Culture-in-vitro method for mouse early embryo
An in vitro culture and embryo technology, applied in embryo cells, culture process, tissue culture, etc., can solve the problem of unclear changes in transcriptomics, and achieve the effect of improving the rate of high-quality embryos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
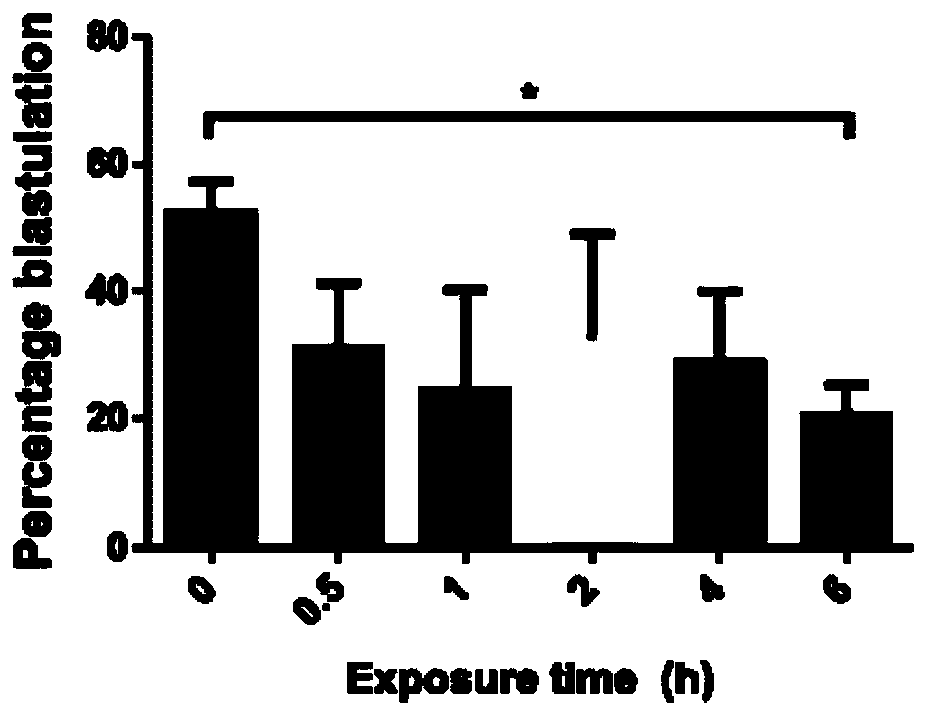
[0017] 1. We collected mouse embryos at the 2-cell stage for different light treatment times. The specific numbers are as follows: no light treatment (0 hours) 227, 0.5 hours 102, 1 hour 98, 2 hours 103, 4 hours 104 and 118 in 6 hours.
[0018] 2. Treat mouse embryos at the 2-cell stage according to different light times, and continue to culture in the dark in a 37-degree Celsius incubator after the treatment is completed.
[0019] 3. Counting the blastocyst generation rate of mice treated with each light time, we found that the blastocyst rate decreased significantly after 6 hours of treatment. The results are as follows figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
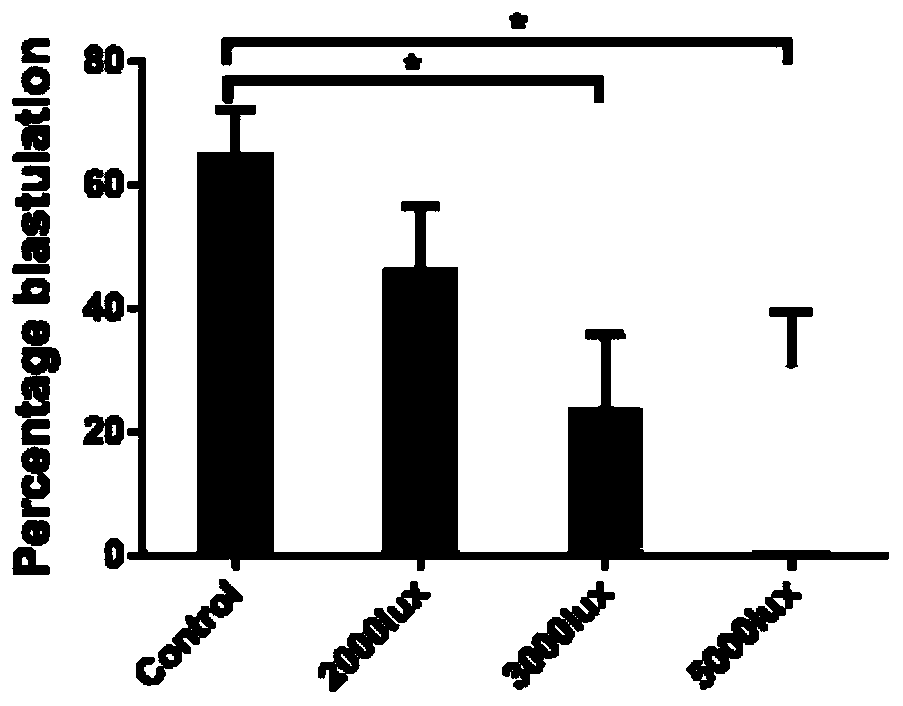
[0021] 1. We collected mouse embryos at the 2-cell stage for different light intensities, and the specific numbers were as follows: no light treatment (0 lux) 332, 2000 lux 131, 3000 lux 152, 5000 lux 191.
[0022] 2. Treat mouse embryos at the 2-cell stage according to different light intensities, and continue to culture in the dark in a 37-degree Celsius incubator after the treatment is completed.
[0023] 3. Counting the blastocyst formation rate of mice treated with each light intensity, we found that the blastocyst rate decreased significantly after 6 hours of treatment. The results are as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0024] 4. Statistics on the morphology of mouse blastocysts treated with each light intensity, the results are as follows image 3 shown.
[0025] 5. Count the diameter of mouse blastocysts treated with each light intensity, and the results are as follows Figure 4 as shown,
Embodiment 3
[0027] 1. We collected the light group (5000 lux light for 6 hours at the 2-cell stage mouse embryo) and the non-light group mouse embryo cells at various stages, and used the Smart-seq2 single-cell transcriptome high-throughput sequencing method, and compared the sequences, Expression calculation Obtain single-cell transcriptome expression data.
[0028] 4. Comparing the principal components of single-cell transcriptomes in the light group and the non-light group in each period, it was found that there were large differences in the transcriptomes of the light group and the non-light group in each period, and they gathered in different positions, such as Figure 5 shown.
[0029] 5. Comparing the differential genes in the transcriptome of single cells in each period between the light group and the non-light group, and performing enrichment analysis of the G0 signaling pathway on these differential genes ( Figure 6 A-E), it was found that the transcriptional regulation (DNA t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com