Method for identifying self-compatibility of diploid potato
A diploid and potato technology, applied in the field of genetic breeding, can solve the problems of time-consuming and labor-intensive identification methods, inaccurate representation, and affecting plants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] A method for identifying whether diploid potatoes are self-compatible, comprising the following steps:
[0103] (1) Genome resequencing of parent materials RH89-039-16 and PI 225689:
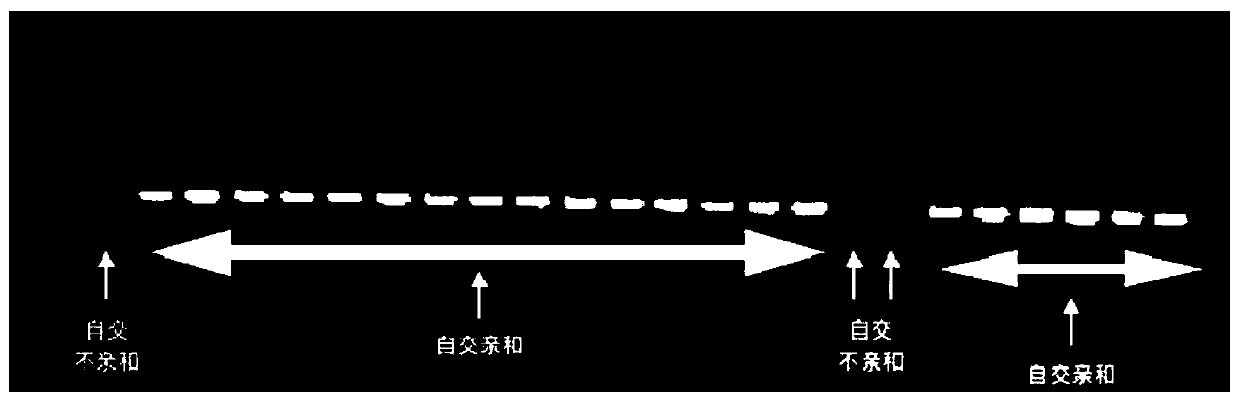
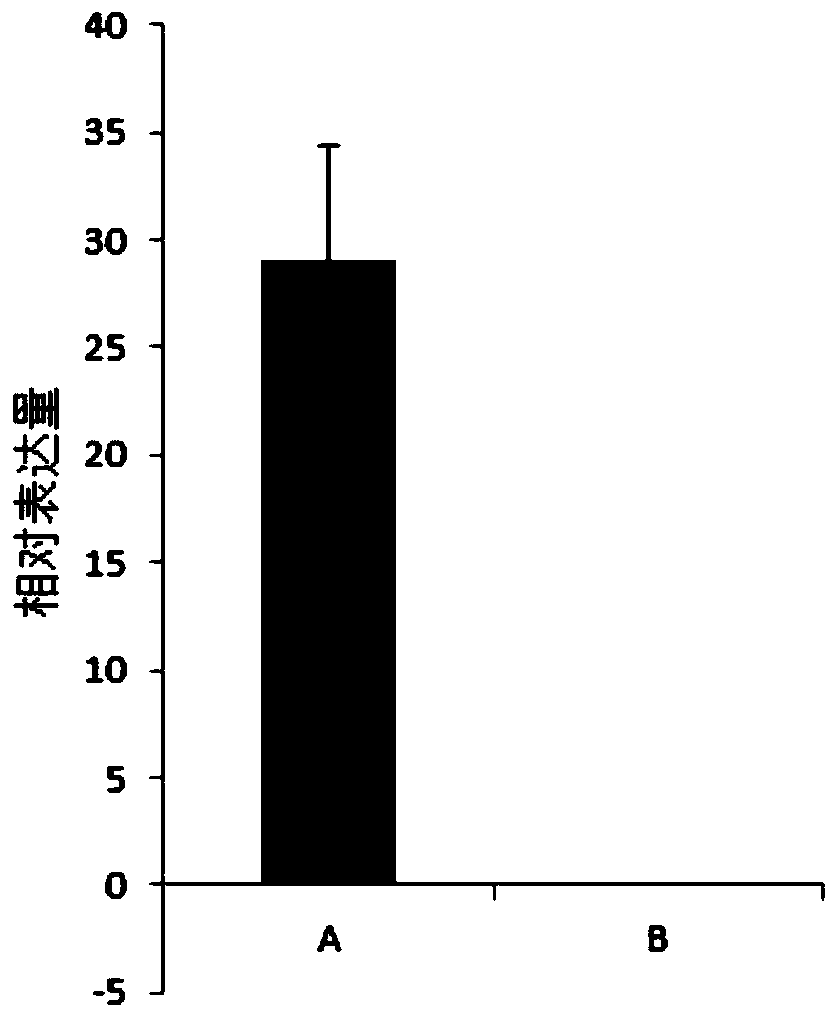
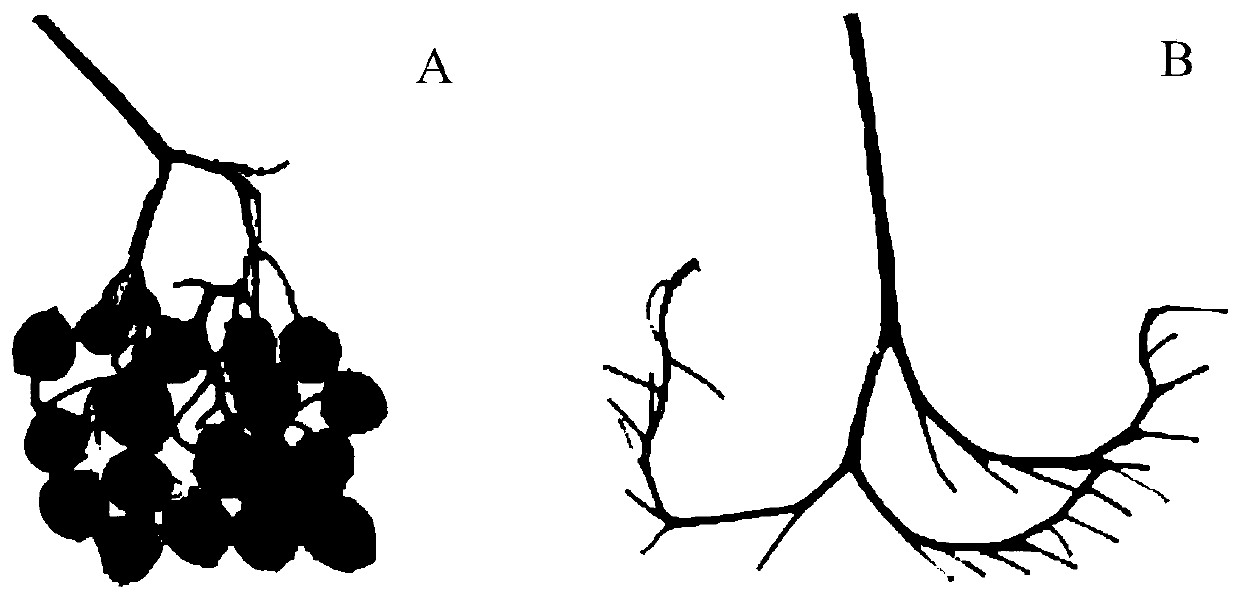
[0104] RH89-039-16 is a self-compatible diploid potato material, and PI 225689 is a self-incompatible diploid potato material. After crossing these two materials as parents, the offspring appeared self-compatibility Separated from the self-incompatibility trait, in order to accurately identify the self-compatibility phenotype of the offspring, the genome resequencing of the parent material RH89-039-16 and PI 225689 was performed to obtain the sequence information of the two materials.
[0105] (2) Develop molecular markers co-segregated with StSCI gene in parent material RH89-039-16 and PI 225689:
[0106] Comparing the sequence information of the chromosomal segment containing the StSCI gene in the parent material RH89-039-16 and PI 225689, it was found that a 538bp (SEQ ID NO.2) nucleo...
Embodiment 2
[0129] A method for screening molecular markers for identifying whether diploid potatoes are self-compatible, comprising the following steps:
[0130] (1) Obtain the genome sequence information of the parent material:
[0131] The self-compatible diploid potato RH89-039-16 and the self-incompatible diploid potato PI225689 were used as parental materials to obtain hybrid offspring, and the genomes of RH89-039-16 and PI225689 were resequenced to obtain genome sequence information;
[0132] (2) Screening for single-base differential sites in parental materials:
[0133] By analyzing the nucleotide sequence of the StSCI gene and the linked nucleotide sequence of the StSCI gene, it was found that RH89-039-16 at 58030614 bp on chromosome 12 is a T base, while the corresponding position on the PI 225689 material is a C base;
[0134] The StSCI gene has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the genetic distance of gene linkage is less than 20cM;
[0135] (3) Design KASP mo...
Embodiment 3
[0140] A method for screening molecular markers for identifying whether diploid potatoes are self-compatible, comprising the following steps:
[0141] (1) Obtain the genome sequence information of the parent material:
[0142] The self-compatible diploid potato RH89-039-16 and the self-incompatible diploid potato PI225689 were used as parental materials to obtain hybrid offspring, and the genomes of RH89-039-16 and PI225689 were resequenced to obtain genome sequence information;
[0143] (2) Screening for indel markers in parental materials:
[0144] By analyzing the nucleotide sequence of the StSCI gene and the linked nucleotide sequence of the StSCI gene, it was screened that at chromosome 12 58136285, RH89-039-16 lacked 11 bp of base sequence relative to PI 225689;
[0145] The StSCI gene has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the genetic distance of gene linkage is less than 20cM;
[0146] (3) Design InDel molecular markers:
[0147] Appropriate primer fragm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com