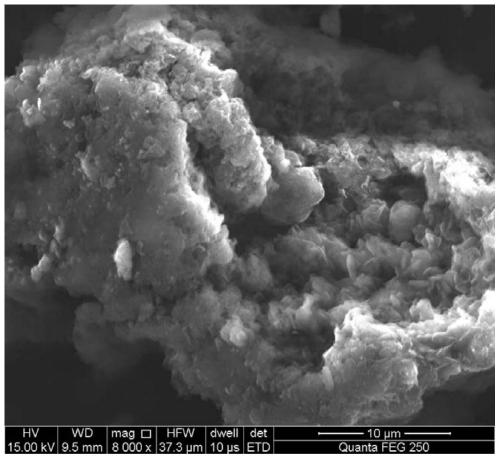
Method for photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics in water body
A technology of antibiotics and photocatalysis, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water treatment of special compounds, light water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of weak separation ability of photogenerated carriers, limited application range of materials, failure to consider impact, etc. problems, achieve high adsorption efficiency and photocatalytic efficiency, enhance photocatalytic performance, and facilitate operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
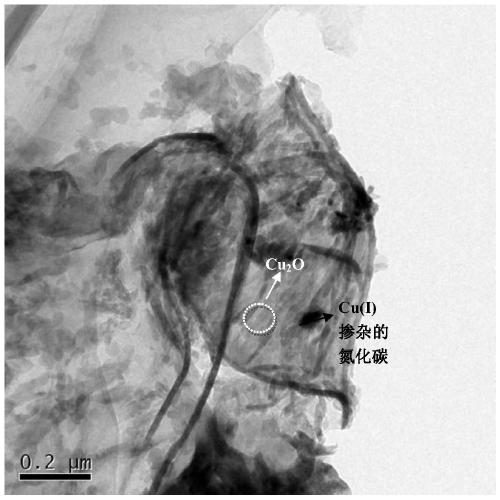
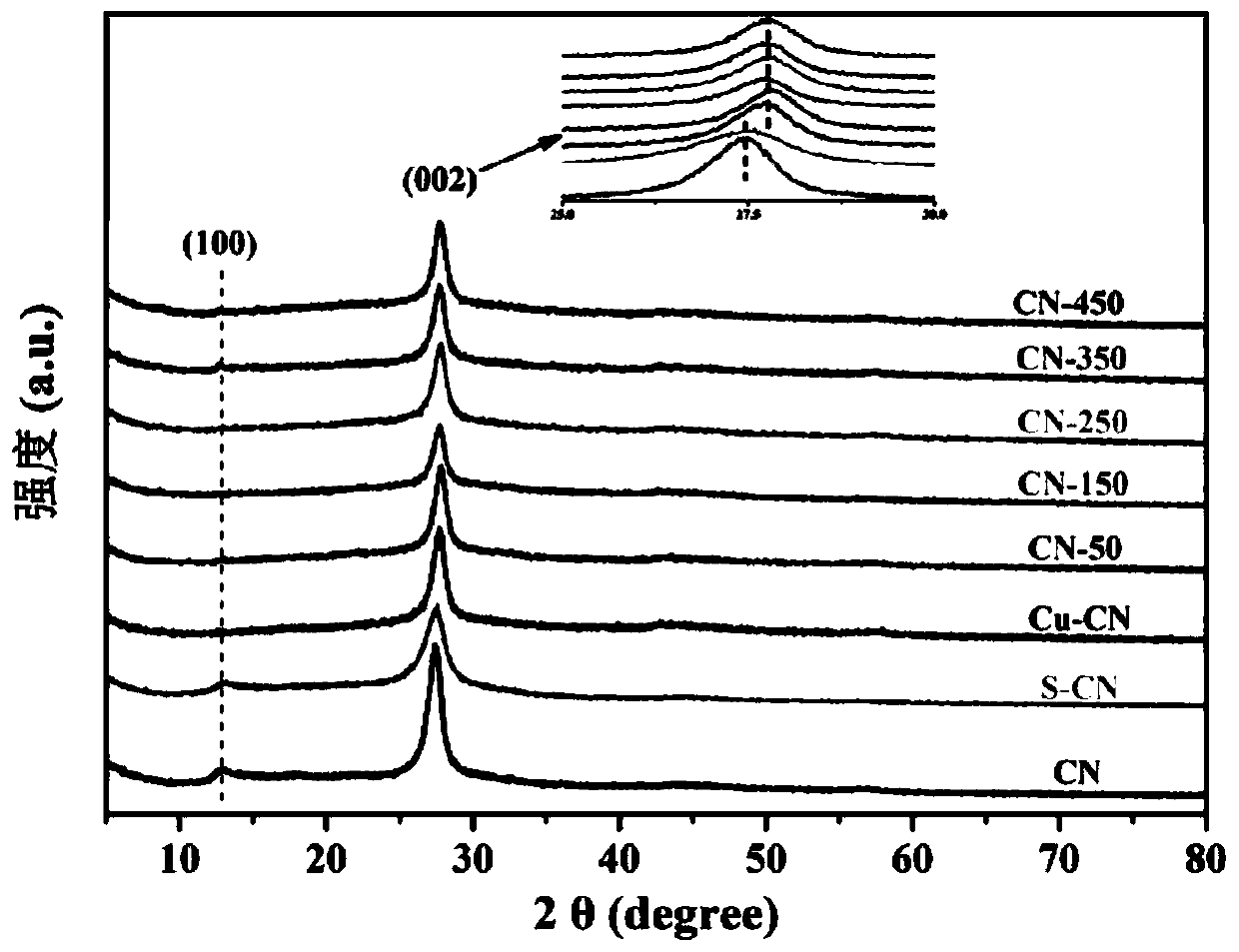
[0039] Embodiment 1, the photocatalyst of the present invention
[0040] An application of the carbon nitride framework material modified by monovalent copper ions of the present invention for photocatalytic degradation of aureomycin hydrochloride in water, comprising the following steps:
[0041] Weighed 80mg of monovalent copper ion modified carbon nitride framework materials CN-250, CN-50, CN-150, CN-350, CN-450 and Cu-CN, S-CN, CN, respectively added to 100mL , in a chlortetracycline hydrochloride solution with a concentration of 20mg / L, magnetic stirring at a speed of 420r / min in a dark place for 1h to reach adsorption equilibrium, then turn on the light source, and irradiate under simulated sunlight for photocatalytic reaction to complete the aureomycin hydrochloride degradation.
[0042] During magnetic stirring, 4 mL samples were taken at regular intervals, and the samples were centrifuged. The upper clear night obtained by centrifugation was measured by a UV-visible...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A method for photocatalytically degrading aureomycin hydrochloride in water using a monovalent copper ion-modified carbon nitride framework material (CN-250), comprising the following steps:
[0057] Weigh 5 parts of the monovalent copper ion-modified carbon nitride framework material (CN-250) prepared in Example 1, each 80 mg, and add respectively to 5 parts of 100 mL 20 mg / L aureomycin hydrochloride solution, the pH of the solution is 2, 3, 4, 5, 7 respectively. Mix and disperse the monovalent copper ion-modified carbon nitride framework material (CN-250) in the aureomycin hydrochloride solution evenly, and magnetically stir for 2 hours at a rotation speed of 420r / min to complete the adsorption equilibrium treatment of the antibiotic solution.
[0058] Then turn on the light source and irradiate the photocatalytic reaction under visible light (λ≥420nm) for 1h. During the process of lighting, stirring and lighting, 4 mL samples were taken every 10 minutes, and the sampl...
Embodiment 3
[0060] A method for photocatalytically degrading aureomycin hydrochloride in water using a monovalent copper ion-modified carbon nitride framework material (CN-250), comprising the following steps:
[0061] Weigh 8 parts of the monovalent copper ion-modified carbon nitride framework material (CN-250) prepared in Example 1, each 80 mg, and add them to 8 parts of 100 mL 20 mg / L aureomycin hydrochloride solution, mix and disperse evenly, The cations in the solution are 10mmol / L Na + 、K + , Zn 2+ , Mg 2+ , the anions in the solution are 10mmol / L Cl in turn - , NO 2 - , NO 3 - , SO 4 2- . Stir magnetically for 2 hours at a rotational speed of 420r / min to complete the adsorption equilibrium treatment of the antibiotic solution. Adsorption equilibrium refers to the state when neither the concentration of the adsorbate in the solution nor the concentration on the surface of the adsorbent changes any more.
[0062] Then turn on the light source and irradiate the photocataly...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com