Method for removing iopamidol in water through ultraviolet/chlorine dioxide combined process
A chlorine dioxide and combined process technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory iopamidol removal effect, poor degradation effect, regular maintenance, etc., to improve feasibility and operability, and degrade Thorough and safe effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
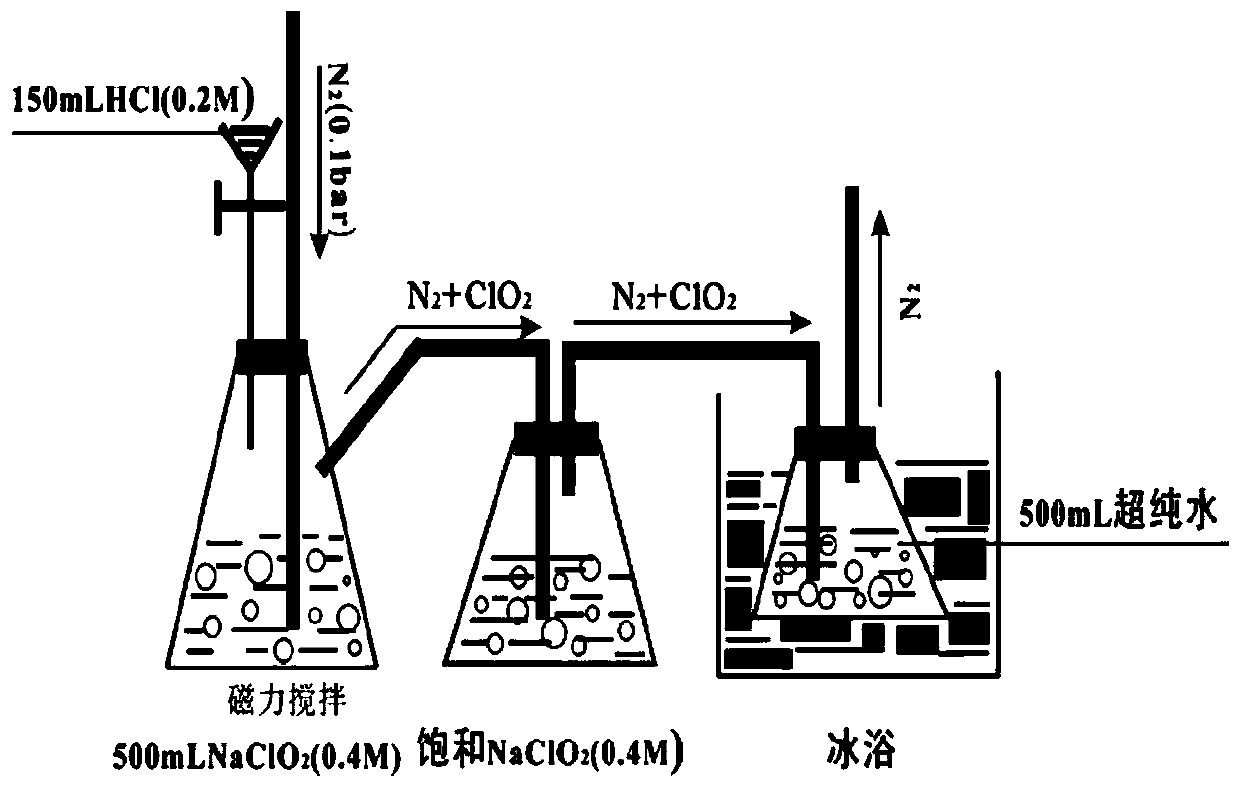
[0054] UV / ClO 2 The method for removing iopamidol from water by combined process, the specific steps are as follows:
[0055] Prepare the initial concentration of iopamidol with ultrapure water to 10μM, adjust the initial pH of iopamidol solution to 7.0 with acid-base solution, and add ClO to the iopamidol solution 2 , The dosage is [ClO 2 ] 0 =200μM, UV irradiation at the same time, control the UV intensity to 2.43mW / cm 2 , Control the reaction temperature to 25°C.
[0056] ClO alone 2 Process (Comparative Example 1), Single UV Process (Comparative Example 2) and UV / ClO 2 The concentration of iopamidol in the combined process (Example 1) varies with time as shown in figure 1 As shown,
[0057] It can be seen that the removal effect of iopamidol is different under different processes. UV / ClO 2 At the same time, it can greatly increase the removal rate of iopamidol. ClO alone 2 The degradation rate of iopamidol by the process is only 0.8%, which proves that ClO alone 2 The iopamidol ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] UV / ClO 2 The method for removing iopamidol from water by combined process, the specific steps are as follows:
[0060] Prepare the initial concentration of iopamidol with ultrapure water to 10μM, adjust the initial pH of iopamidol solution to 7.0 with acid-base solution, and add ClO to the iopamidol solution 2 , Respectively control the addition of ClO 2 The amount is [ClO 2 ] 0 =0μM, 50μM, 100μM, 200, 500μM, 1000μM, UV irradiation at the same time, control the UV intensity to 2.43mW / cm 2 , During the reaction, control the reaction temperature to 25℃, the degradation of iopamidol after 300s of reaction is as image 3 Shown.
[0061] From image 3 It can be seen that the removal efficiency of iopamidol increases with ClO 2 The increase in dosage increases. Under the same UV intensity, with ClO 2 The concentration increased from 0-1000μM, and the removal rate increased from 70.85% to 78.76%, indicating the increase of ClO 2 The dosage can promote the removal of iopamidol. This...
Embodiment 3
[0063] UV / ClO 2 The method for removing iopamidol from water by combined process, the specific steps are as follows:
[0064] Prepare the initial concentration of iopamidol with ultrapure water to 10μM, adjust the initial pH of iopamidol solution to 7.0 with acid-base solution, and add ClO to the iopamidol solution 2 , The dosage is [ClO 2 ] 0 =200μM, while UV irradiation, control the UV intensity to 0mW / cm 2 , 2.43mW / cm 2 , 4.94mW / cm 2 , 7.34mW / cm 2 , 9.76mW / cm 2 , Under the test condition that the reaction temperature is controlled to 25℃, the degradation of iopamidol after 300s reaction is detailed in Figure 4 .
[0065] Have Figure 4 It can be seen that the UV light intensity directly determines the production rate of ·OH in the system, and as the UV intensity increases, the photodegradation rate of iopamidol gradually increases. UV intensity is 9.76mW / cm 2 , The degradation rate of iopamidol reached 99.32% in only 150s. UV / ClO 2 The effectiveness of degrading iopamidol is as...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com