Library-building sequencing method for detecting full length of bacterial 16S rDNA
A full-length, sequencing technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, sequence analysis, chemical library, etc., can solve the problems of inability to accurately determine the ecological structure of environmental microorganisms, inability to detect strain levels, etc., to achieve good fidelity, The effect of accurate ecological structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
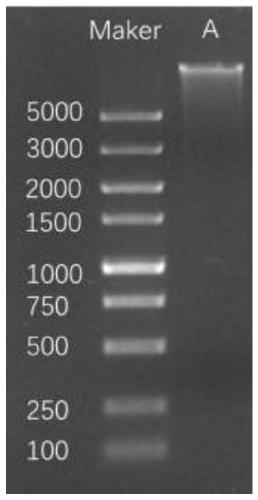
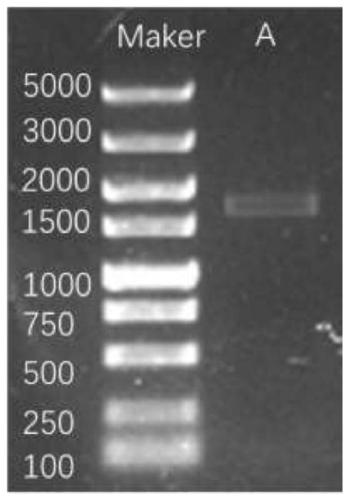
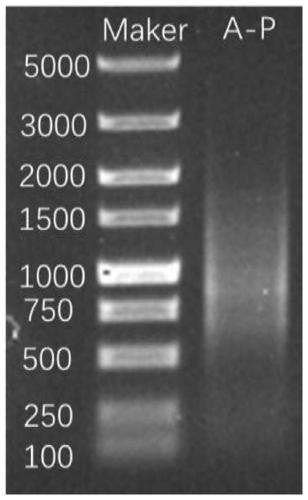
[0047] (1) Extraction of sample DNA
[0048] 1.1 The present invention uses Qiagen's DNeasy PowerSoil Kit to extract total DNA from a stool sample, which is marked as sample A.
[0049] Specific steps:
[0050] a. Shake the collection tube containing 3ml of protective agent stool samples, divide them into two 1.5ml centrifuge tubes, remove the supernatant at 2500g for 10min, transfer the precipitate to the Power Beads Tube with a 1ml wide-mouth pipette tip, and gently vortex to mix.
[0051] b. Add 60μl C1 and vortex for 10min.
[0052] c. Centrifuge at 10000g for 30s.
[0053] d. Transfer the supernatant to a 2ml collection tube.
[0054] e. Add 250μl C2 to the collection tube, shake for 5s, and incubate at 4°C for 5min.
[0055] f. Centrifuge at 10000g for 1 min.
[0056] g. Transfer 600μl of supernatant to a 2ml collection tube.
[0057] h. Add 200μl C3, shake and mix, and incubate at 4°C for 5min.
[0058] i. Centrifuge at 10000g for 1min.
[0059] j. Transfer 750μl of supernatant to a new...
Embodiment 2
[0133] The DNA samples of four known strains (Streptococcus_pneumoniae, Enterococcus_faecalis, Streptococcus_pyogenes, Streptococcus_agalactiae) were mixed according to the abundance of the flora of 1:1:1:1 to form a mock community, using the 16S-FAST technology of the present invention Detect the fidelity of the sample flora abundance. The result is Image 6 Shown from Image 6 The results show that the fidelity of the bacterial population abundance determined by the technology of the present invention is very good, and is basically close to the true ratio.
Embodiment 3
[0135] Using the method of the present invention to detect the 16S full length of the sample as the experimental group, using the V3V4 segment sequencing detection method in the prior art as the control group, comparing the detection results of the two, as shown in Table 2:
[0136] Table 2 Abundance of the top 20 genus of two methods
[0137] Generic name A-V3V4 A-16S Prevotella60.8760.56 Megamonas19.6121.54 Bacteroides5.855.81 Roseburia3.872.72 Faecalibacterium1.501.89 Enterobacter1.360 Sutterella1.172.07 Ruminococcus1.130.68 Clostridium0.860.01 Dorea0.721.08 Parabacteroides0.690.77 Blautia0.600.37 Coprococcus0.580.02 Eubacterium0.311.43 Gemmiger0.150 Bifidobacterium0.080 Klebsiella0.080.32 Butyricicoccus0.070.03 Leuconostoc0.070 others 0.420.7
[0138] From Table 2 and Figure 7 It can be seen that the correlation coefficient R of the abundance of the genus determined by the two methods 2 Is: 0.998, indicating that the genus categories determined by the two...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com