm×250mm, 5μm)
[0137] Mobile phase A: methanol-acetonitrile (1:3);
[0138] Mobile phase B: 1.74g / L (0.01mol / L) anhydrous dipotassium hydrogen phosphate solution (use phosphoric acid with a volume ratio of 10%, or potassium hydroxide solution with a mass volume ratio of 10%, to adjust the pH to 8.9);
[0139] The mobile phase carries out gradient elution as shown in Table 5;
[0140] Table 5 Example 3 gradient elution table
[0141]
[0142] Detection wavelength: 210nm;
[0143] Column temperature: 60°C;
[0144] Flow rate: 1.0ml / min;
[0145] Injection volume: 50μL;
[0146] Diluent: ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution (weigh 1.73g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, add water to dissolve and dilute to 1000ml, use ammonia test solution to adjust the pH valu...
Embodiment 4
[0156] The instrument and chromatographic conditions adopted are as follows:
[0157] High performance liquid chromatography: Shimadzu LC-16PDA;
[0158] Chromatographic column: Waters XTerra MS C18 column (4.6mm×250mm, 5μm);
[0159] Mobile phase A: methanol-acetonitrile (1:3);
[0160] Mobile phase B: 0.005mol / L anhydrous dipotassium hydrogen phosphate solution (use phosphoric acid with a volume ratio of 10%, or potassium hydroxide solution with a mass volume ratio of 10%, to adjust the pH to 8.9);
[0161] The mobile phase carries out gradient elution as shown in Table 7;
[0162] Table 7 Example 4 gradient elution table
[0163]
[0164]
[0165] Detection wavelength: 210nm;
[0166] Column temperature: 60°C;
[0167] Flow rate: 1.0ml / min;
[0168] Injection volume: 50μL;
[0169] Diluent: ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution (weigh 1.73g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, add water to dissolve and dilute to 1000ml, use ammonia test solution to adjust the pH ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com