Method for preparing L-glucan by utilizing lignocellulose biomass
A technology of lignocellulose and levoglucosan, which is applied in the field of levoglucosan preparation, can solve the problems of reducing the conversion rate of lignocellulosic levoglucosan and low selectivity of levoglucosan, so as to improve the utilization value , high yield and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
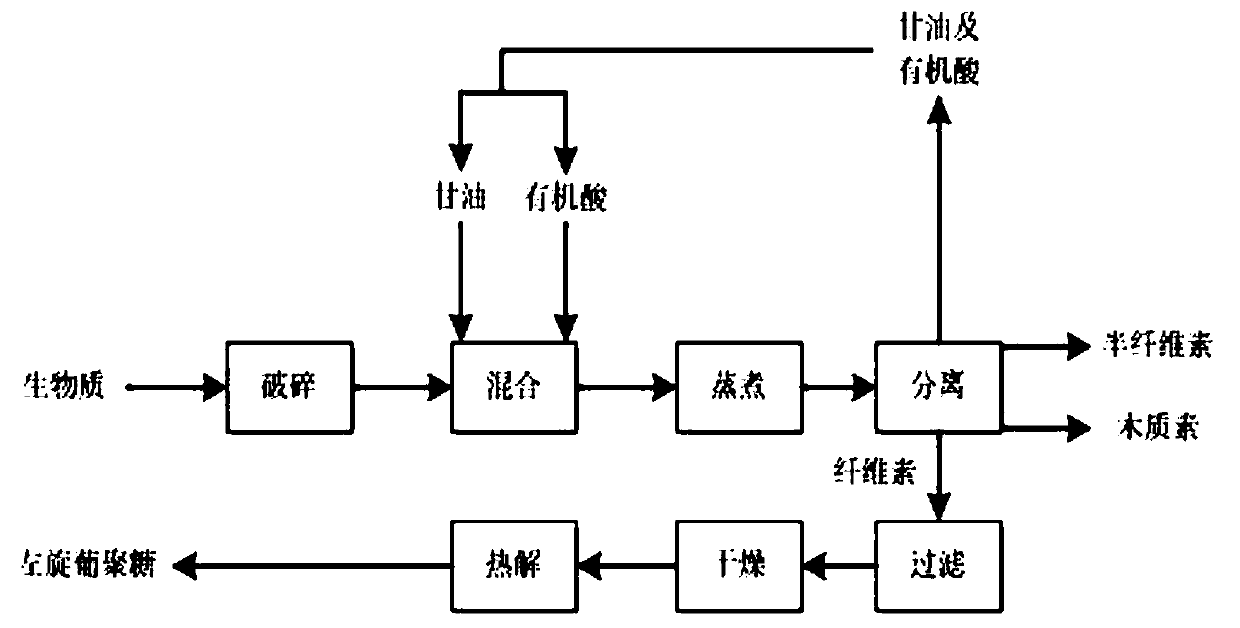
[0023] Embodiment 1: utilize pine wood to prepare the method for levoglucosan, comprise the following steps:
[0024] 1) Crushing the pine wood until the particle size is less than 80 mesh.
[0025] 2) Mix the pine wood treated in step (1) with glycerin and formic acid in a ratio of 1:10:1. Under the condition of higher ratio of liquid to solid and organic acid, it is beneficial to the dissolution of soluble matter in pine wood.
[0026] 3) The mixture obtained in step (2) was reacted at 100° C. for 3 hours. Under the above reaction conditions, 90% hemicellulose and 70% lignin in the pine wood powder were dissolved into the mixture of glycerol and organic acid, and the cellulose remained solid. At the same time, 90% of the alkali metal and ash in the pine wood powder can be dissolved into the mixed solution of glycerin and organic acid.
[0027] 4) The reaction product in step (3) was subjected to liquid-solid separation to obtain a solid product, and dried at 110° C. for 0...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Referring to Example 1, the method for preparing levoglucosan using straw stalks is different in that:
[0035] 1) Crushing the straw stalks until the particle size is less than 60 mesh.
[0036] 2) Mix the straw treated in step (1) with glycerin and acetic acid in a ratio of 1:30:5.
[0037] 3) The mixture obtained in step (2) was reacted at 200°C for 0.5 hours.
[0038] 4) The reaction product in step (3) was subjected to liquid-solid separation to obtain a solid product, and dried at 60° C. for 5 hours, and then kept at 600° C. for 1 second for rapid pyrolysis to obtain levoglucosan.
[0039] In this example, the conversion rate of cellulose into levoglucosan in the straw straw was 45%.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Referring to Example 1, the method for preparing levoglucosan using furniture processing waste sawdust as a raw material is different in that:
[0042] 1) The sawdust is further crushed to a particle size of less than 100 mesh.
[0043] 2) Mix the pine wood treated in step (1) with glycerin and organic acid in a ratio of 1:20:3; the organic acid refers to a mixture of acetic acid and oxalic acid in any ratio.
[0044] 3) React the mixture obtained in step (2) at 190° C. for 1.5 hours.
[0045] 4) The reaction product in step (3) was subjected to liquid-solid separation to obtain a solid product, and dried at 100° C. for 3 hours, and then kept at 550° C. for 2 seconds for rapid pyrolysis to obtain levoglucosan.
[0046] In this example, the conversion rate of cellulose into levoglucosan in the straw straw was 50%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com