CD44 gene-knocked-out dairy cow mammary epithelial cell line and construction method thereof
A breast epithelial cell and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as siRNA interference and unstable inheritance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
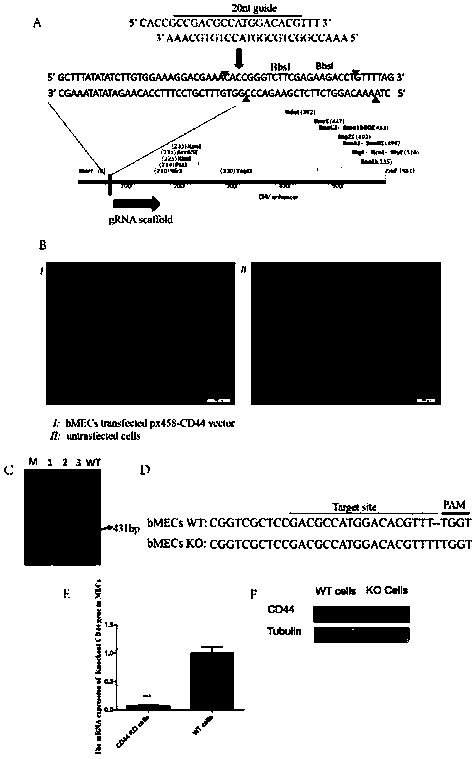
[0041] Example 1 The setting of CD44 gene knockout target site and the design of sgRNA
[0042] First, determine the position of the conserved domain of the CD44 (ENSBTAT00000015381.4) gene protein to better ensure the knockout effect. Design the target sequence to be knocked out in the corresponding coding region, that is, the first exon of the CD44 gene, design sgRNA, and design a pair of recognition sequences (sgRNA), as follows,
[0043] CD44 gRNA: CCGACGCCATGGACACGTTT TGG (SEQ ID NO: 1).
[0044] Design DNA oligos to synthesize double-stranded gRNA, and the specific primer sequences are as follows:
[0045]CD44 gRNA F: CACCGCCGACGCCATGGACACGTTT (SEQ ID NO: 2);
[0046] CD44 gRNA R: AAACAAACGTGTCCATGGCGTCGGC (SEQ ID NO: 3).
[0047] CD44 detection primer F: 5'-CTCCCCTCTTAGGTCACTCTCTCAA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 4);
[0048] CD44 detection primer R: 5'-ACAAAACGGTGCTTCCCAC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 5).
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 Construction of gRNA expression vector
[0050] 1. Experimental method
[0051] Anneal the forward and reverse single-stranded oligonucleotide sequences to obtain a double-stranded oligonucleotide fragment, and connect it with the PX458 vector that was digested by BBSI and linearized to obtain a recombinant plasmid, which is designated as PX458-CD44 -gRNA
[0052] The specific operation is as follows:
[0053] (1) After gRNA synthesis, use ddH 2 The primer (SEQ ID NO: 2-3) was dissolved in O water to 100 μM, and the single-stranded oligonucleotide was annealed to obtain a double-stranded oligonucleotide.
[0054] Annealing reaction system: add 1 μL each of the upstream and downstream primers, ddH 2 O 43 μL, NEB buffer (10×) 5 μL.
[0055] Annealing reaction conditions: React at 95°C for 10 minutes on a PCR instrument, then gradually lower the temperature at a rate of 5°C / min until the temperature drops to 25°C. The annealed primers were diluted 50 times ...
Embodiment 3
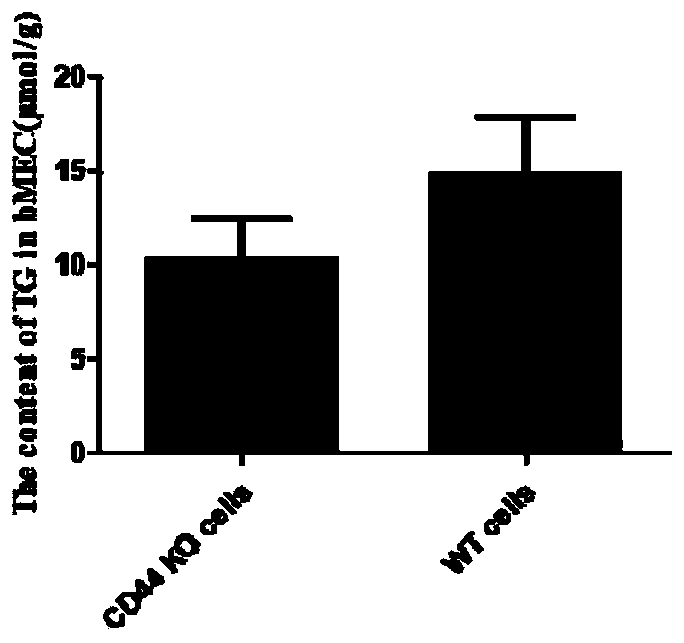
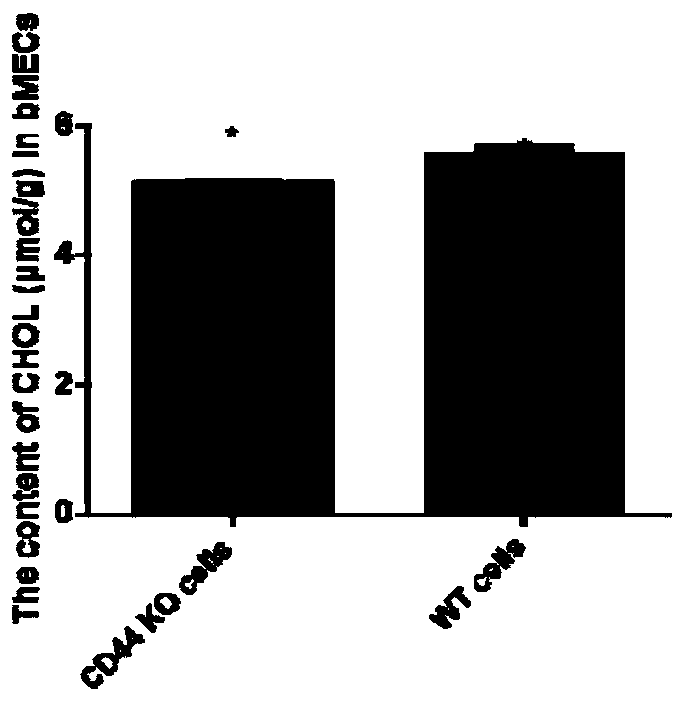
[0065] Construction of Example 3 Knockout Cell Lines
[0066] The recombinant plasmid was transiently transfected into cow mammary gland epithelial cells, a single positive cell expressing green fluorescent protein was screened by flow cytometry, and the positive cell line of CD44 gene knockout was obtained by expanding culture.
[0067] 1. Experimental method
[0068] (1) Transfection of cell lines
[0069] The dairy cow mammary gland epithelial cell line established by the research group was used as the research object. The cells were cultured in a 6-well plate, replaced with fresh DMEM / F12 medium containing 10% FBS, and transfected when the cell confluence reached 80%. .
[0070] Dilute 2.5 μg of recombinant plasmid and 6 μL of Fugene HD transfection reagent into 200 μL of DMEM / F12 medium, mix gently, and after standing for 20 minutes, gently add it dropwise to the cells that have been replaced with fresh medium in advance, and place at 37 Cultivate in a cell incubator a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com