Method for evaluating service condition of high-temperature alloy turbine blade
A technology of turbine blades and high-temperature alloys, applied in the direction of applying stable tension/pressure to test material strength, biological neural network models, instruments, etc., can solve subjective errors, accuracy and operability cannot be achieved very high, further consideration is needed Deepening and other issues, to achieve the effect of reliable evaluation results, exclusion of complex influences, strong engineering application significance and broad prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The following examples will further illustrate the present invention in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, so that those skilled in the art can better understand the advantages and features of the present invention.
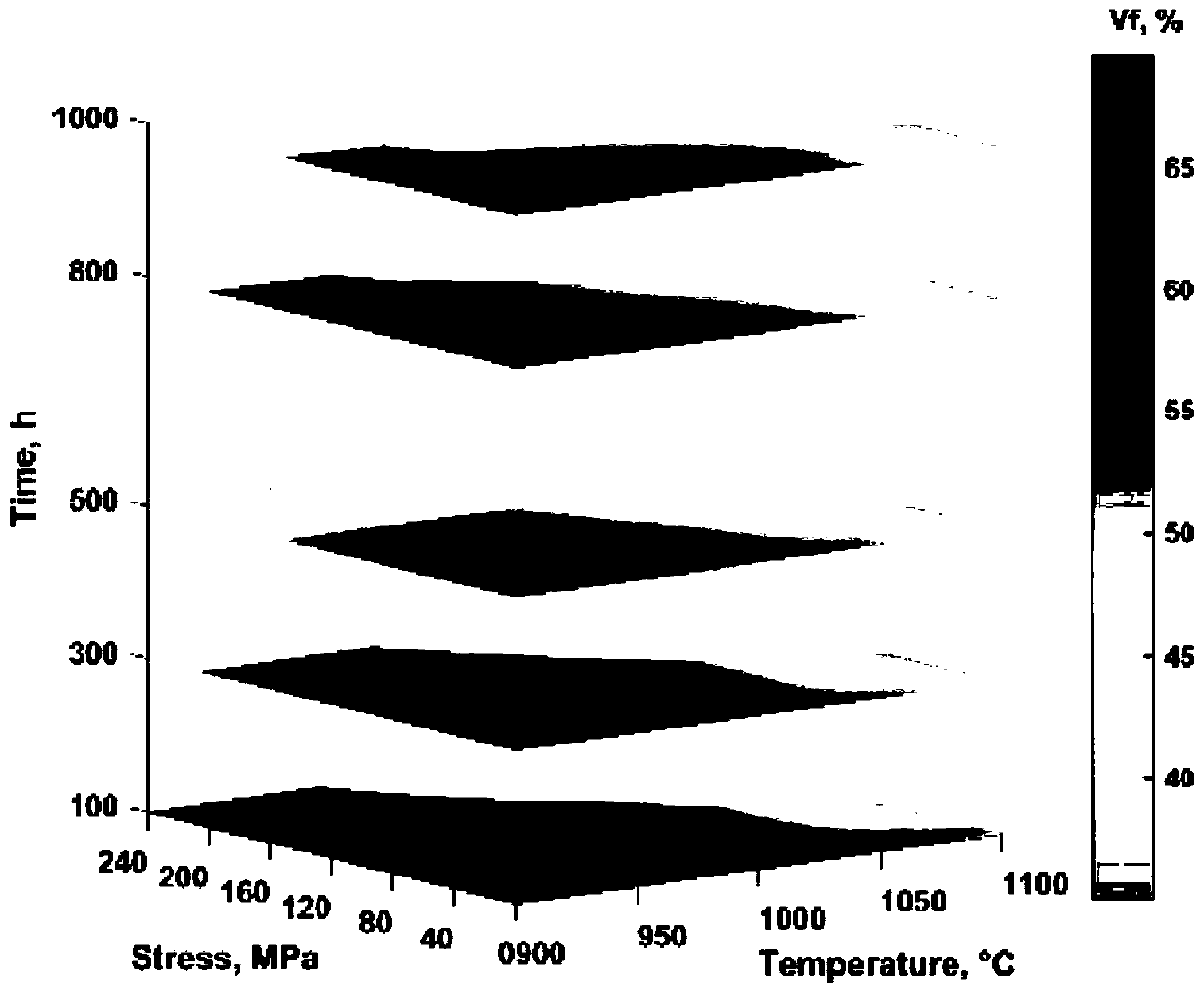
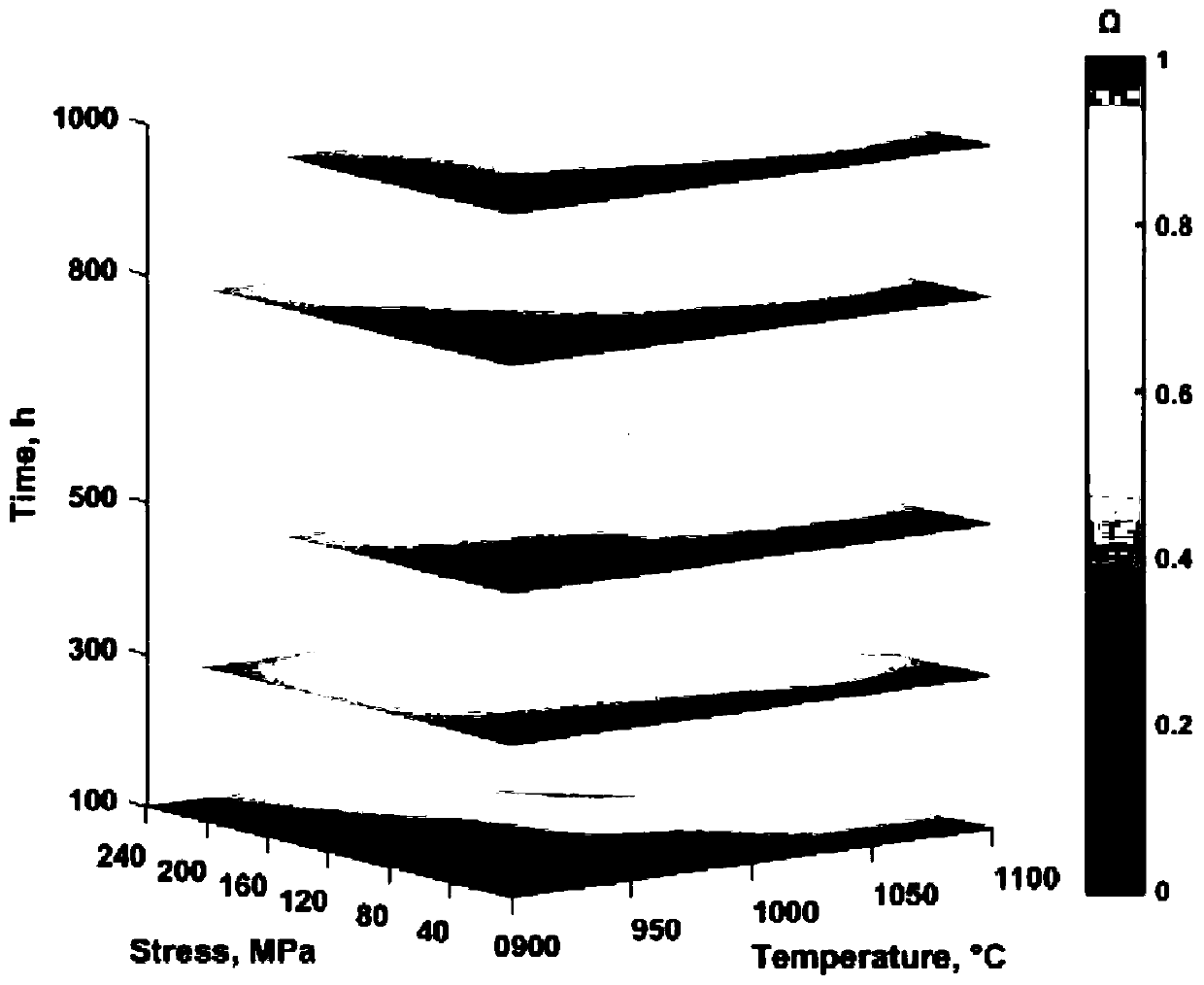
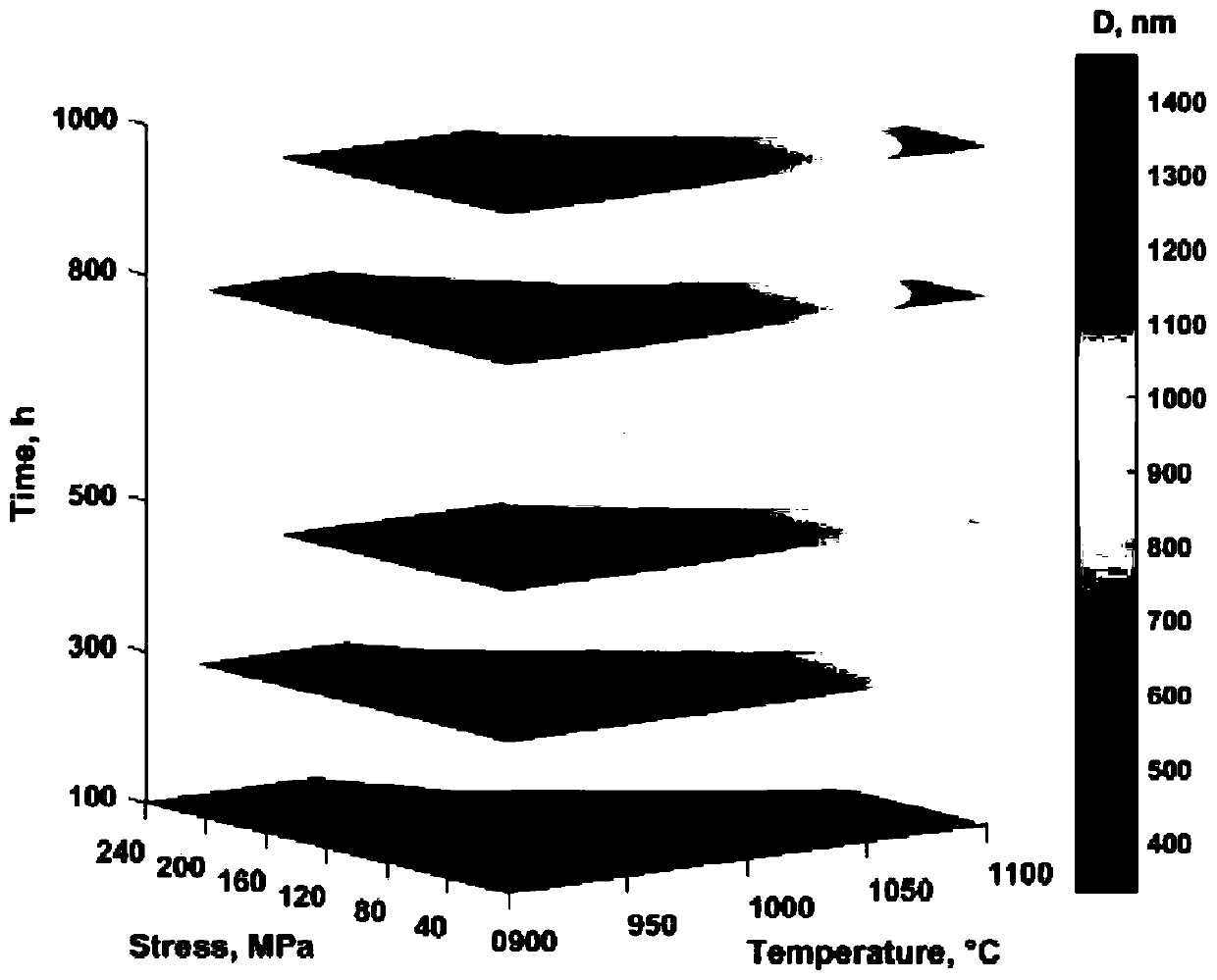
[0028] First, the blade material DZ125 alloy after standard heat treatment was subjected to persistent interruption experiments under different temperature, stress and time conditions to obtain microstructures with different damage states. Refer to the grid point method in GB / T 15749 to quantitatively count the volume fraction (Vf) of the γ' phase. Set 216 grid intersection points, when the intersection point is located in the γ′ phase, it is counted as 1, when the intersection point is located at the interface between the γ′ phase and the matrix, it is counted as 0.5, when the intersection point is located in the matrix, it is counted as 0, the ratio of the above statistical results to the total number of intersection points is is Vf. Use the an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com