Nucleic acid polypeptide complex probe and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for polypeptide complexes and nucleic acids, which is used in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient sensitivity for detection, etc., and achieves a simple, easy, and time-consuming preparation method. , highly selective effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
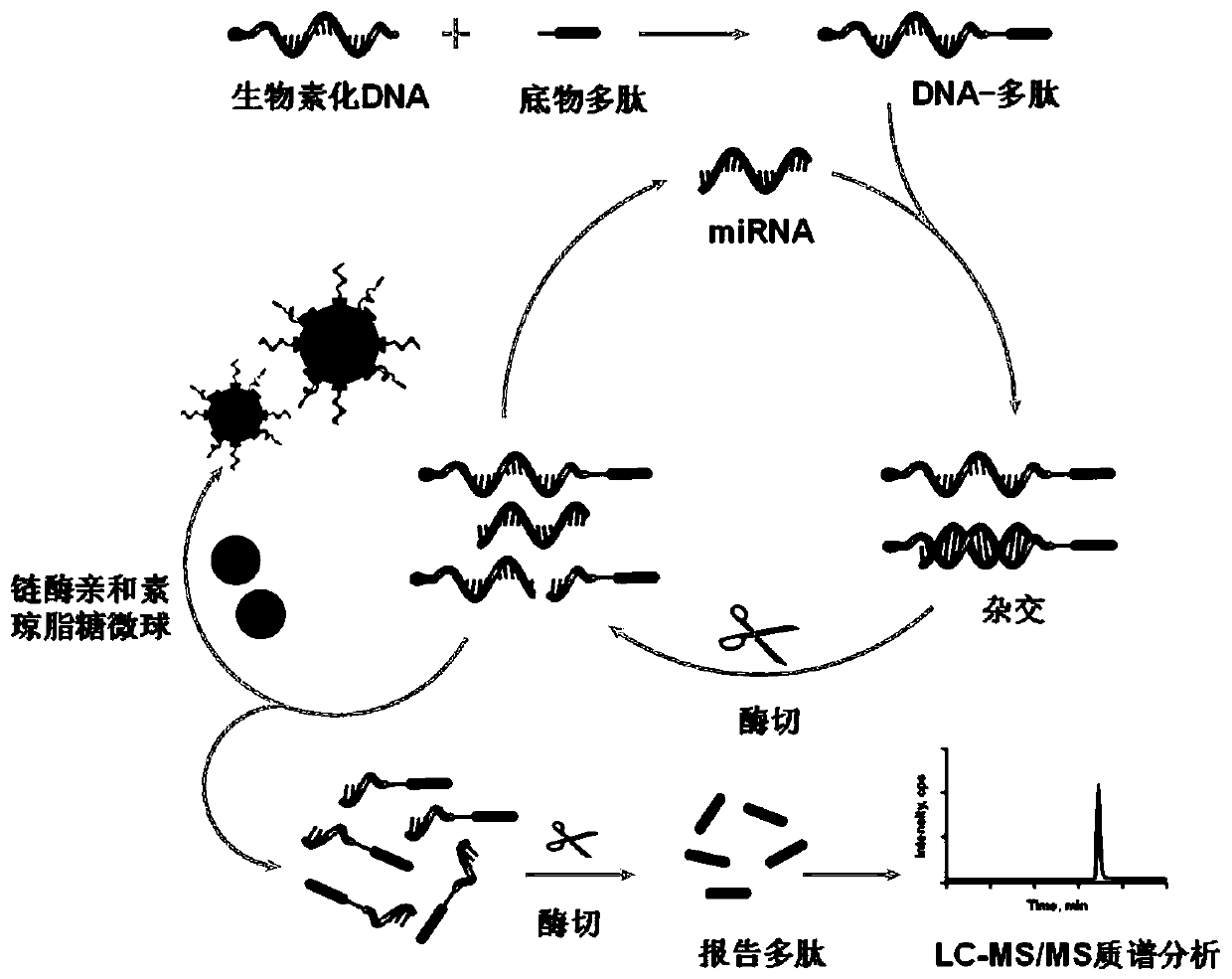
[0033] Preparation and Identification of Example 1 Nucleic Acid Polypeptide Complex Probe
[0034] (1) Preparation and purification of nucleic acid-polypeptide complex probes
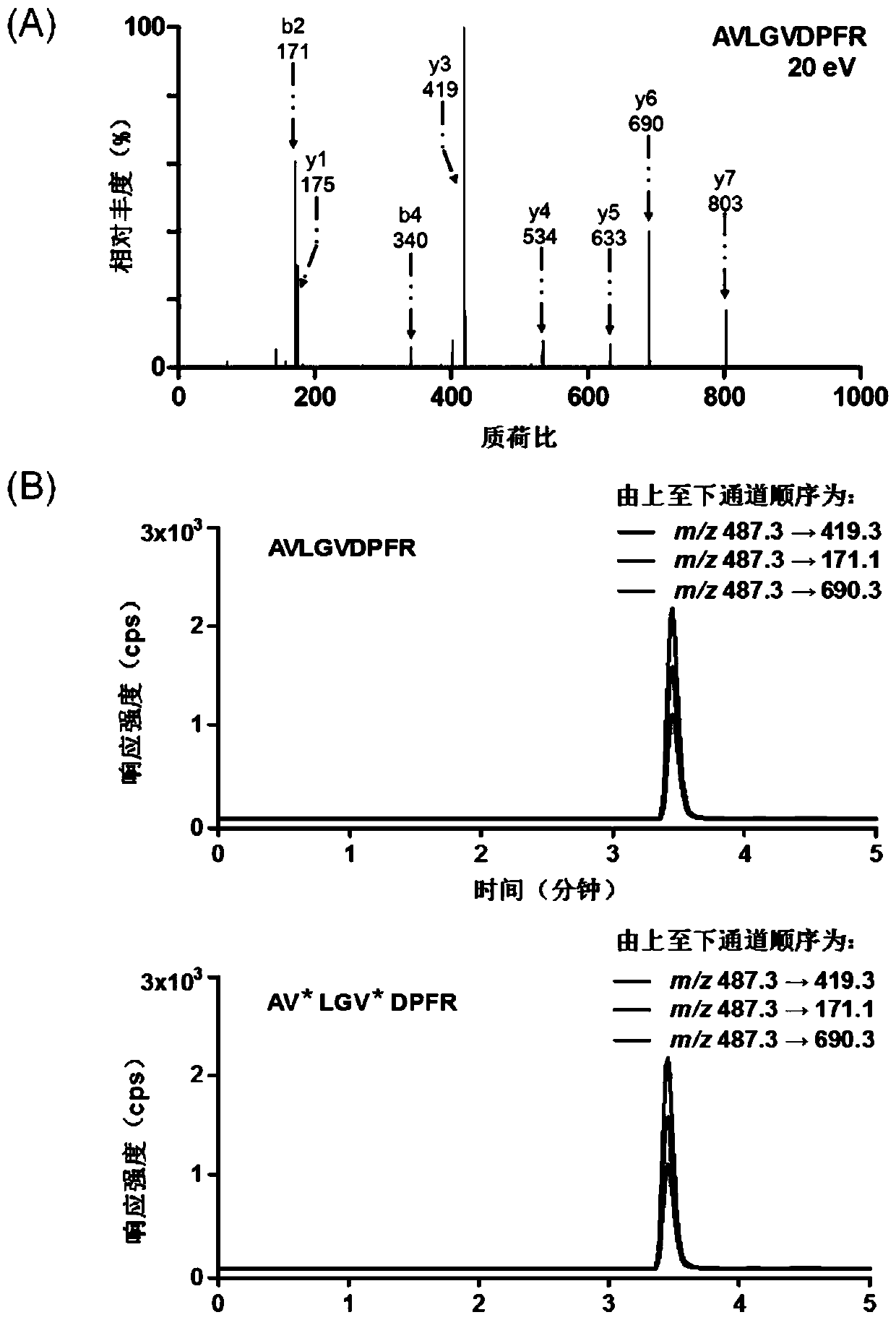
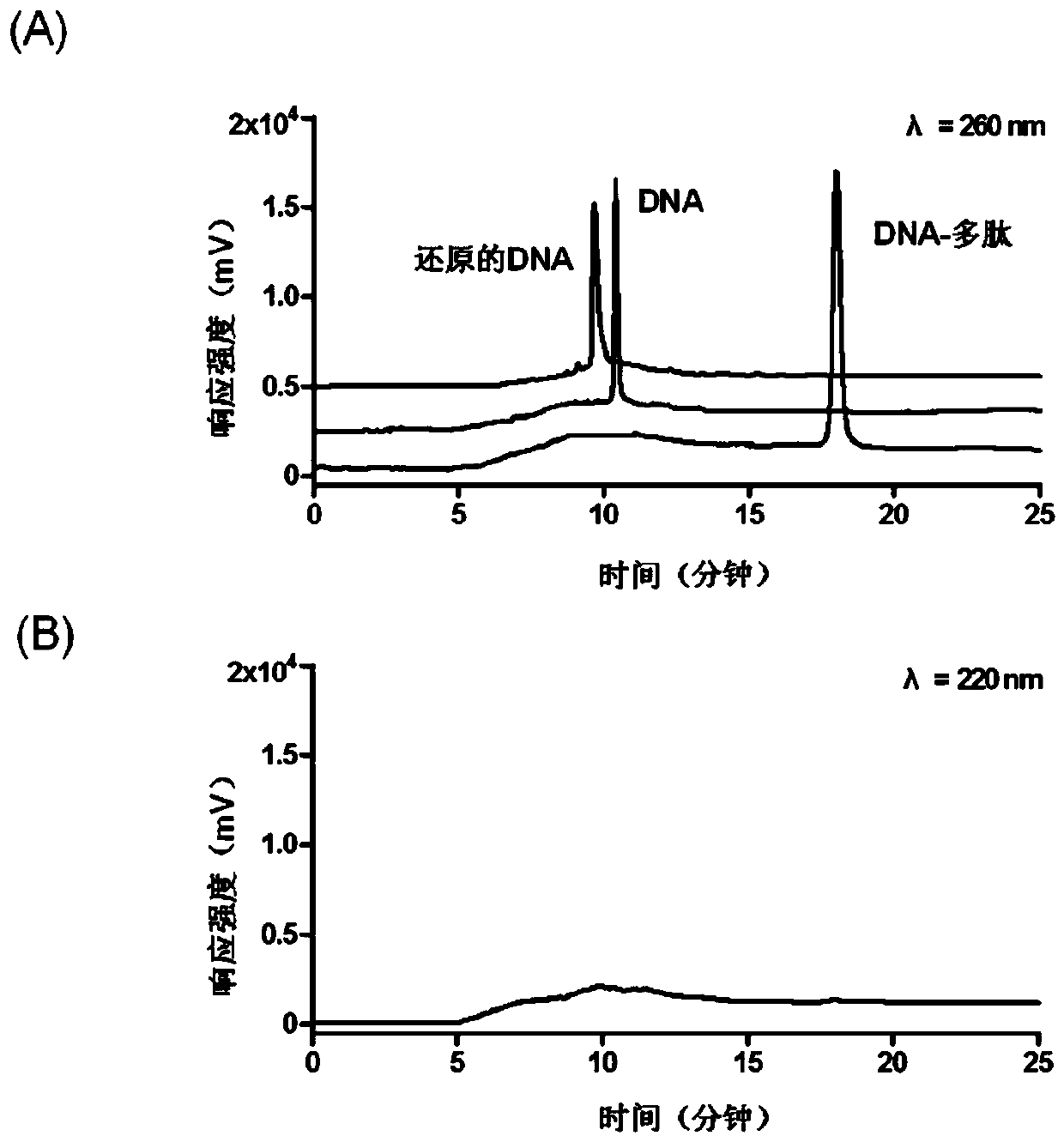
[0035] Using trichloroethyl phosphate as the reducing agent, 200 μL of 3’-end disulfide bond-modified DNA at a concentration of 1 μM: 5’-biotin-TCCATCATTACCCGGCAGTATTA-3’ (Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai) and 20 μL of TCEP reduction beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) mixed, reacted and shaken at 37°C for 2h; then centrifuged the sample at 1000×g for 6min; took the supernatant containing the reduced DNA prepared above, and added the same A volume of 20 μM N-terminal maleimide-modified substrate polypeptide: GDKAVLGVDPFR (Genetide Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai), shaking at 37°C for 4 hours for conjugation reaction, followed by using the difference in retention time before and after conjugation (DNA And the retention time of the DNA-polypeptide complex is 10.4min and 18.2min respectively, ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 Double-strand-specific nuclease-mediated isothermal amplification strategy
[0039] (1) Optimization of conditions for double-strand-specific nuclease-mediated amplification
[0040] Double-strand-specific nuclease-mediated amplification relies on the specific enzymatic selectivity of double-strand-specific nucleases for double-stranded DNA or DNA strands in DNA:RNA hybrid duplexes. In this study, the occurrence of DNA-polypeptide complex and miR-200c hybridization and double-strand-specific nuclease cleavage was confirmed by HPLC analysis. Such as Figure 6 As shown, the retention times of miR-200c and nucleic acid-polypeptide complex probes were 7.3 and 17.9 minutes, respectively. After hybridization with excess miR-200c, the nucleic acid-polypeptide complex probe peak disappeared, and a newly formed hybridization product appeared at 17.3 minutes. After further treatment with double-strand-specific nuclease, only partial DNA-polypeptide fragments generate...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3 Quantification of miR-200c in BCSCs using double-strand-specific nuclease-mediated amplification combined with LC-MS / MS
[0054] Using the method in Example 2, the content of miR-200c in MCF-7 cells and breast cancer stem cells was measured, which were (5.86±1.40)×10 3 copies / cell and (3.80±0.66)×10 2 copies / cell. The level of miR-200c in breast cancer stem cells was lower than that in cancer cells (p Figure 11 ). Compared with our method, the level of miR-200c detected by qRT-PCR was slightly lower, but no significant difference was observed between the two methods.
[0055] In addition, we quantified miR-200c in magnetically sorted stem cells from 16 human breast cancer tissue samples. The results showed that BCSCs accounted for 12.1 ± 4.3% (range: 3.0-21.5%) of the total cells in the tumor ( Figure 12 ); the level of miR-200c was quantified as (1.43±0.96)×10 3 copy / breast cancer stem cell (range: (0.50-3.13)×103 copy / breast cancer stem cell) ( Figur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com