ASO for targeting long-chain non-coding RNA DDX11-AS1 and kit and application thereof in treatment of liver cancer
A technology of RNADDX11-AS1 and DDX11-AS1, which is applied in the field of ASO targeting long-chain non-coding RNA DDX11-AS1, and the application field of liver cancer treatment, can solve the problems of scarcity and limitation of specific targets, and achieve the reduction of expression level, Broad application prospects, the effect of inhibiting proliferation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
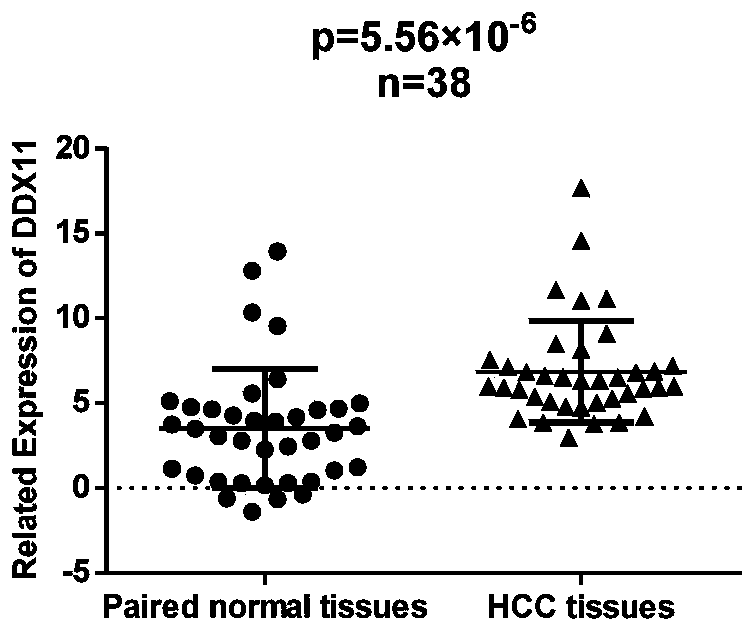
[0035] Example 1: Screening of lncRNA associated with liver cancer
[0036] 1. Sample collection: 38 cases of clinically diagnosed liver cancer and paired liver cancer tissue samples were taken. These samples were surgical resection specimens of patients with liver cancer. The samples were all from the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine. All the above samples were obtained with the approval of the institutional ethics committee of the hospital. Clinical data of tissue samples, including clinical characteristics such as tumor size, capsule, lung metastasis, TNM stage, distant metastasis, histopathological grade, postoperative disease-free survival time and survival time.
[0037] 2. Extraction of total RNA from hepatocellular carcinoma and paired hepatocarcinoma tissues
[0038]Take 100mg of frozen tissue and grind it quickly and fully in liquid nitrogen, add 1mL Trizol and about 1 / 5 volume of chloroform, turn it upside down for 2min, let stand...
Embodiment 2
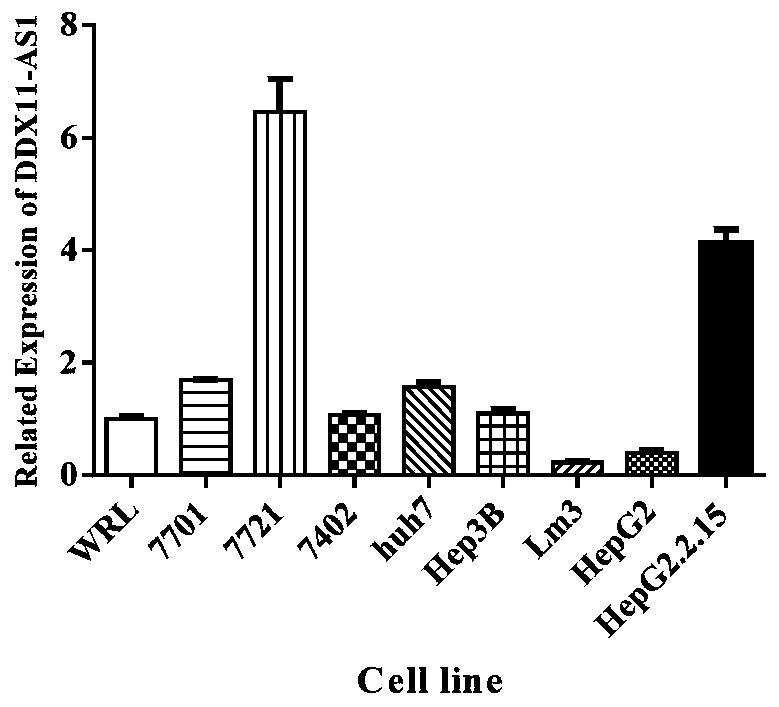
[0043] Example 2: Expression of DDX11-AS1 in liver cancer cell lines
[0044] 1. Cell culture
[0045] The routine culture of SMMC-7721 cell line adopts 1640 cell culture medium containing 10% inactivated fetal bovine serum and 1% double antibody (penicillin-streptomycin); the routine culture of Huh7 cell line adopts the medium containing 10% inactivated fetal bovine serum and 1 % double antibody (penicillin-streptomycin) in DMEM high glucose medium. and placed at 37°C, 5% CO 2 , CO under saturated humidity conditions 2 cultured in an incubator. When the cells are confluent to about 80% of the culture dish, they are subcultured, the original culture medium is sucked out, and an appropriate amount of trypsin (containing phenol red) solution is added to digest the cells. Observe the state of the cells under an inverted microscope. When the cells are round (cytoplasm retracts), aspirate the trypsin, add 1ml of RPMI1640 or DMEM high-glucose complete medium to stop digestion, r...
Embodiment 3
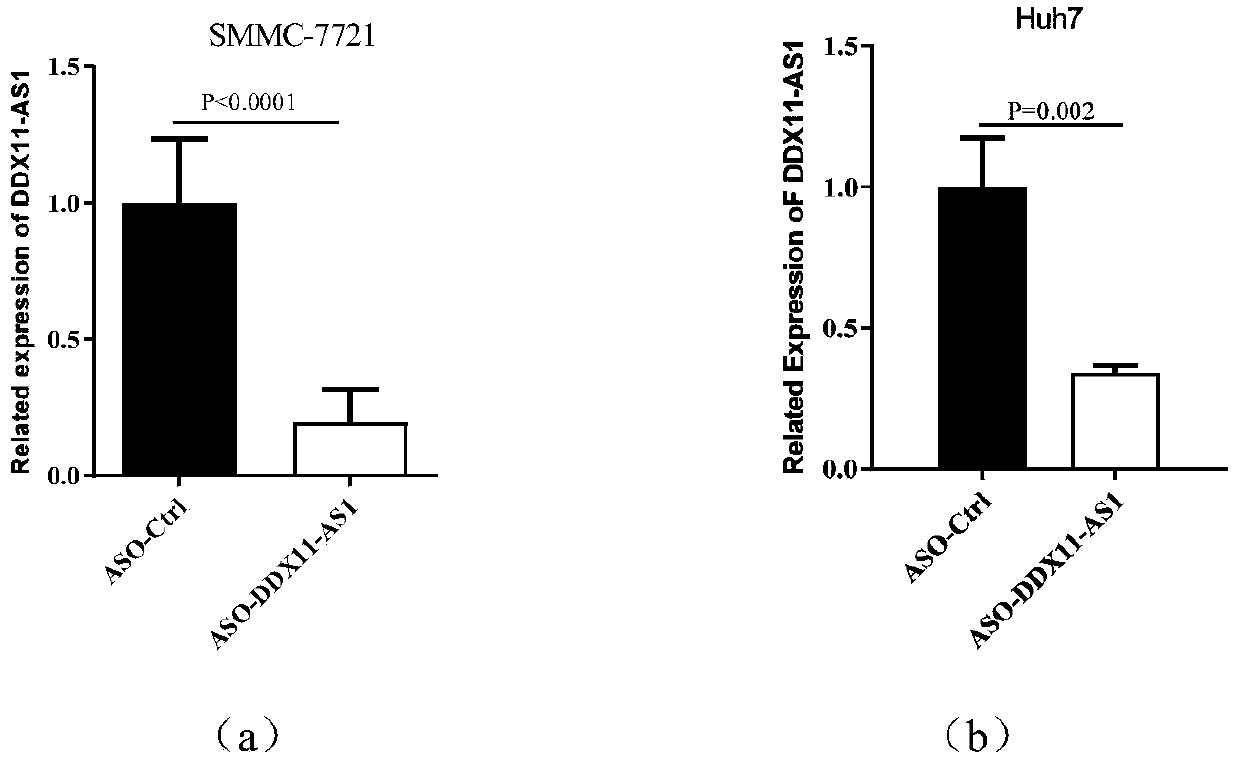
[0052] Example 3: The effect of ASO on the function of liver cancer cells after inhibiting the expression of DDX11-AS1
[0053] 1. Materials
[0054] Cells: Human liver cancer cell lines SMMC-7721 and Huh7 were purchased from the Cell Resource Center of Shanghai Institute of Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
[0055] Reagents: Lipofectamine 2000, a transfection reagent, was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific, and CCK8 and PI cell cycle detection kits were purchased from MULTISCIENCES, China.
[0056] 2, cell culture is the same as embodiment 2
[0057] 3. Design and synthesis of ASO sequence targeting DDX11-AS1
[0058] The DDX11-AS1 gene sequence (NR-) and mfold software were obtained from the NCBI database, and specific targeting ASOs were designed according to the secondary structure of the long-chain non-coding RNA DDX11-AS1, and three of them were selected for synthesis and made into an ASO mixture (equal molar ratio), the specific sequence of ASO ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com