Use of biomarkers in identifying cancer patients that will be responsive to treatment with a prmt5 inhibitor
A technology for inhibitors and patients, applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, ICT adaptation, biomaterial analysis, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
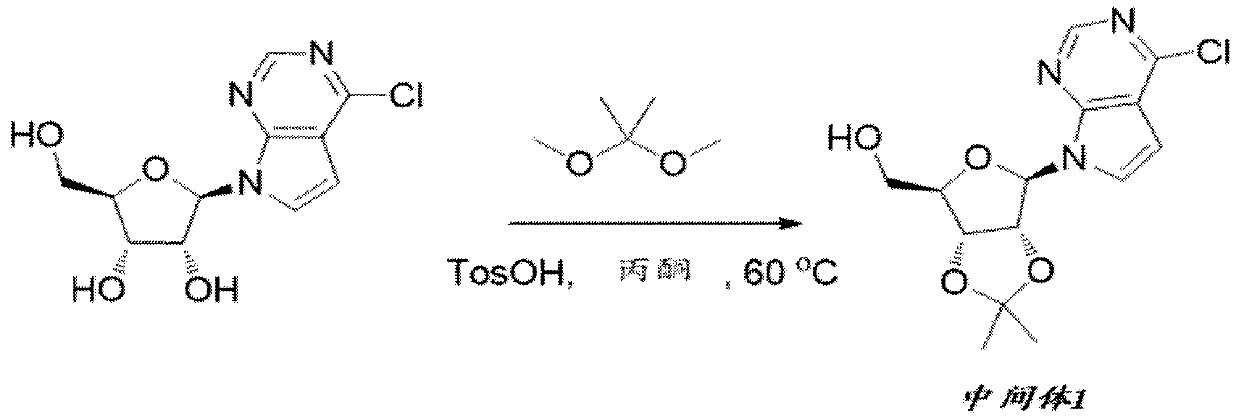
[0108] Preparation of Intermediate 1
[0109]
[0110]To a mixture of 6-chloro-7-deazapurine β-d-nucleoside (25.0 g, 87.5 mmol) in acetone (330 mL) was added 2,2-dimethyl in one portion at 25 °C under N2 Oxypropane (18.2 g, 175 mmol) and 4-methylbenzenesulfonic acid (TosOH) (1.51 g, 8.75 mmol). The mixture was stirred at 60°C for 2 hours. The mixture was cooled to 25°C. The reaction was quenched by slow addition of saturated NaHCO3 (100 mL) and then extracted with ethyl acetate (125 mL x 5). The combined organic phases were washed with saturated brine (120 mL), dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (gradient elution: DCM / ethyl acetate from 1:0 to 2:1) to afford crude Intermediate 1 (38.0 g) as a pale yellow gum.
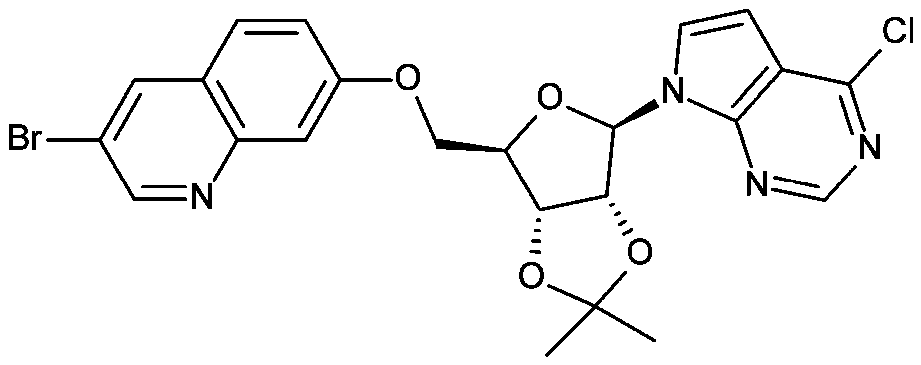
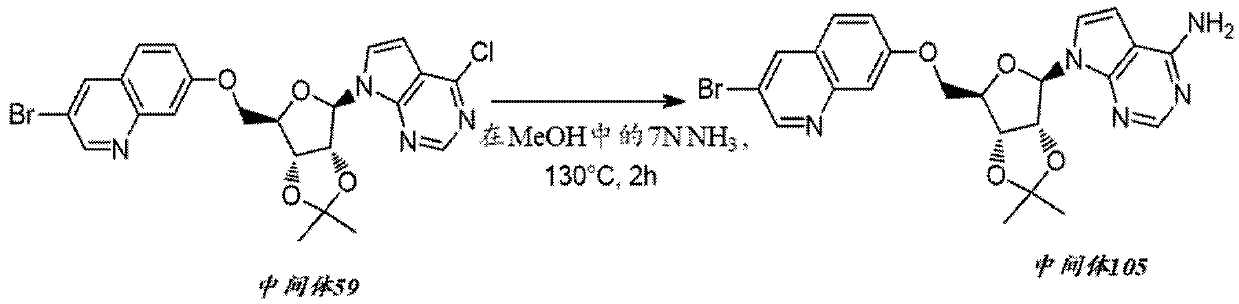
[0111] Preparation of intermediate 59
[0112]
[0113] Diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (0.221 mL, 1.125 mmol) was added dropwise to Intermediate 1 (0.27 g, 0.80 mmol), 3-bromo...
example 1
[0181] Example 1: PIK3CA activating mutations are associated with PRMT5 inhibitor sensitivity in SCLC.
[0182] The cellular sensitivity profile of Compound 2 was evaluated in the SCLC subclass of a broad panel of lung cancer cell lines. Strikingly, some of the most sensitive cell lines carried different gain-of-function mutations in the PIK3Cα gene and are mentioned in Table 2. Activation of the PI3Kα pathway (gain-of-function mutation or pathway stimulation) as a tumor response to standard therapy (cisplatin) or even to targeted drugs (like the latest generation of PARP inhibitors) implicates a key role in the resistance process, which May be associated with poor overall survival of SCLC patients after treatment.
[0183] cell line PIK3CA mutation Histological subtype GI50 NCI-H1048 H1047R SCLC 94.62nM LU99a T1025A SCLC 128.53nM H69V G106_R108del SCLC 85.62nM
[0184] Table 2
example 2
[0185] Example 2: In NSCLC, spliceosome alterations are associated with PRMT5 inhibitor sensitivity
[0186] Cancer-specific splicing events are known to initiate malignancy and also contribute to disease progression. So far, two proteins involved in splicing, U2AF1 and RBM10, have been described to be misregulated in NSCLC.
[0187] U2AF1 is a well-characterized splicing factor that carries a gain-of-function hotspot mutation (S34F) in 3%-8% of NSCLC patients. Recently, the RNA-binding protein RBM10, which is also critical for spliceosome assembly, has been classified as a tumor inactivated by loss-of-function mutations, mainly in NSCLC patients with a history of smoking (approximately 8%) inhibitory factor.
[0188] The Sm protein, which is critical for spliceosome assembly, has been described as a direct substrate of PRMT5, and thus, PRMT5 function is linked to regulating spliceosome activity.
[0189] Since the S34F gain-of-function mutation in U2AF1 has been identifi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com