Modified silicate grounding module and manufacturing method and manufacturing mold thereof
A technology of Portland and Portland cement, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, contact parts, connecting contact materials, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient contact between metal materials and soil, inadequate anti-corrosion measures for welding parts, and accelerated internal metal materials. Corrosion and other problems, to achieve superior thermal stability, save manpower and material resources, and increase corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
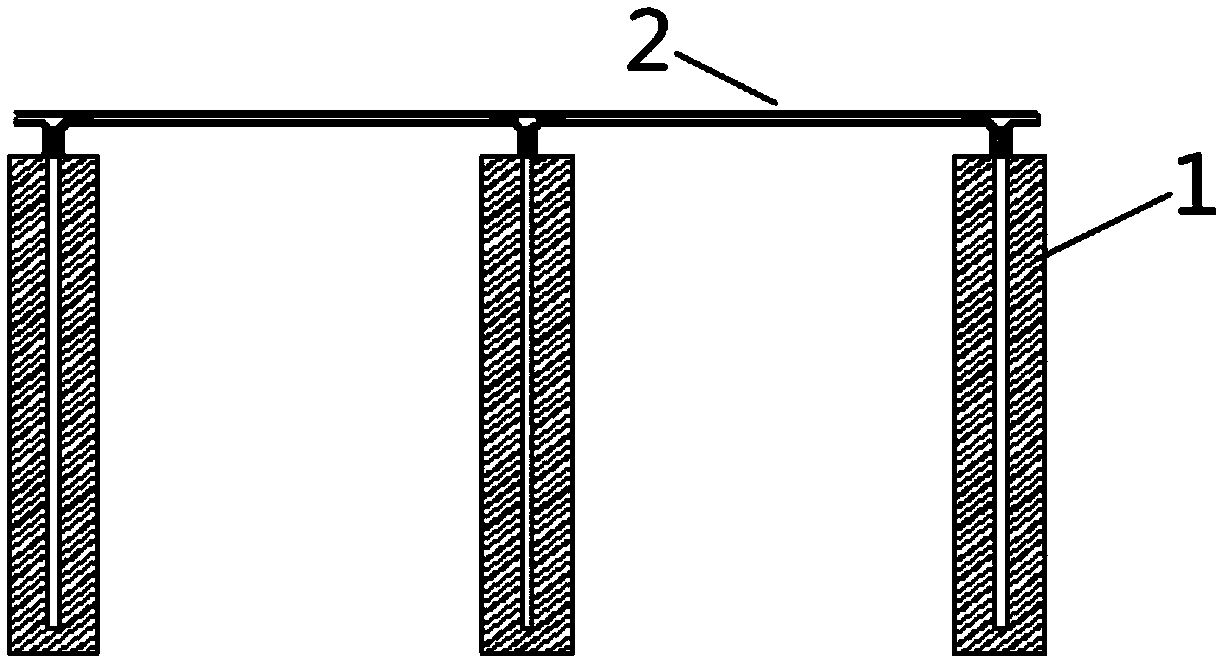
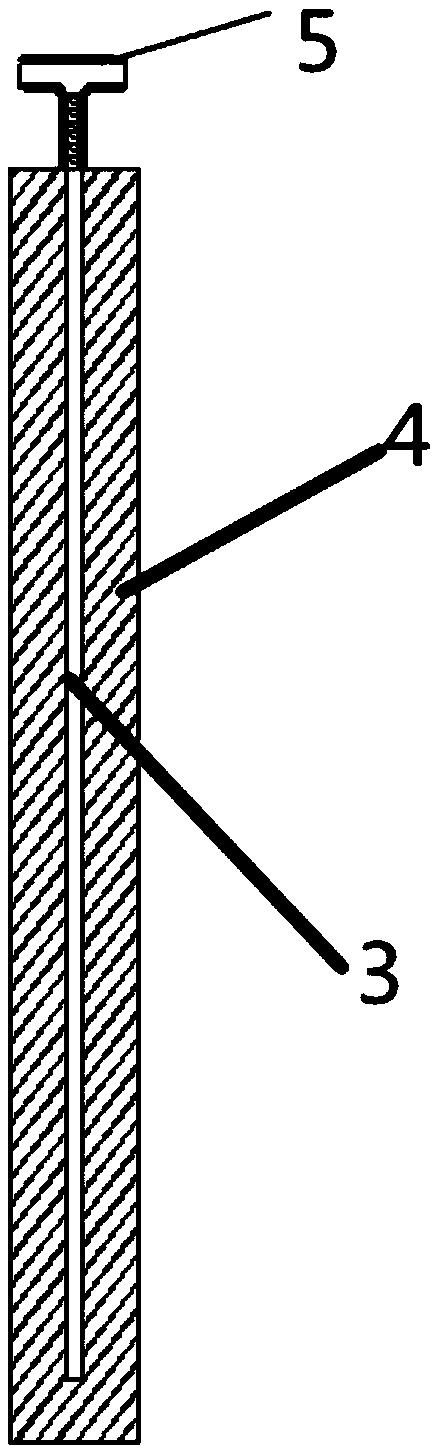
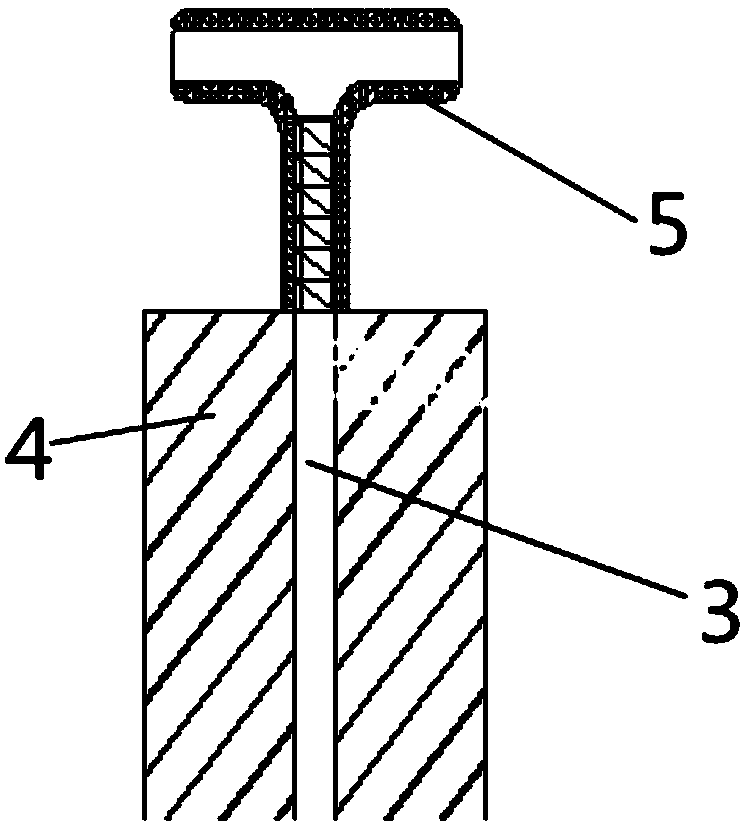
[0049] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 5 As shown, the present invention provides a modified silicate grounding module, which includes a grounding module 1 sequentially connected by a connecting wire 2; the module 1 includes a metal core material 3 and covers the metal core The modified silicate composite layer 4 of the material 3; the upper end of the metal core 3 penetrates the modified silicate composite layer 4 and is connected to the connection wire 2 through a connecting piece.
[0050] The modified silicate composite layer 4 includes the following components by mass fraction:
[0051] Portland cement: 20%, bentonite: 15%, graphite: 5%, nano-carbon fiber 5%, stainless steel fiber: 10% and polyacrylamide 5%.
[0052] The modified silicate composite layer 4 is columnar, and its cross-section is square.
[0053] The metal core material 3 is columnar, and the ratio of the cross-sectional area of the metal core material 3 to the cross-sectional area of the modified silicate c...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The structure of this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the composition ratio of the modified silicate composite layer 4, the cross-sectional area of the metal core material 3 and the composite of the modified silicate The ratio of the cross-sectional area of layer 4 and the angle between adjacent connecting lines 2:
[0059] The modified silicate composite layer 4 includes the following components by mass fraction:
[0060] Portland cement: 35%, bentonite: 20%, graphite: 10%, nano-carbon fiber 1%, stainless steel fiber: 5% and polyacrylamide 1%.
[0061] The metal core material 3 is columnar, and the ratio of the cross-sectional area of the metal core material 3 to the cross-sectional area of the modified silicate composite layer 4 is 1:15.
[0062] The included angle between adjacent connecting lines 2 is 180°.
Embodiment 3
[0064] The structure of this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the composition ratio of the modified silicate composite layer 4, the cross-sectional area of the metal core material 3 and the composite of the modified silicate The ratio of the cross-sectional area of layer 4 and the angle between adjacent connecting lines 2:
[0065] The modified silicate composite layer 4 includes the following components by mass fraction:
[0066] Portland cement: 25%, bentonite: 17%, graphite: 7%, nano-carbon fiber 2%, stainless steel fiber: 6% and polyacrylamide 2%.
[0067] The metal core material 3 is columnar, and the ratio of the cross-sectional area of the metal core material 3 to the cross-sectional area of the modified silicate composite layer 4 is 1:20.
[0068] The included angle between adjacent connecting lines 2 is 120°.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com