Method for removing USEPA PAHs in agricultural soil by using aboriginal PAHs degradation bacterial community
A technology for degrading bacteria and communities, which is applied to the methods of using microorganisms, the restoration of contaminated soil, and methods based on microorganisms. It can solve the problems of large amounts of microorganisms, undiscovered, unfavorable natural soil microbial population balance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the examples, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited thereto.
[0040] 1. Preparation of indigenous PAHs degrading bacterial community:
[0041] (1) Preparation of soil leachate: Mix uncontaminated soil and water at a ratio of 1:10 and stir evenly. After standing for 2 hours, centrifuge the supernatant at 5000 rpm / min for 10 minutes to remove insoluble impurities, and sterilize at 121°C. Store at room temperature after 20 min.
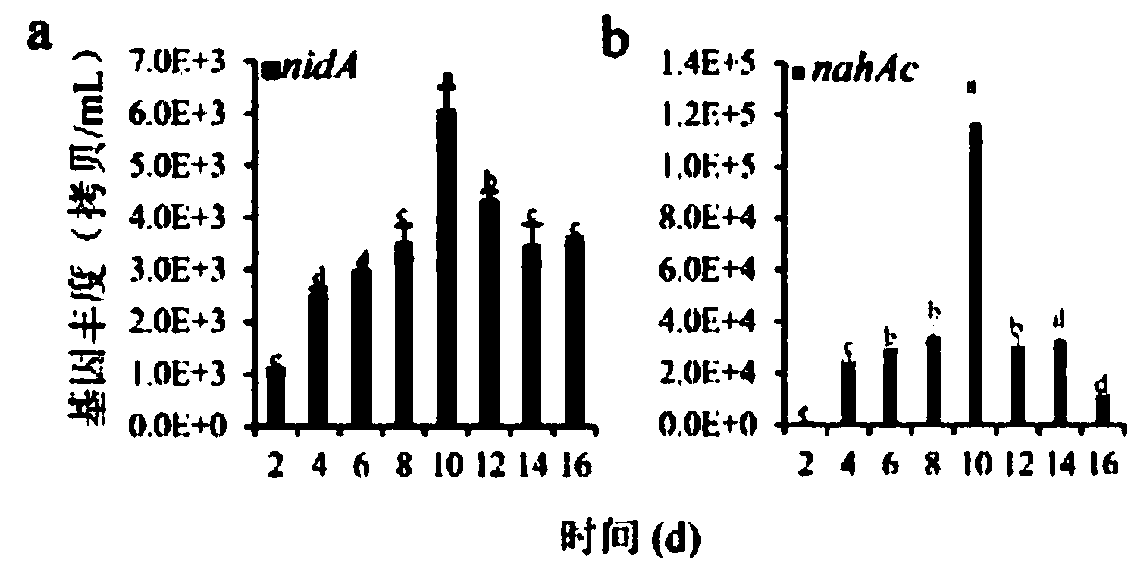
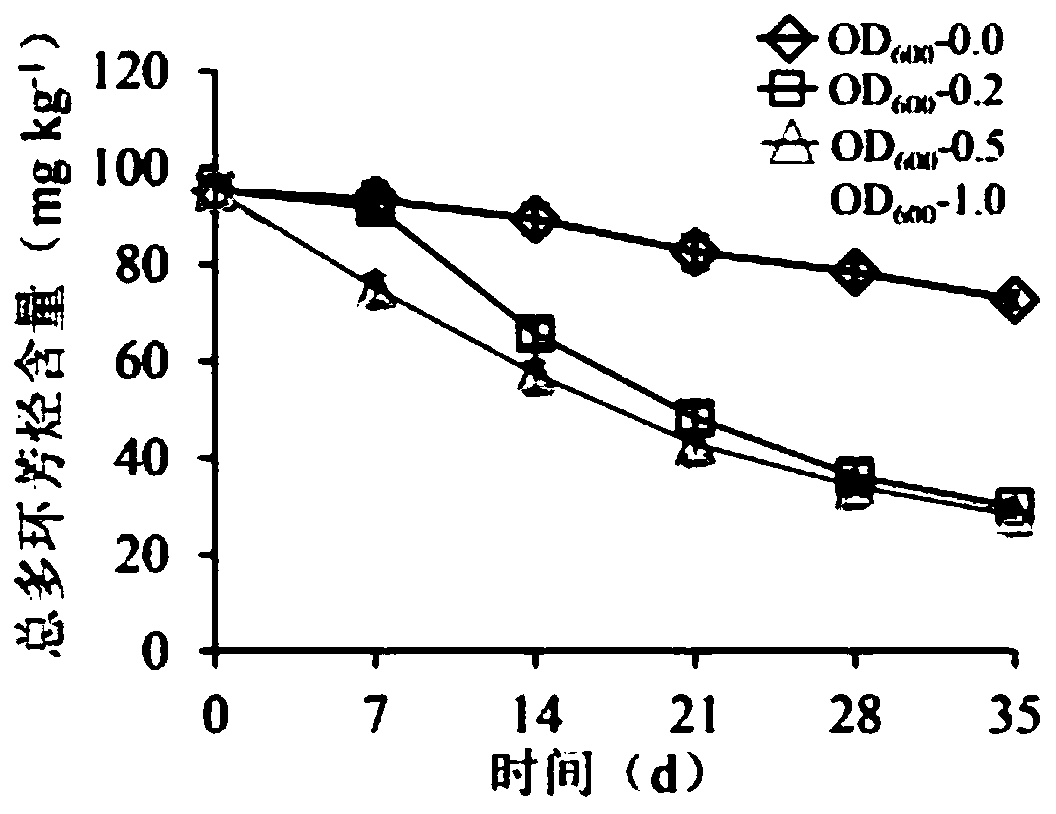
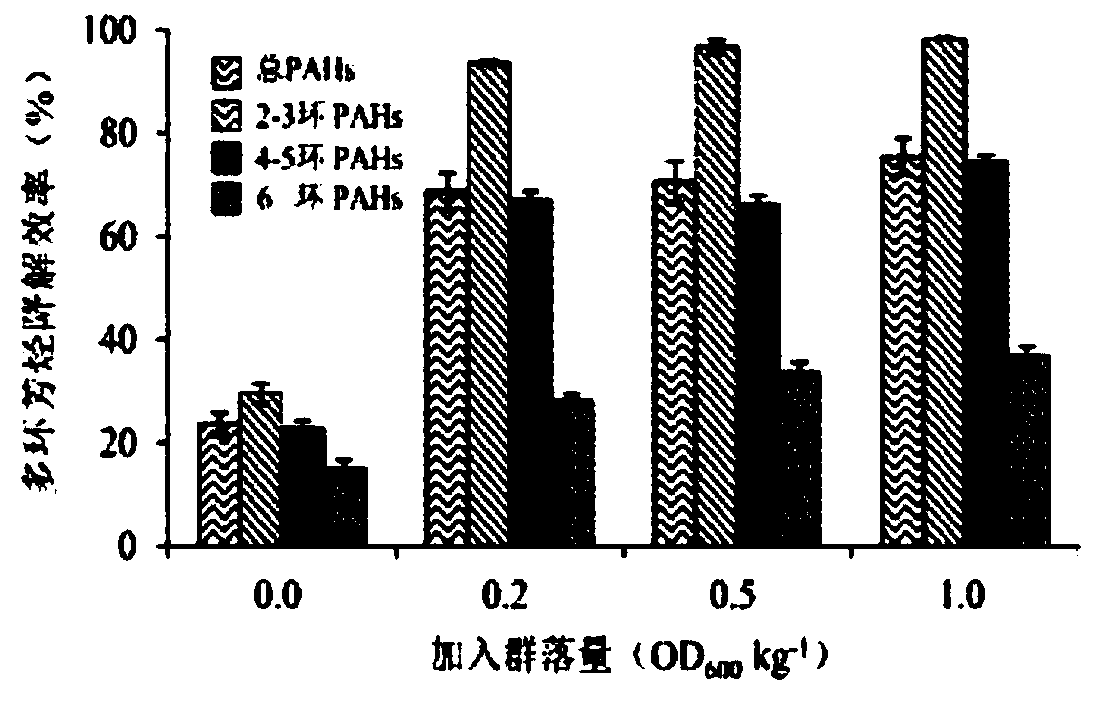
[0042] (2) First-class seed solution: inoculate the suspension of polluted soil into the soil leach solution according to the inoculation amount of 10%, and then add the final concentration of 30mg L -1 The 10 kinds of PAHs were domesticated and enriched after 16 days. Sampling once every two days, part of the culture solution was centrifuged at 5000rpm / min to extract its genomic DNA, and the other part was added with glycerol with a final conce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com