Production method of Luneberg lens
A Lumber lens and production method technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, antennas, etc., can solve the problems of difficult control of drilling density and precision, discontinuity of dielectric constant, complex structure, etc., and achieve easy control of lens characteristics and excellent lens performance. The effect of excellent indicators and simple production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
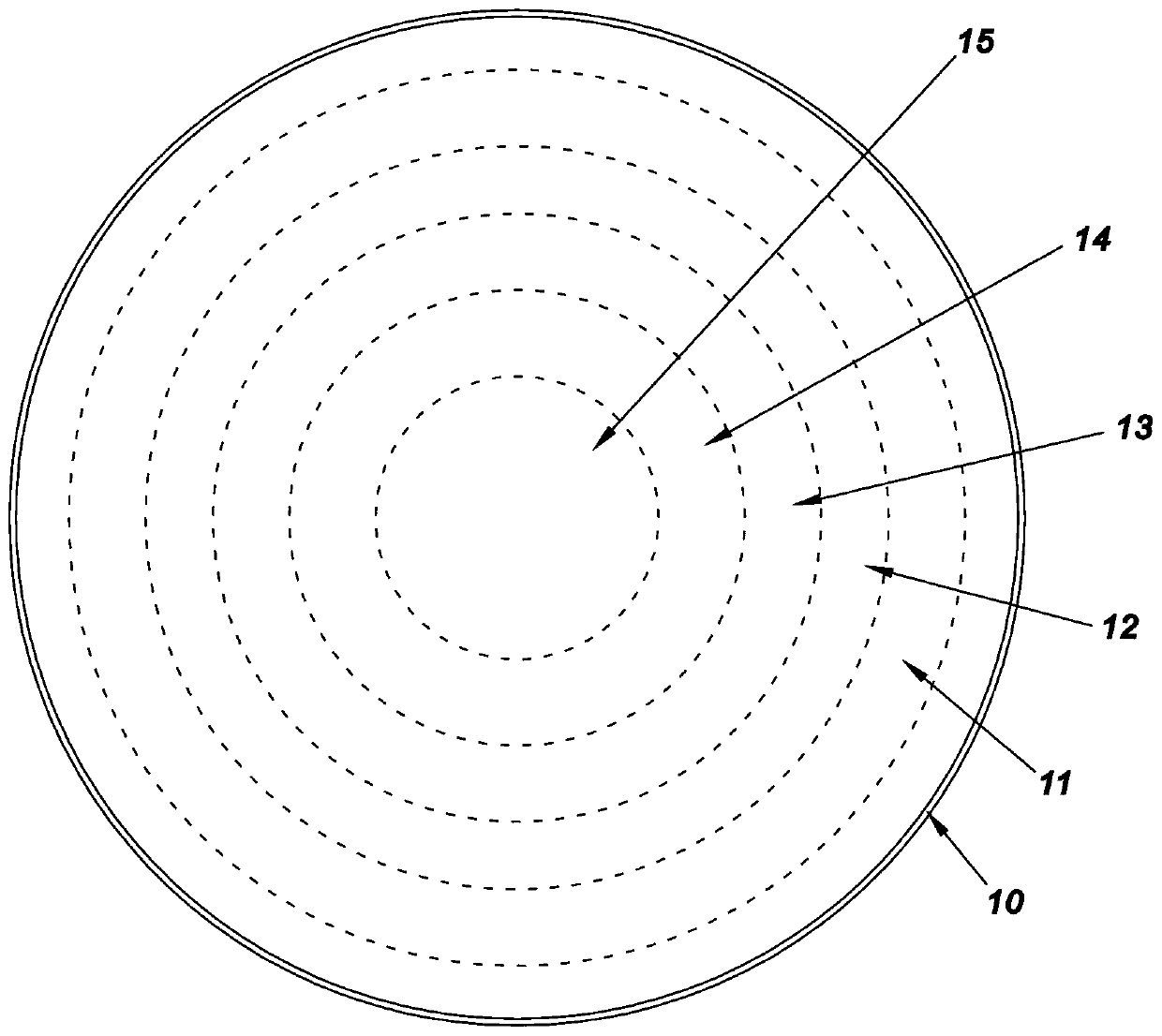
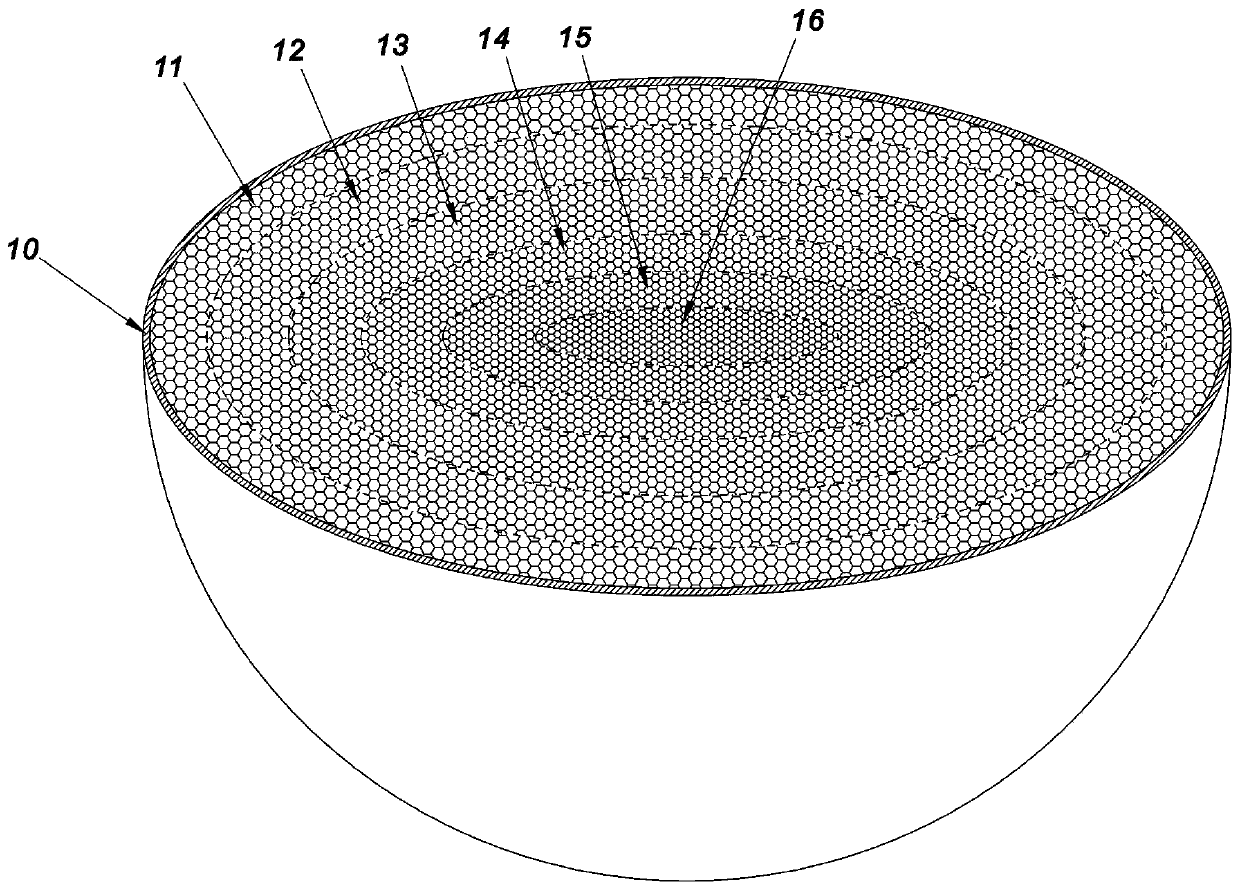
[0049] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment takes the production of a spherical Lunberg lens with 5 dielectric layers as an example. Such a Luneberg lens is sequentially composed of a lens half shell 10, a first dielectric layer 11, a second dielectric layer 12, a third dielectric layer 13, a fourth dielectric layer 14, a fifth dielectric layer 15 and a half inner core 16 from outside to inside. .
[0050] Its processing method is as follows:
[0051] Step 1): Prepare a hemispherical shell as the lens half shell 10 .
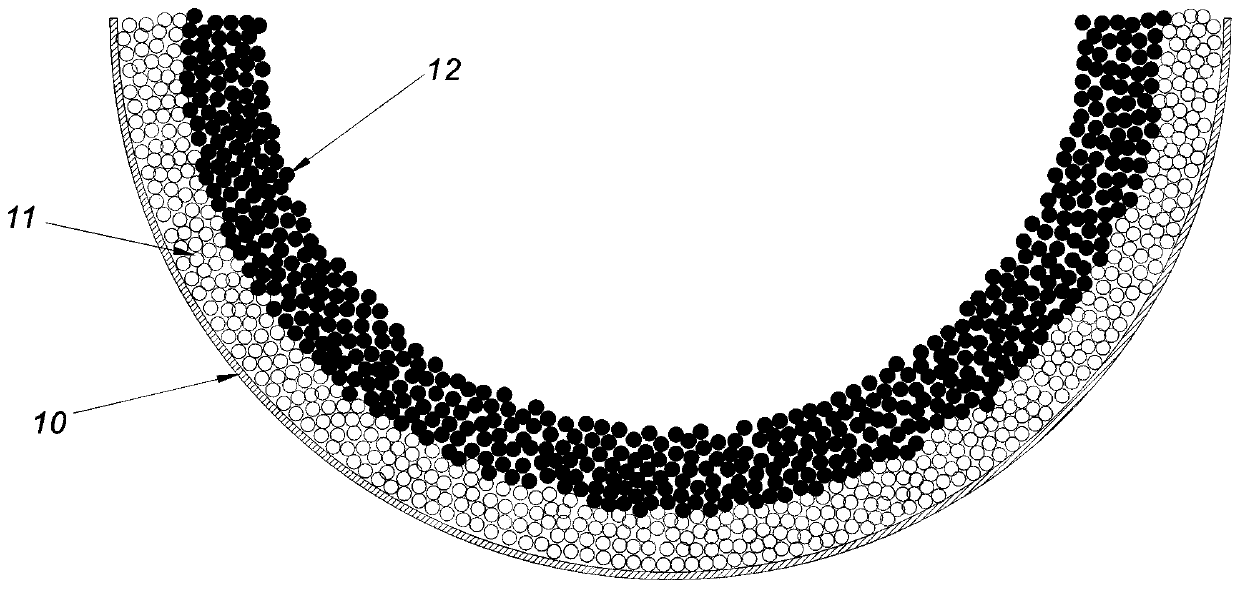
[0052] Step 2): put the lens half-shell 10 into a hemispherical die, the outer wall of the lens half-shell 10 is in contact with the hemispherical die, and this hemispherical die is used to fix the lens half-shell 10 and to bear the punch force, so as to prevent the lens half-shell 10 from being deformed by force. Spray adhesive on the inner wall surface of the lens half-shell 10, pour the prefabricated first granular material into the lens half-shell ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] In this embodiment, the production of a spheroidal Luneberg lens with 5 dielectric layers is taken as an example.
[0068] A spheroid can be understood as a three-dimensional shape formed by rotating an ellipse along its major axis, such as Figure 4 As shown, such a three-dimensional shape is a three-dimensional shape that can be separated axisymmetrically. There are two methods for axisymmetrically separating the three-dimensional shape: one is to divide the three-dimensional shape into two axisymmetric halves by the plane passing through the major axis of the ellipse , for example with Figure 4 The other is to divide the three-dimensional shape into two axisymmetric halves by a plane passing through the minor axis of the ellipse and perpendicular to the major axis, for example, Figure 4 The B plane to separate.
[0069] In the two halves obtained by the previous separation method, neither half is a rotating body. Therefore, when making a half-side Lunberg lens, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com