Charged filter medium and method for manufacturing charged filter medium
A technology of filter material and charged layer, applied in the field of charged filter material, which can solve the problems of decreased collection efficiency and increased pressure loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0152] (Preparation method of fine fiber fabric)
[0153] Relative to the volume resistivity value of 10 16 (Ω·cm) about 100 parts by mass of a commercially available polypropylene resin, mixed with 4 parts by mass of a commercially available hindered amine light stabilizer as a charging aid, and spun by a melt-blowing method to prepare a melt having the following composition: Spray non-woven fabric.
[0154] Resin constituting the fiber: Polypropylene resin
[0155] Fiber cross section shape: round
[0156] Median fiber diameter: 1.44 μm
[0157] Basis weight: 7g / m 2
[0158] Thickness: 0.07mm
[0159] Pressure loss when the wind speed is 10cm / s: 12.5Pa
[0160] In addition, the pressure loss (Pa) of a meltblown nonwoven fabric was calculated|required by providing a meltblown nonwoven fabric with the calculation method demonstrated in the item (calculation method of pressure loss and collection efficiency).
[0161] (Preparation method of support fabric)
[0162] A s...
Embodiment 2~6、 comparative example 1~6
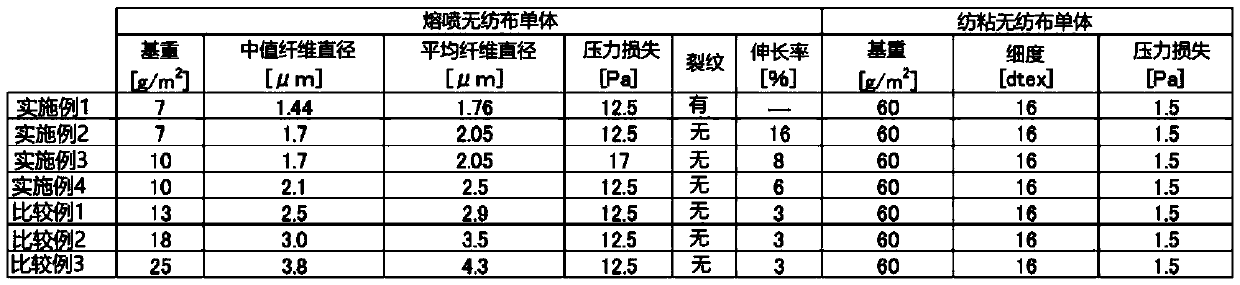
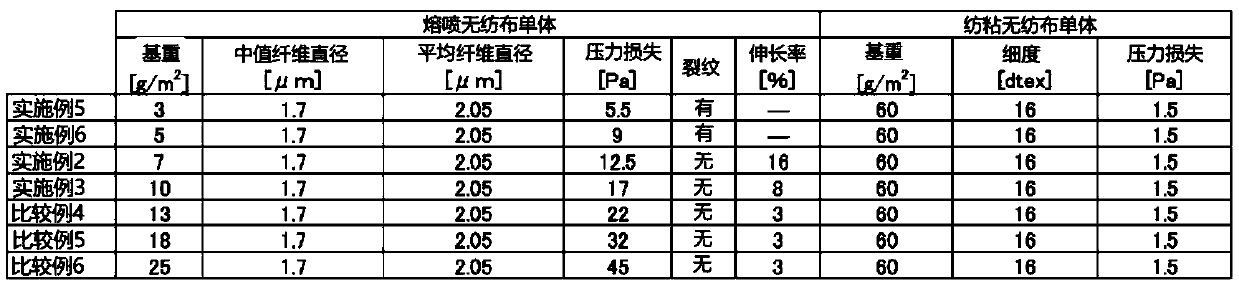
[0188] A charged filter material was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the basis weight and median fiber diameter of the melt-blown nonwoven fabric used in the preparation of the charged filter material were changed.
[0189] In addition, each of the prepared charged filter materials has a configuration in which a thin fiber layer derived from a melt-blown nonwoven fabric and a support fiber layer derived from a spunbonded nonwoven fabric are laminated and integrated.
[0190] Tables 1 to 4 summarize the configurations and measurement results of the charged filter materials of Examples and Comparative Examples prepared as described above.
[0191] In addition, when there are cracks on the main surface of the meltblown nonwoven fabric alone or the charged filter material (charged laminate), the length on the main surface of the fabric cannot be measured, so the elongation (%) cannot be calculated. . When the elongation (%) could not be calculated, it was ...
Embodiment 7
[0201] A charged filter material was prepared in the same manner as in Example 2 except that a melt-blown nonwoven fabric was prepared using only a polypropylene resin without mixing a charging auxiliary agent.
[0202] In addition, the prepared charged filter material has a structure in which a thin fiber layer derived from a meltblown nonwoven fabric and a supporting fiber layer derived from a spunbonded nonwoven fabric are laminated and integrated.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| loss value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com