Method for separating and purifying lactic acid from lactic acid fermentation broth
A technology of lactic acid fermentation and lactic acid, applied in the separation/purification of carboxylic acid compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the cost of waste treatment, affecting the purity, and the low crystallization rate of calcium lactate, so as to reduce the discharge of waste liquid and reduce the The effect of extracting costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] The preparation of above-mentioned lactic acid fermentation liquid, step is as follows:
[0061] ① Activated strains: Take the above-mentioned Lactobacillus sake preservation tube out of the -80°C low-temperature refrigerator, streak the single bacteria on the MRS plate with a sterile inoculation loop, and culture in a 30°C incubator for 18 hours;
[0062] ②Cultivate the monobacteria in MRS broth at 30°C for 12 hours;
[0063] ③Inoculate lactic acid bacteria into 1L of MRS broth according to the inoculum amount of 2%, and culture at 30°C for 36 hours;
[0064] ④ Detection of lactic acid: L-lactic acid, the concentration is 56.50mg / mL, and the total mass is 56.50g.
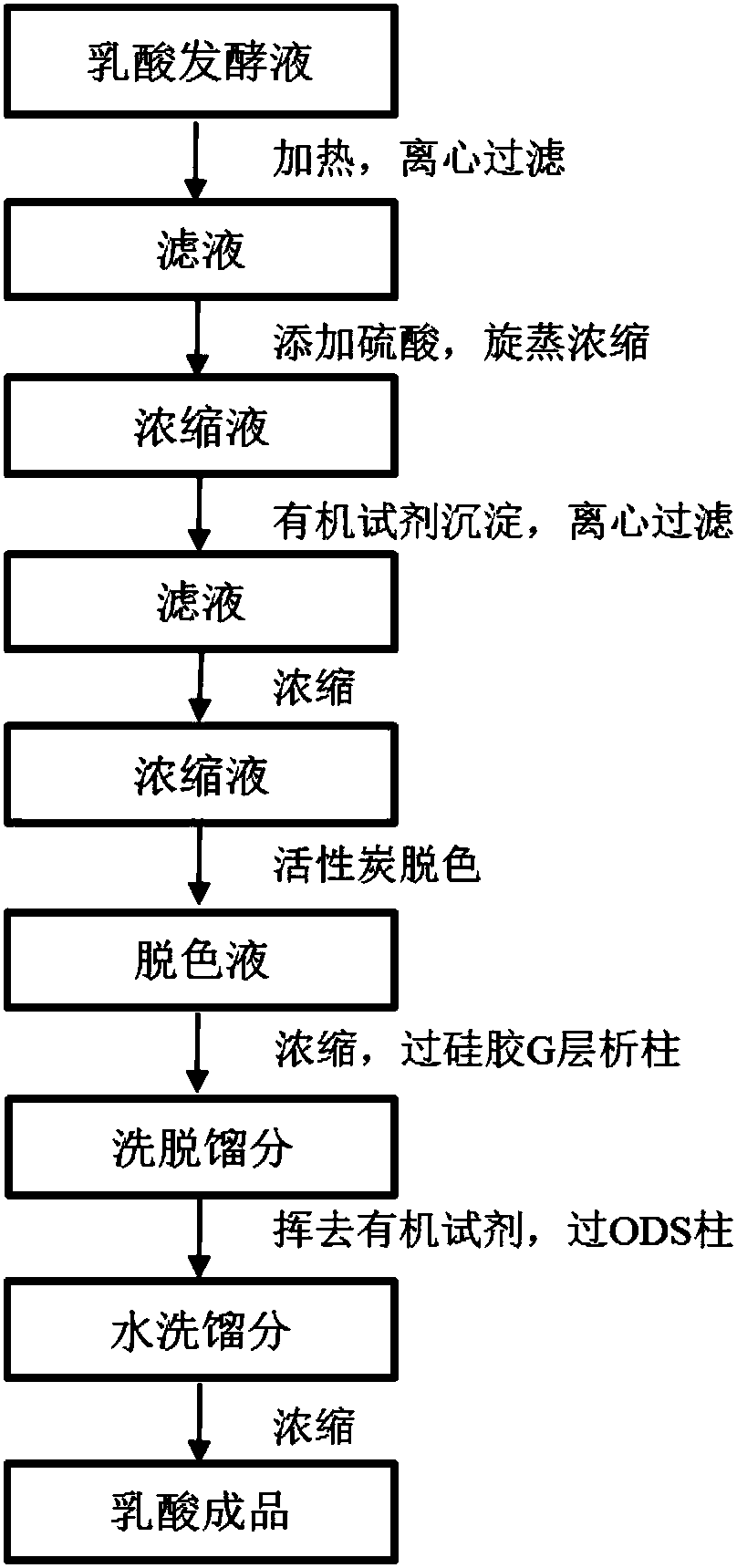
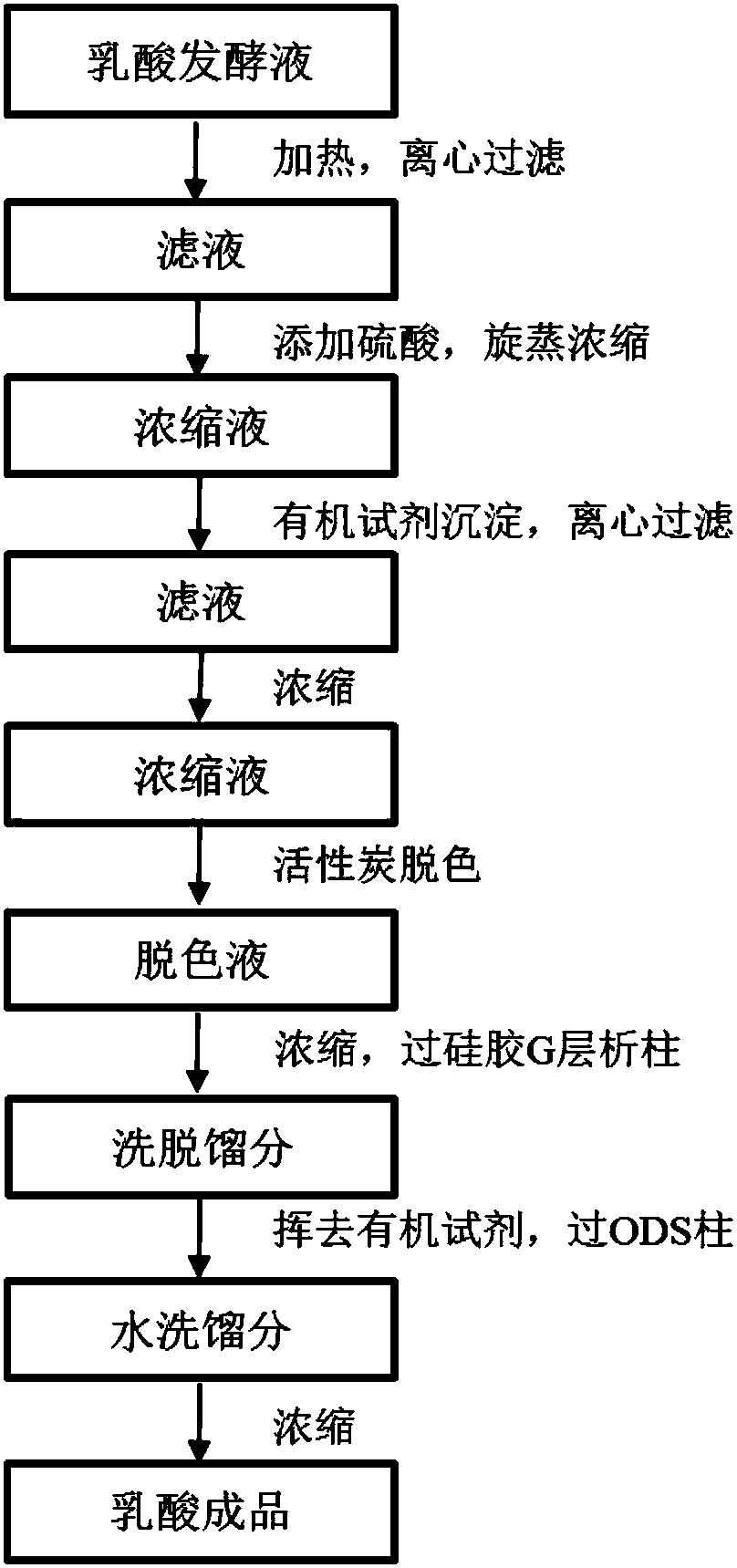
[0065] The separation and purification of lactic acid in lactic acid fermentation broth is as follows:
[0066] (1) heat treatment and removal of insoluble impurities such as bacteria:
[0067] Heat the fermentation broth to 70°C, stir at constant temperature for 9 minutes, and then centrifuge (rotating a...
Embodiment 2
[0083] The preparation of the above-mentioned lactic acid fermentation broth is the same as in Example 1.
[0084] The separation and purification steps of lactic acid in lactic acid fermentation broth are as follows:
[0085] (1) heat treatment and removal of insoluble impurities such as bacteria:
[0086] Heat the fermentation broth to 90°C, stir at a constant temperature for 8 minutes, and then centrifuge (9000 g for 15 minutes) to remove insoluble impurities such as bacteria and residual calcium carbonate, and filter the supernatant to obtain filtrate 1;
[0087] (2) Organic reagent precipitation to remove fat-soluble impurities:
[0088] ①Add 50% sulfuric acid to the filtrate 1 until the pH is 1.0, so that all the calcium lactate in the filtrate 1 is converted into lactic acid, concentrate by rotary evaporation at 70°C to a thick paste, and add ethanol to the concentrated solution (final concentration is 75%) , mix well, stand at 4°C for 4h, centrifuge (rotating speed i...
Embodiment 3
[0102] The preparation of the above-mentioned lactic acid fermentation broth is the same as in Example 1.
[0103] The separation and purification steps of lactic acid in lactic acid fermentation broth are as follows:
[0104] (1) heat treatment and removal of insoluble impurities such as bacteria:
[0105] Heat the fermentation broth to 85°C, stir at a constant temperature for 5 minutes, and then centrifuge (10000 g for 10 minutes) to remove insoluble impurities such as bacteria and residual calcium carbonate, and filter the supernatant to obtain filtrate 1;
[0106] (2) Organic reagent precipitation to remove fat-soluble impurities:
[0107] ① Add 60% sulfuric acid to the filtrate 1 until the pH is 1.0, so that all the calcium lactate in the filtrate 1 is converted into lactic acid, concentrate by rotary evaporation at 70°C to a thick paste, and add ethanol to the concentrated solution (final concentration is 60%) , mix well, stand at 4°C for 8 hours, centrifuge (rotating ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com