Two-stage lightning current withstanding fusing structure and fuse adopting same
A two-stage, lightning current technology, used in circuits, electrical components, emergency protection devices, etc., can solve the problems of continuous lightning current resistance and fuse blowing at small currents, achieving small size, long life, good safety effect of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] First of all, this embodiment is a fuse structure suitable for a fuse, which can effectively prevent the main circuit from malfunctioning caused by the pulse current. The existing fuse structure is usually a single homogeneous linear structure, which is connected with the electrodes at both ends of the fuse to form a series structure. Once subjected to overload current, the entire fuse will generate a certain amount of heat to cause its temperature to rise. When the temperature is higher than its melting point, it will melt or gasify (melting or gasification depends on its temperature rise time, if the temperature rises too fast , it may lead to gasification of the fuse), thereby forming an open circuit and avoiding damage to the main circuit. But now many fuses are combined with SPD to form a backup protector, so as to comprehensively protect the entire circuit.
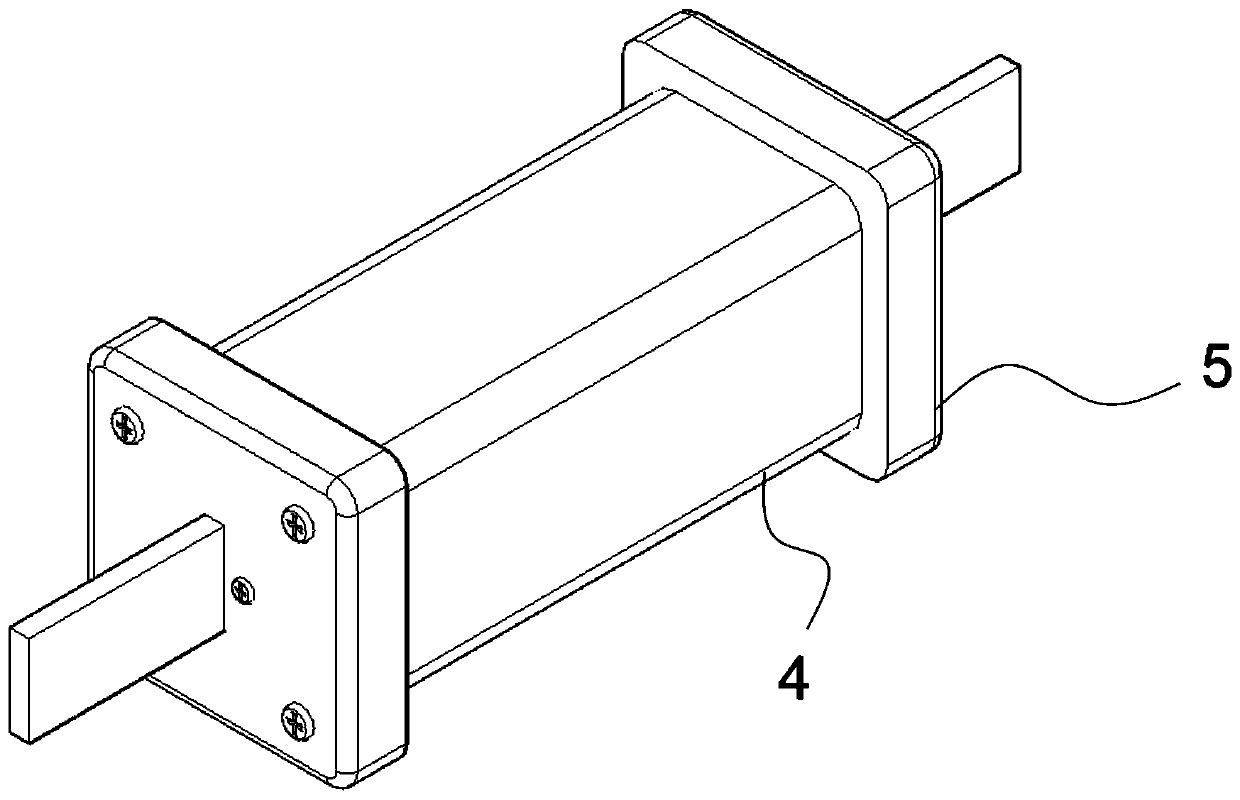
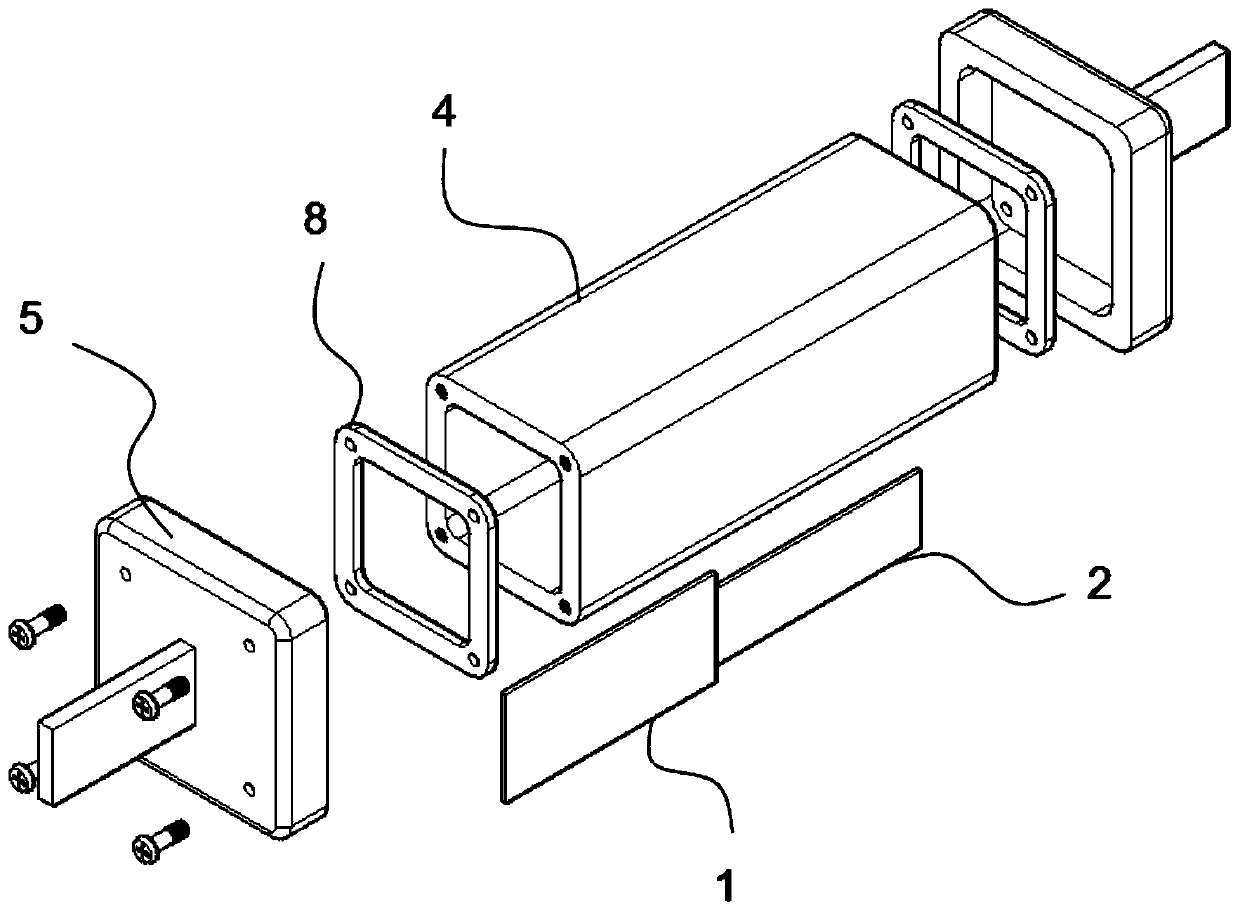
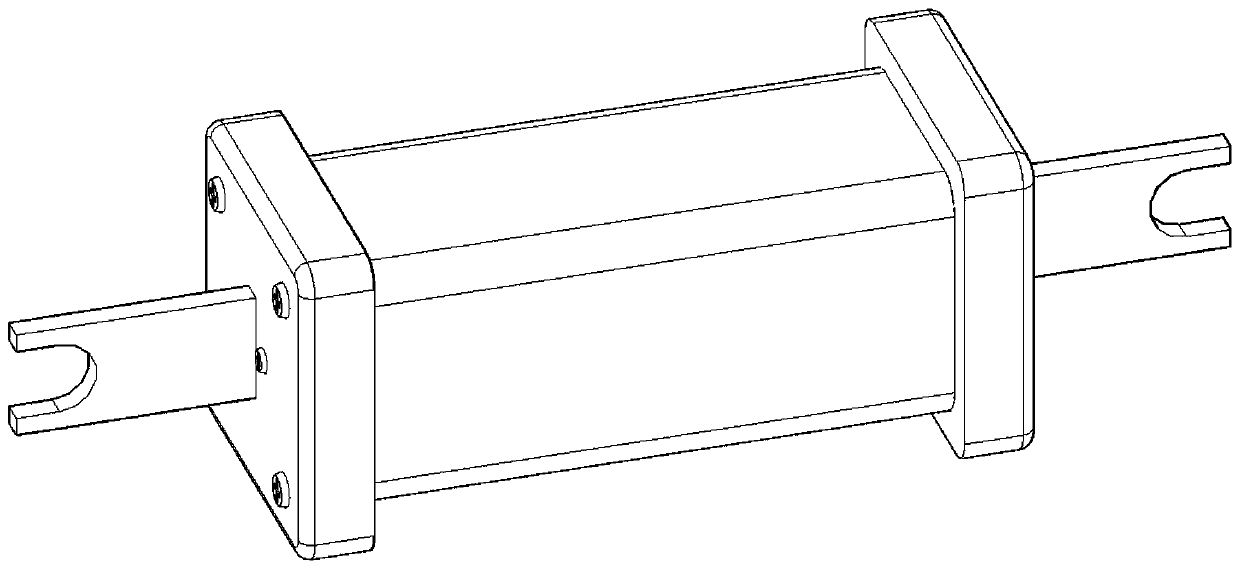
[0045] Such as Figure 1-5 As shown, this embodiment is a two-stage lightning current-resistant fusing s...
Embodiment 2
[0050] This embodiment is a two-stage lightning current-resistant fusing structure, including a first-stage conductor 1 connected to an electrode and a second-stage conductor 2 connected to another electrode, the first-stage conductor 1 and the second-stage conductor 2 in series; the melting point of conductor 1 in the first stage is higher than the melting point of conductor 2 in the second stage, conductor 1 in the first stage is energized and heats up and is transmitted to conductor 2 in the second stage, and when the temperature is higher than the melting point, conductor 2 in the second stage is fused and disconnected, and the first stage The cross-sectional area of conductor 1 is smaller than the cross-sectional area of conductor 2 in the second stage.
[0051] In the first stage, the conductor 1 is a conductive structure with a high melting point and a certain resistance value. It is made of tungsten alloy material, and its melting point is about 3100°C. In the seco...
Embodiment 3
[0055] This embodiment is a two-stage lightning current-resistant fusing structure, including a first-stage conductor 1 connected to an electrode and a second-stage conductor 2 connected to another electrode, the first-stage conductor 1 and the second-stage conductor 2 in series.
[0056] The melting point of conductor 1 in the first stage is higher than the melting point of conductor 2 in the second stage. Conductor 1 in the first stage energizes and generates heat and transmits it to conductor 2 in the second stage, and when the temperature is higher than the melting point, conductor 2 in the second stage is fused and disconnected, and conductor 1 in the first stage crosses the circuit. The cross-sectional area is smaller than the cross-sectional area of the conductor 2 in the second stage.
[0057] The fusing structure also includes a heat dissipation structure 3 arranged around the second-stage conductor 2 for heat dissipation, and an insulating medium is provided betwee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com