Method of utilizing caprolactam waste alkalis to prepare sodium fluoride and white carbon black
A technology of caprolactam and sodium fluoride, applied in the directions of alkali metal fluoride, silicon oxide, silicon dioxide, etc., can solve the problems of narrow use of sodium fluorosilicate, high cost, waste of fluorine resources, etc., and achieve easy washing, removal, adsorption, etc. Moderate effect and high stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
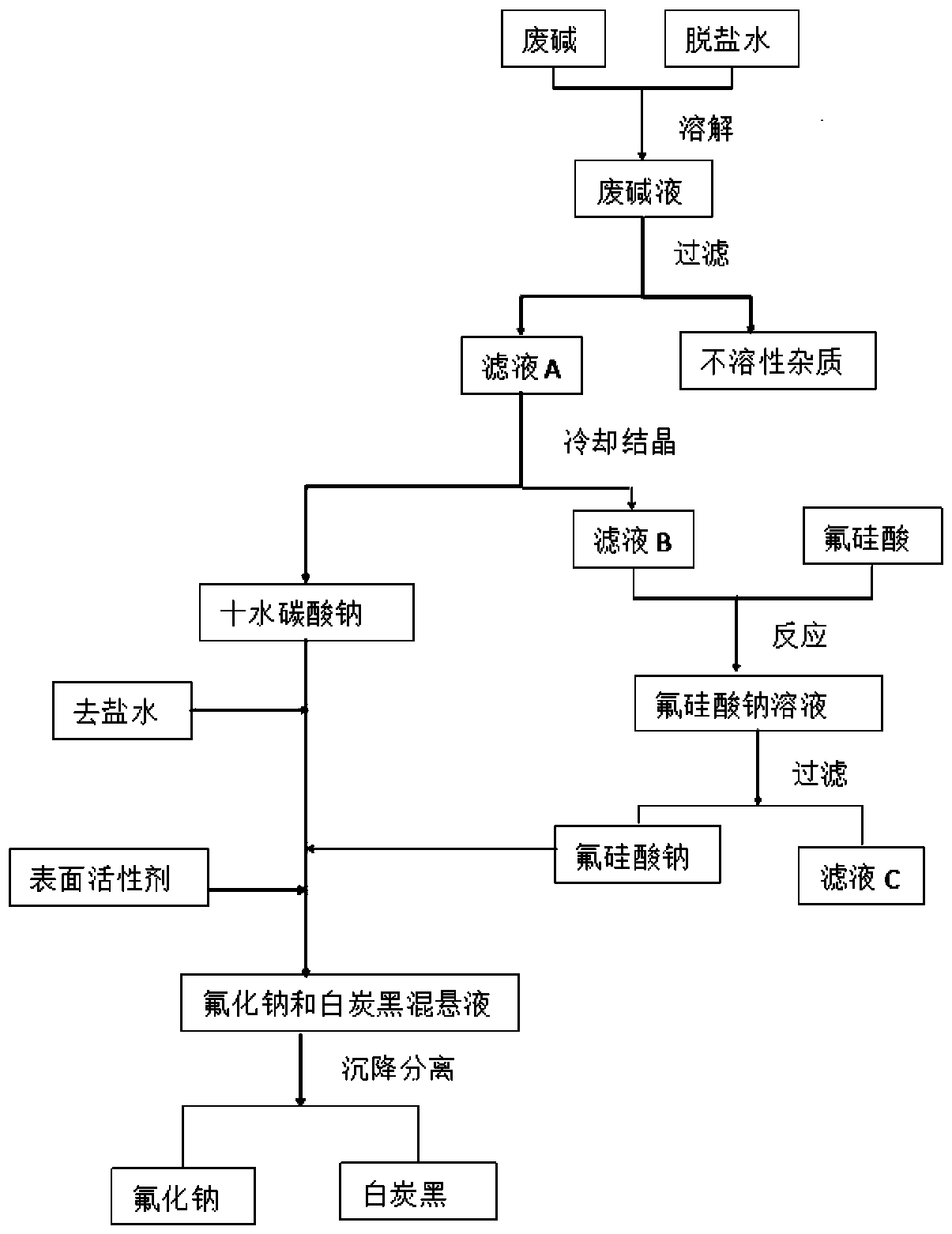
[0031] like figure 1 As shown, weigh 100g of spent caustic soda (80wt% of sodium carbonate and 18wt% of sodium sulfate), add 120g of desalted water and mix, heat to 60°C, stir and dissolve into spent caustic soda. Keep warm at 60°C, filter while hot, remove insoluble impurities, and obtain filtrate A. The filtrate A was cooled to 20°C for cooling and crystallization for 2 hours, and the fine slurry formed by cooling and crystallization was filtered under reduced pressure to obtain 45 g of sodium carbonate decahydrate crystals and filtrate B.
[0032] Add 20g of fluorosilicic acid to the filtrate B while stirring, and the sodium carbonate and sodium sulfate in the filtrate B react with the fluorosilicic acid to generate sodium fluorosilicate and the corresponding acid. After the reaction, grow crystals, wash and separate 26 g of sodium fluorosilicate crystals and filtrate C, and filtrate C is recycled for reuse.
[0033] Mix the sodium fluorosilicate crystals and sodium carbo...
Embodiment 2
[0041]Weigh 100g of spent caustic soda (including 75% sodium carbonate and 24% sodium sulfate), add 180g of desalted water and mix, heat to 45°C, stir and dissolve to form spent caustic soda. Keep warm at 45°C, filter while hot, remove insoluble impurities, and obtain filtrate A. The filtrate A was cooled to 15°C for cooling and crystallization for 2 hours, and the fine slurry formed by cooling and crystallization was filtered under reduced pressure to obtain 27 g of sodium carbonate decahydrate crystals and filtrate B.
[0042] Add 25g of fluorosilicic acid to the filtrate B under stirring, and the sodium carbonate and sodium sulfate in the filtrate B react with the fluorosilicic acid to generate sodium fluorosilicate and the corresponding acid. After the reaction, grow crystals, wash and separate 30 g of sodium fluorosilicate crystals and filtrate C, and filtrate C is recycled for reuse.
[0043] Mix the sodium fluorosilicate crystals obtained in the above steps with the so...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Weigh 100g of spent caustic soda (including 67% sodium carbonate and 30% sodium sulfate), add 150g desalted water and mix, heat to 55°C, stir and dissolve to form spent caustic lye. Keep warm at 55°C, filter while hot, remove insoluble impurities, and obtain filtrate A. The filtrate A was cooled to 12°C for cooling and crystallization for 2 hours, and the fine slurry formed by cooling and crystallization was filtered under reduced pressure to obtain 20 g of sodium carbonate decahydrate crystals and filtrate B.
[0047] Add 18g of fluorosilicic acid to the filtrate B under stirring, and the sodium carbonate and sodium sulfate in the filtrate B react with the fluorosilicic acid to generate sodium fluorosilicate and the corresponding acid. After the reaction, grow crystals, wash and separate 22 g of sodium fluorosilicate crystals and filtrate C, and filtrate C is recycled for reuse.
[0048] Mix the sodium fluorosilicate crystals obtained in the above steps with the sodiu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com