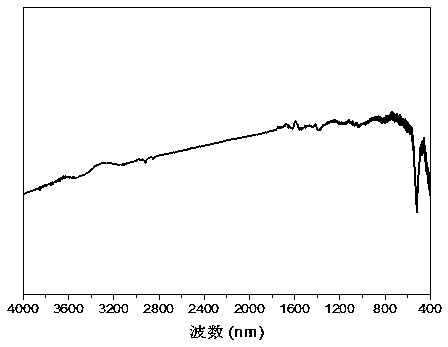
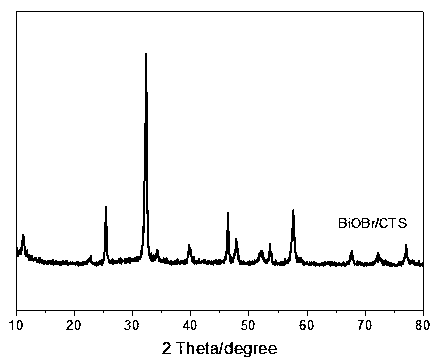
Chitosan hybrid bismuth oxybromide micro-nano multi-layer material and preparation and application thereof
A technology of bismuth oxybromide and chitosan, applied in the field of composite materials and photocatalysis, can solve the problems of complicated operation, few active sites, small absorption range, etc., and achieve high photocatalytic activity, good application prospect, and the effect of broadening absorption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Take 1.0 g of chitosan with a molecular weight of 15 kDa, add it to 20 mL of nitric acid solution (2 mol / L), stir to make it completely dispersed, and obtain a chitosan dispersion;
[0028] (2) Take 5.0 g of bismuth nitrate, add it to 30 mL of nitric acid solution (2 mol / L), stir to dissolve it completely, and obtain bismuth nitrate solution;
[0029] (3) Take 2.0 g of cetyl ammonium bromide, dissolve it in 10 mL of water, stir it to dissolve completely, and obtain bromide salt solution;
[0030] (4) Under magnetic stirring, slowly add the chitosan dispersion into the bismuth nitrate solution, and magnetically stir for 20 minutes to ensure that the reaction system is evenly dispersed; Slowly added to the reaction system, and stirred for 40 min; then, the reaction system was moved into a PPL-lined stainless steel reactor, and hydrothermally reacted at 200°C for 9 h. The obtained product was separated by suction filtration, washed 6 times with distilled water, and vac...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Take 1.5 g of chitosan with a molecular weight of 20 kDa, add it to 30 mL of acetic acid solution (10 wt%), stir to make it completely dispersed, and obtain a chitosan dispersion;
[0033] (2) Take 3.0 g of bismuth nitrate, add it to 30 mL of glacial acetic acid solution (10 wt%), stir to dissolve it completely, and obtain a bismuth nitrate solution;
[0034] (3) Dissolve 1.5 g of potassium bromide in 10 mL of water, stir to dissolve completely, and obtain potassium bromide solution;
[0035](4) Under magnetic stirring, slowly add the chitosan dispersion into the bismuth nitrate solution, and magnetically stir for 20 minutes to ensure that the reaction system is evenly dispersed; then slowly add the potassium bromide solution into the reaction system within 5 minutes under stirring and stirred for 40 min; then, the reaction system was transferred into a PPL-lined stainless steel reactor, and hydrothermally reacted at 120 °C for 15 h. The obtained product was separat...
Embodiment 3
[0037] (1) Take 0.5 g of chitosan with a molecular weight of 5 kDa, add it to 15 mL of nitric acid solution (4 mol / L), stir to make it completely dispersed, and obtain a chitosan dispersion;
[0038] (2) Take 2.5 g of bismuth bromide, add 25 mL of acetic acid solution (10 wt%), stir to dissolve completely, and obtain bismuth nitrate solution;
[0039] (3) Take 1.0 g of hexadecyl ammonium bromide, dissolve it in 10 mL of aqueous solution, stir to dissolve it completely, and obtain potassium bromide solution;
[0040] (4) Under magnetic stirring, slowly add the chitosan dispersion into the bismuth nitrate solution, and magnetically stir for 30 minutes to ensure that the reaction system is evenly dispersed; then slowly add the potassium bromide solution into the reaction system within 15 minutes under stirring and stirred for 40 min; then, the reaction system was transferred into a PPL-lined stainless steel reactor, and hydrothermally reacted at 220 °C for 12 h. The obtained prod...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decolorization rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decolorization rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com