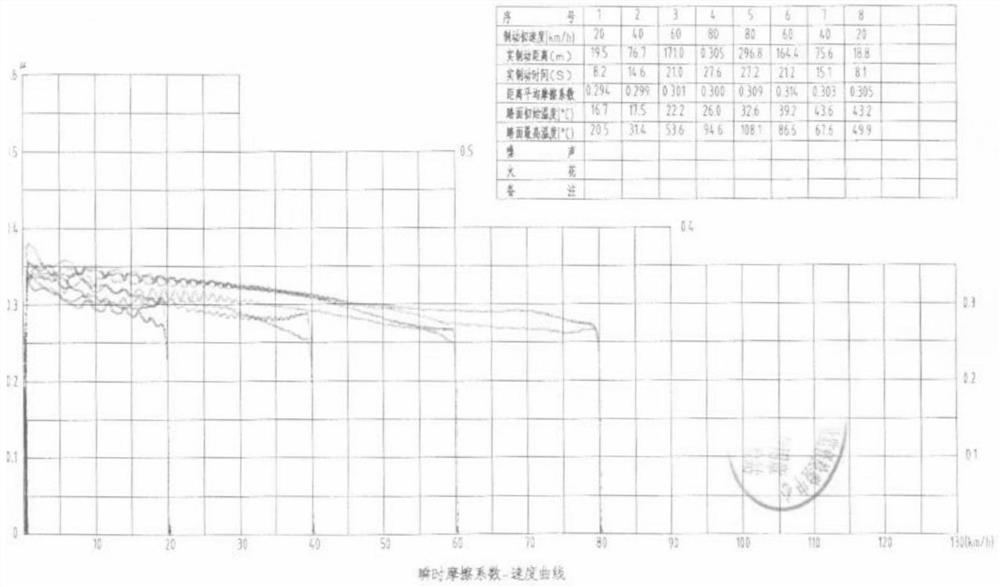
A method capable of improving wet braking performance of microporous friction material
A friction material and microporous technology, applied in the field of friction materials, can solve the problems of endangering the driving safety of subway vehicles, unstable wet friction coefficient, metal inlay and large wear, etc., to prolong the service life, and stabilize the friction coefficient. long life effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] A method capable of improving the wet braking performance of a microporous friction material, comprising adding a hydrophobic agent to the components of the microporous friction material, specifically comprising the following steps:
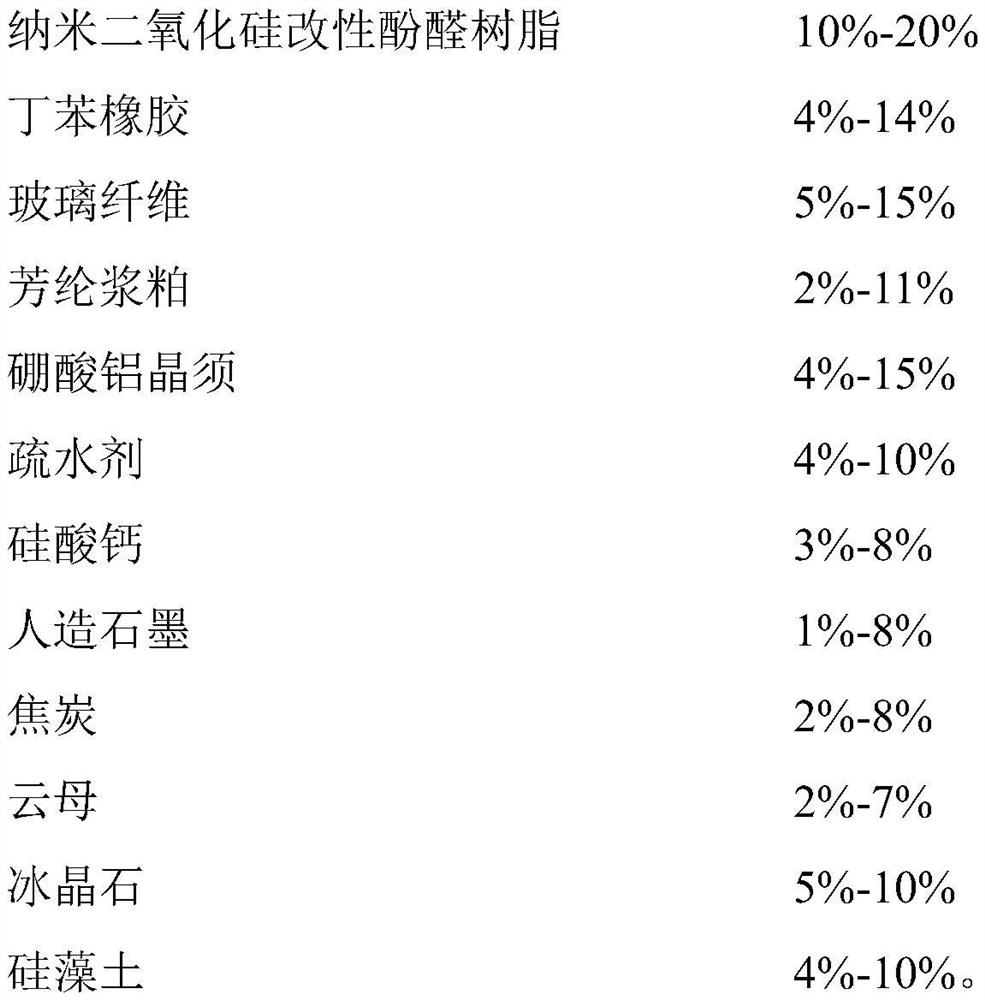
[0050] (1) The preparation of raw materials, including the following components and weight percentages:
[0051]
[0052] (2) Preparation:
[0053] The above-mentioned raw materials are mixed in a high-speed mixer in sequence in proportion; the steel back and the mixture are placed in a mold for compression molding to obtain a blank; the blank is heated and solidified in an oven, and finally machined to obtain a brake shoe .
[0054] Mixing material: Add each component into a high-speed mixer in proportion to mix and stir, the speed is 2500r / min, and the time is 25min;
[0055] Pressing: Put the mixture and steel back into the mold for pressing, the mold temperature is 60°C, the molding pressure is 20MPa, deflate 5 times within 10 min...
Embodiment 2
[0060] A method capable of improving the wet braking performance of a microporous friction material, comprising adding a hydrophobic agent to the components of the microporous friction material, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0061] (1) The preparation of raw materials, including the following components and weight percentages:
[0062]
[0063]
[0064] (2) Preparation:
[0065] The above-mentioned raw materials are mixed in a high-speed mixer in sequence in proportion; the steel back and the mixture are placed in a mold for compression molding to obtain a blank; the blank is heated and solidified in an oven, and finally machined to obtain a brake shoe .
[0066] Mixing material: Add each component into a high-speed mixer in proportion to mix and stir, the speed is 2500r / min, and the time is 30min;
[0067] Pressing: Put the mixture and steel back into the mold for pressing, the mold temperature is 80°C, the molding pressure is 25MPa, deflate 10 times ...
Embodiment 3
[0072] A method capable of improving the wet braking performance of a microporous friction material, comprising adding a hydrophobic agent to the components of the microporous friction material, specifically comprising the following steps:
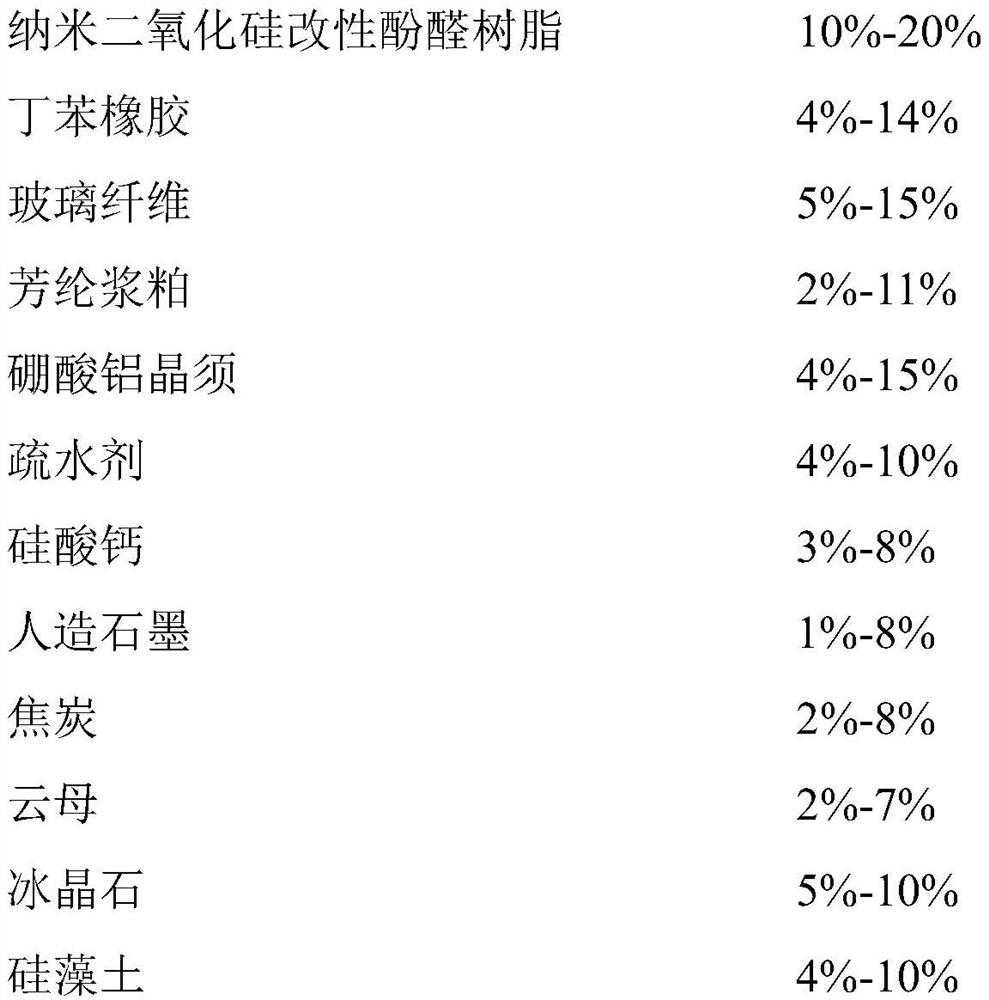
[0073] (1) The preparation of raw materials, including the following components and weight percentages:
[0074]
[0075]
[0076] (2) Preparation:
[0077] The above-mentioned raw materials are mixed in a high-speed mixer in sequence in proportion; the steel back and the mixture are placed in a mold for compression molding to obtain a blank; the blank is heated and solidified in an oven, and finally machined to obtain a brake shoe .
[0078] Mixing material: Add each component into a high-speed mixer in proportion to mix and stir, the speed is 2500r / min, and the time is 35min;
[0079] Pressing: Put the mixture and steel back into the mold for pressing, the mold temperature is 100°C, the molding pressure is 30MPa, deflate 7 times ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com