Application of Epimedin B to preparation of medicines for treating neuroinflammation
A technology of neuroinflammation and epimedin, applied in the fields of cell biology and pharmacology, can solve the problems of epimedin B neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases that have not yet been seen, achieve high clinical application value and development prospects, reduce Expression, reducing the effect of dopaminergic neuron damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
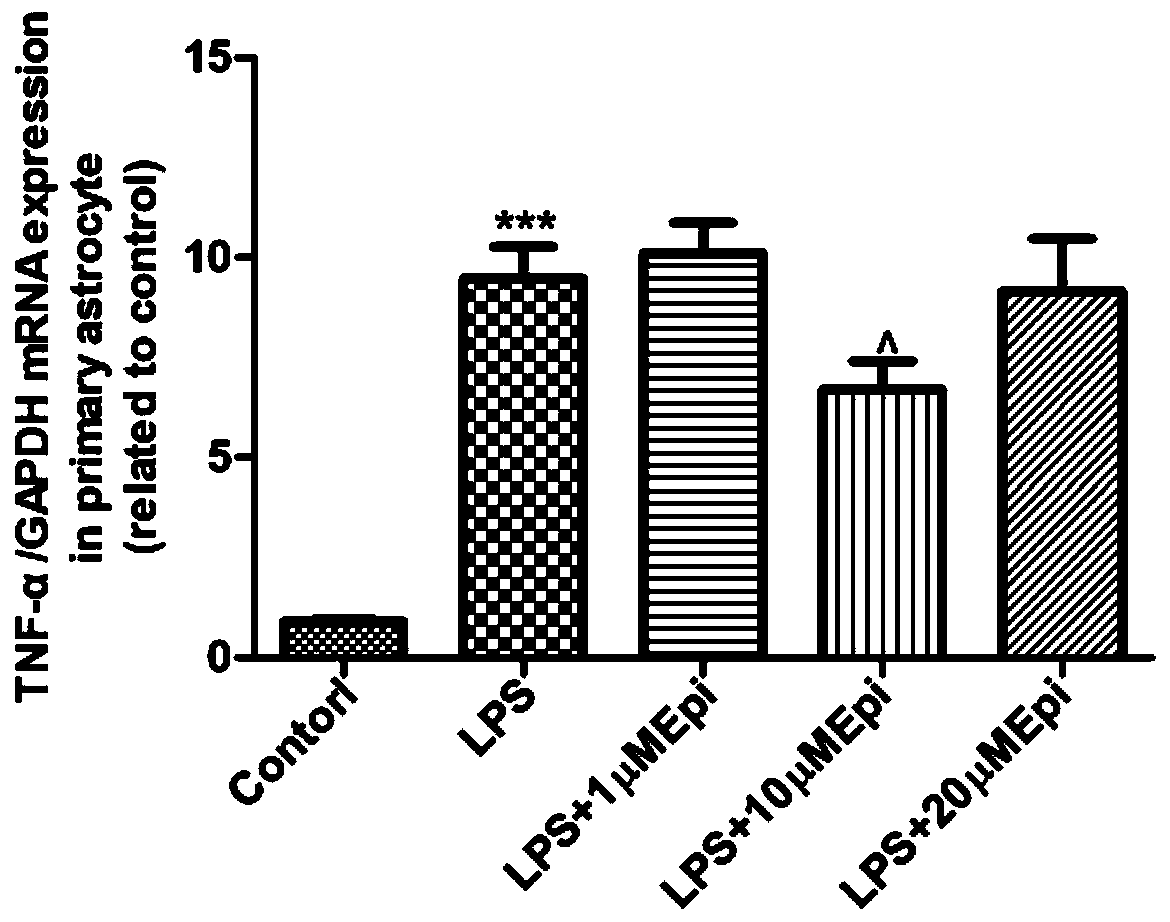
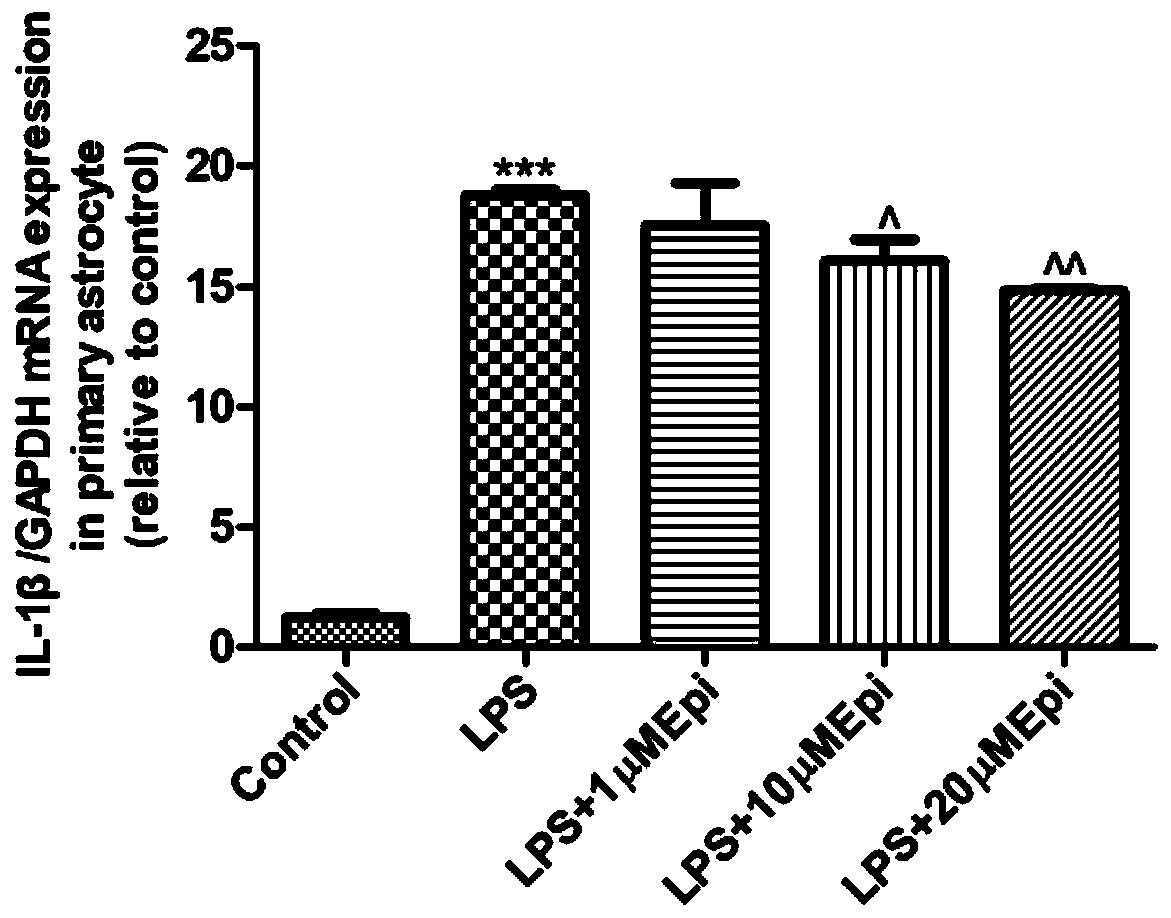
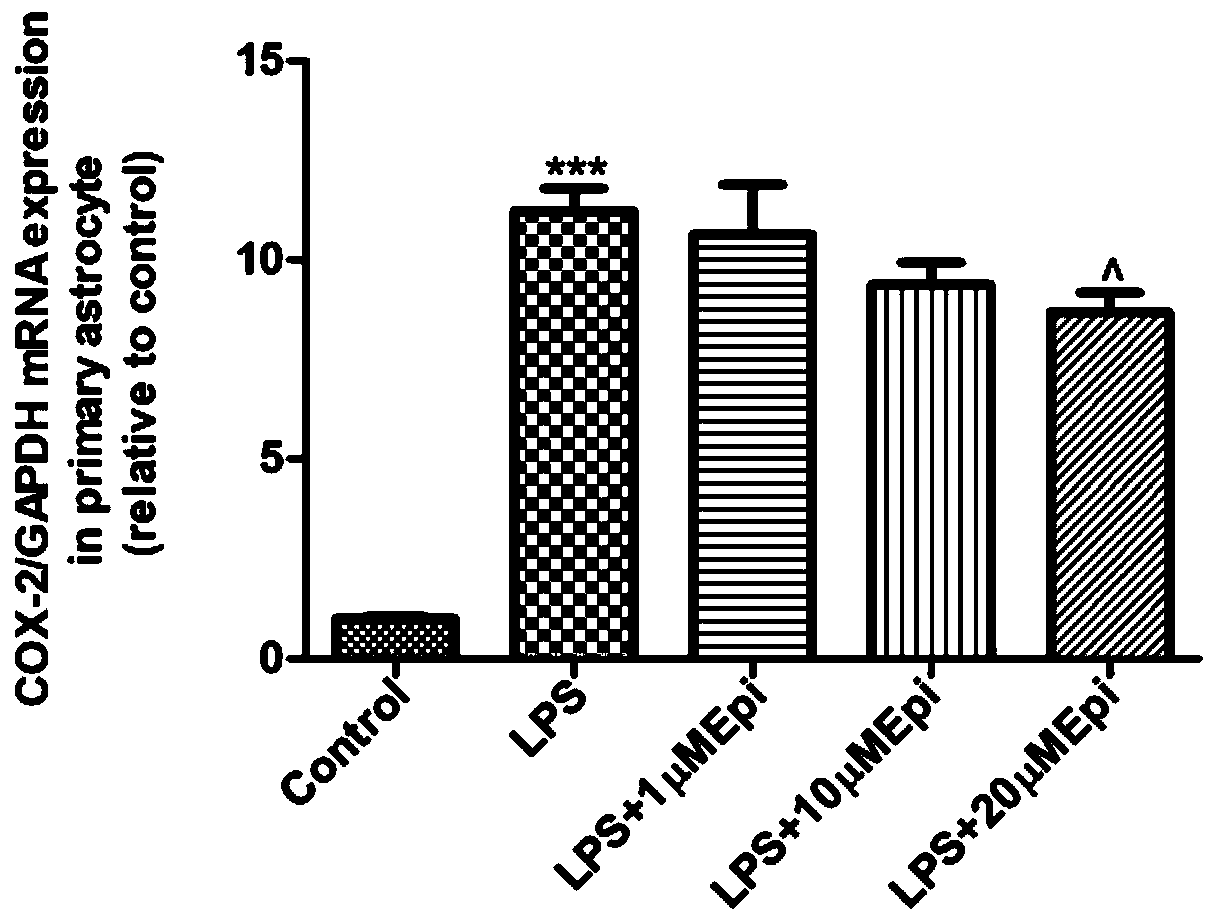
[0033] Example 1. Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR technology detects the inhibitory effect of different concentrations of Epimedin B on the inflammatory response of primary astrocytes induced by LPS
[0034] 1. Materials and methods
[0035] (1) Culture of primary microglia and astrocytes in the midbrain
[0036] Select newborn SD rats (SPF grade) within 1-2 days after birth, immerse them in 75% alcohol for disinfection for 15 seconds, take out the whole brain in an aseptic operating table, separate the midbrain, wash 3 times with sterilized PBS, and Gently peel off the meninges and blood vessels, avoiding damage to the brain tissue. Cut the tissue into small pieces, blow the tissue gently with 1000 μL, 200 μL, and 10 μL pipette tips in turn to disperse the cells, collect the cell suspension into a large centrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 5 min. Discard the supernatant, then add DMEM / F12 complete medium (containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100IU / mL penici...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2. Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR technology detects the mechanism of action of Epimedin B in inhibiting the inflammatory response of primary astrocytes
[0061] G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), as a new type of membrane estrogen receptor, plays an important role in the treatment of inflammation. GPER-specific blocker G15 and Epimedin B co-treated cells to detect its Effects on astroglial inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-1β as well as iNOS and COX-2 gene expression.
[0062] After culturing the rat midbrain astrocytes by the same method as in Example 1, when the cell density in the six-well plate reaches 80%-90%, the drug can be added for treatment. Experimental groups 4 and 5 were pretreated with 10 μM Epimedin B for 1 hour, and then added LPS (final concentration 1 μg / ml) to act together for 6 hours; G15 was added 1 hour before Epimedin B pretreatment, and then added LPS together Works for 6 hours. Total mRNA was extracted according to t...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3. Detection of the inhibitory effect of Epimedin B on the inflammatory response of primary microglial cells induced by LPS and the blocking effect of G15 on this effect by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR technology
[0070] The inflammatory response caused by excessive activation of microglia can invade dopaminergic neurons, causing progressive damage and loss of neurons. The inflammatory factors released by microglia can also activate astrocytes, promote the aggravation of the inflammatory response, and damage neurons. The distribution density of microglia in the substantia nigra is very high, and inflammatory factors can damage dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra over time, so inflammation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of PD.
[0071] In this example, cells were co-treated with GPER-specific blocker G15 and Epimedin B, and their effects on gene expression of microglial inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-1β were detected.
[0072]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com