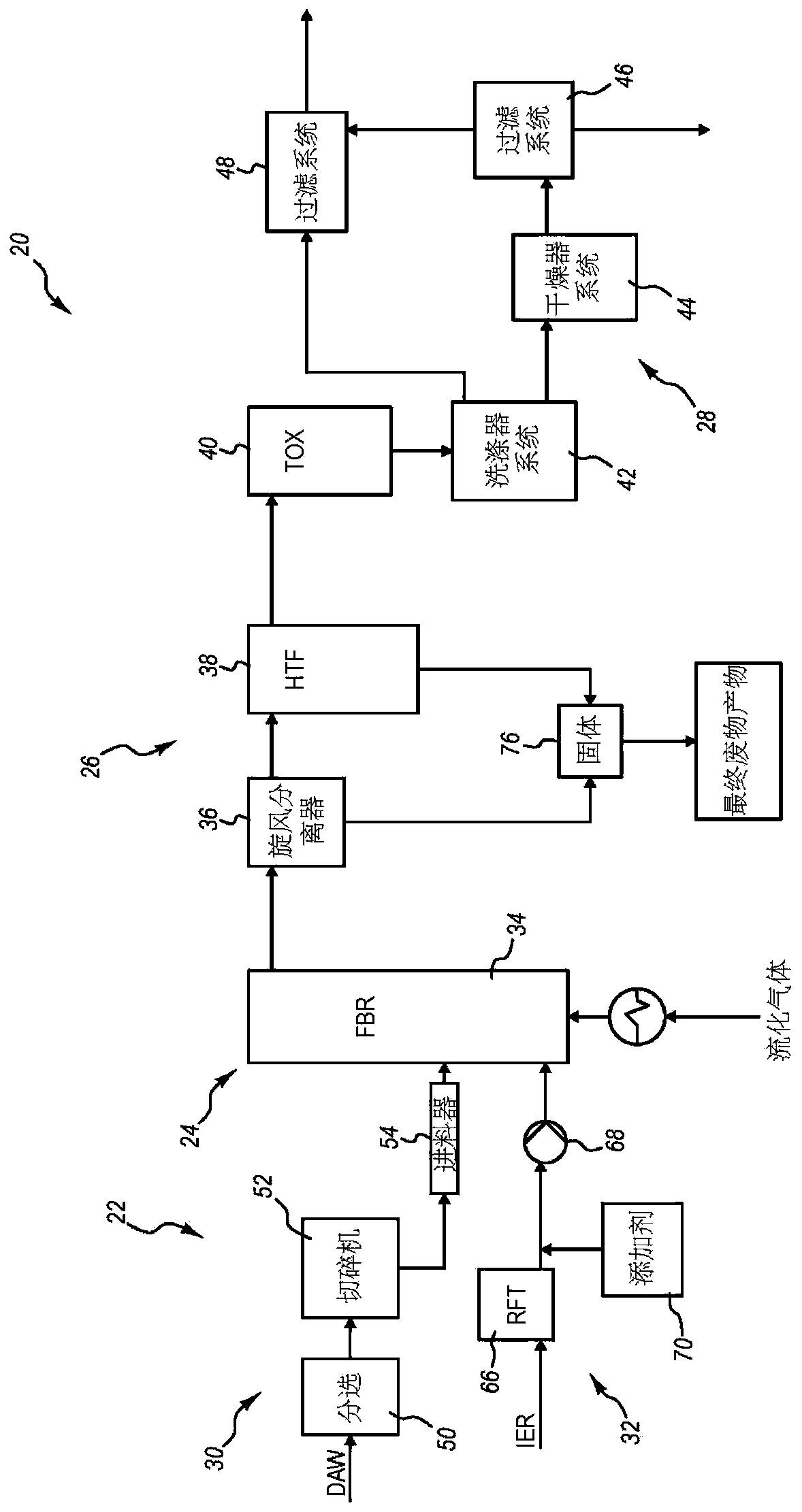
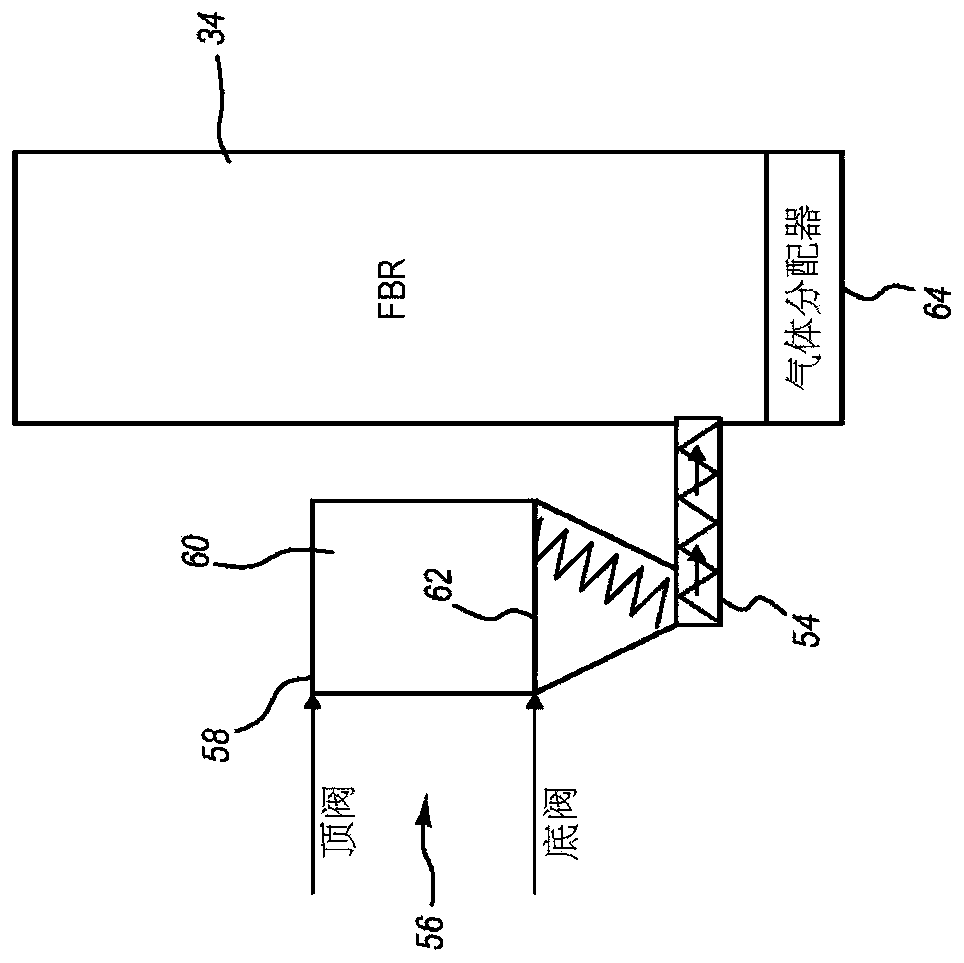
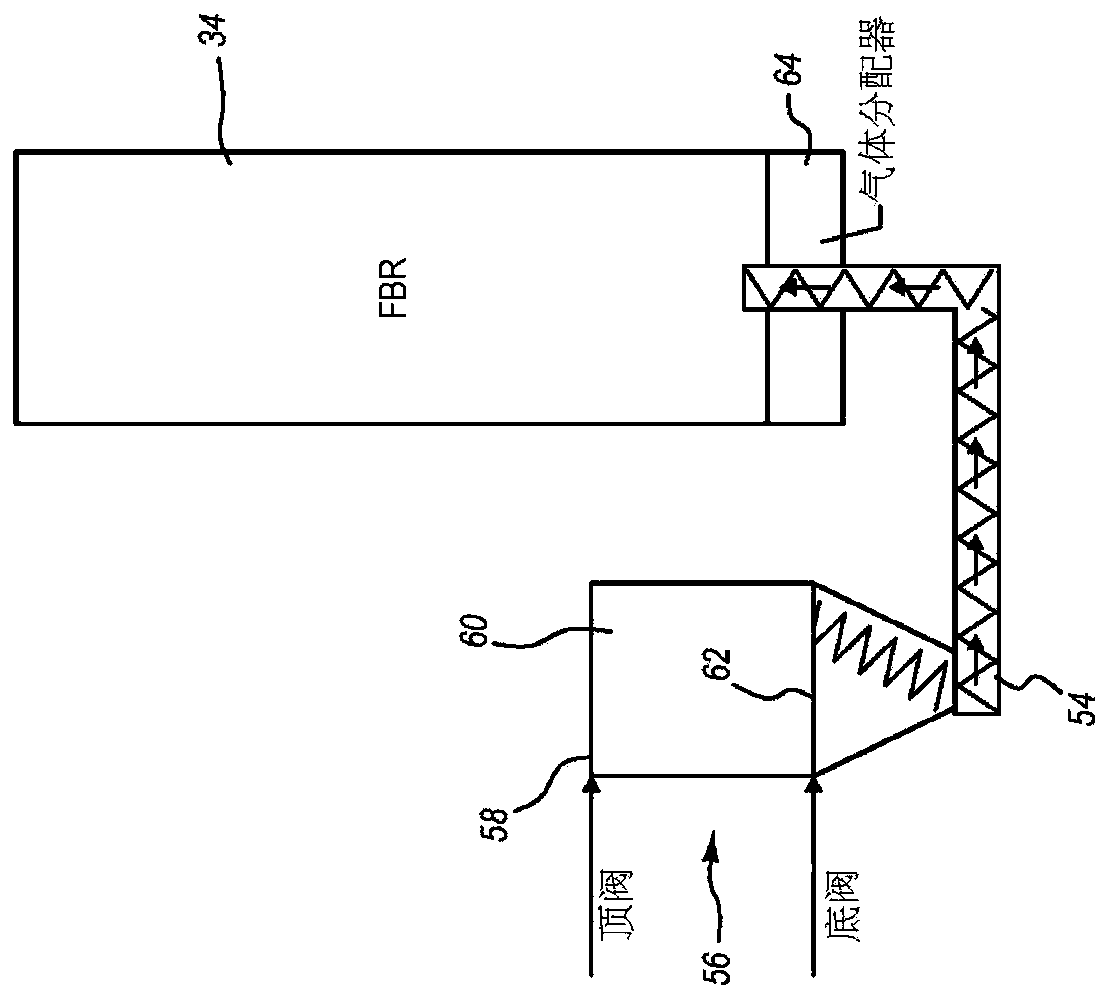
Thermal volume reduction of radioactive wastes
A technology of radionuclide and waste, which is applied in the direction of radioactive purification, educts, and production of combustible gases, etc., and can solve the problems of inability to co-process waste streams, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0148] In this example, a thermal volume reduction process was tested using a dehydrated ion exchange resin (IER) feed and an IER slurry feed to determine how the different feeds affect the process. The dehydrated IER feed had a water content of about 55% and was fed into the fluidized bed reactor using a screw extruder without a die. The IER slurry feed had a water content of about 85% and was fed into the fluidized bed reactor using a peristaltic pump. The diameter of the fluidized bed reactor was 15 inches.
[0149] The IER slurry feed was tested in a single run. Testing the dehydrated IER feed was tested in two runs where the feed rate for the second run was 50% higher than that for the first run. The test results are shown in Table 1 below.
[0150] Table 1 - IER Feed Options: IER Slurry vs. Dewatered IER
[0151]
[0152] The data show that feeding dehydrated IER to a fluidized bed reactor provides at least two advantages. First, it allows for a significant reduc...
example 2
[0154] In this example, the thermal volume reduction process was tested using different feed compositions to determine how they affected the process. The feed compositions tested were: (1) IER slurry feed; (2) dry active waste (DAW) feed; (3) a mixture of DAW and IER (DAW and IER were mixed before entering the fluidized bed reactor) and (4) continuously co-feeding DAW and IER into the fluidized bed reactor (DAW and IER are fed separately into the reactor). Feed 1 was fed into the fluidized bed reactor by pumping, and feeds 2-4 were fed into the fluidized bed reactor by screw feeding using an extruder without a die. The test results are shown in Table 2 below.
[0155] Table 2 - Feed Composition Comparison
[0156]
[0157] The data show that processing the DAW and IER together provides at least two advantages. First, it does not require any char addition during steady state operation. This reduces the cost of the process and minimizes the negative impact of waste volume...
example 3
[0159] In this example, the ability to successfully feed dry active waste (DAW) into a fluidized bed reactor of a thermal volume reduction process was tested. The conventional method of adding DAW to a fluidized bed reactor is to mix it with water to form a slurry and then add the slurry to the reactor. Water acts as a coolant to prevent the DAW from reacting before entering the fluidized bed reactor. This test was performed to determine if DAW could be fed into the reactor without being in slurry form.
[0160] Connect the screw extruder to the fluidized bed reactor using a feed adapter set. The feed adapter assembly extended 13.5 inches through the wall of the fluidized bed reactor, which consisted of a metallic outer wall and an inner refractory lining. The housing of the feed adapter device includes internal fluid passages through which a coolant fluid is circulated to cool the device. Coolant fluid was supplied at a temperature of -3°C and circulated at a rate of 5 gpm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com