A CTL epitope polypeptide of Cryptosporidium parvum and its application and vaccine
A technology of Cryptosporidium parvum and epitope peptides, which can be used in applications, medical preparations containing active ingredients, peptide sources, etc., can solve the problems that hinder the research and application of epitope vaccines of Cryptosporidium parvum, and achieve great development and application. potential effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Selection and synthesis of CTL epitope polypeptide of Cryptosporidium parvum Gp15 protein.
[0033]Scan the main pathogenic protein and surface protein GP15, GP40, CSL, GP900, HSP70, CP15 and CP23 of Cryptosporidium parvum, select a polypeptide with amino acid sequence such as SEQ ID No.1, named P1, and its nucleotide sequence Research was carried out as shown in SEQ ID No. 2 in the Sequence Listing. Polypeptide P1 is derived from GP15 protein. Polypeptide P1 is synthesized by solid-phase peptide synthesis method (Fmoc / tBu strategy). After synthesis, it is purified by HPLC with a purity of 98%.
[0034] The present invention first uses the bioinformatics analysis method to predict the H-2Kb, H-2Db restricted polypeptide, and screens a large number of polypeptides from these epitopes for testing, and finally screens out 8 polypeptides with strong predicted affinity ( peptide1-peptide8, peptide2 are polypeptides with amino acid sequences such as SEQ ID No.1, named P1), a...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Detection of Binding Ability of Cryptosporidium parvum CTL Epitope Polypeptide to Mouse H-2kb and Human HLA-A*0201 Molecules by Protein Refolding Experiment
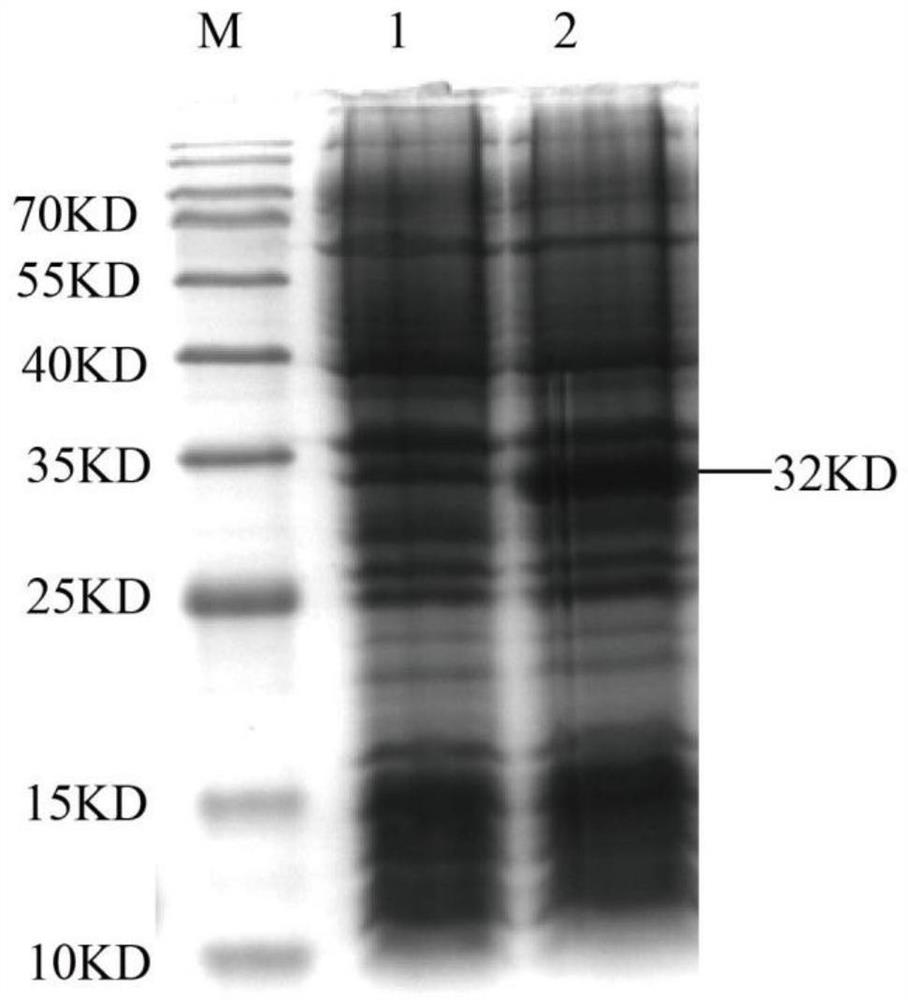
[0037] 1. Preparation of mouse MHC class I molecule (H-2Kb) and light chain β2m (mouseβ2m, mβ2m) inclusion body protein
[0038] The DNA molecule ( The nucleotide sequence is inserted between the prokaryotic expression plasmid pET-21a (+) restriction site Nde I and Xho I (as shown in SEQ ID No.4 in the sequence table) to obtain a recombinant expression plasmid named pET-21a ( +) / H-2kb.
[0039] The constructed pET-21a(+) / H-2Kb recombinant expression plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli BL21(ED3) competent cells, cultured overnight at 37°C, and recombinant transformants were screened by ampicillin (Amp) resistance. Single colonies of positive recombinant bacteria (named BL21(ED3) / H-2Kb) were picked and inoculated in 100 mL of LB medium containing Amp. After cultured with shaking at 37°C,
[0040] Accor...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The specific CTL immune response of Cryptosporidium parvum CTL epitope polypeptide immunized mice was detected by ELISPOT method.
[0055] The MHC I / antigenic peptide complex is a key factor in the activation of specific CTL immune responses. C57BL / 6N mice have a clear MHC genetic background and can be used as an experimental animal model for studying cellular immune responses to Cryptosporidium parvum. Rasmussen et al. showed that C57BL / 6N mice (whose MHC genotype is: H-2Kb, H-2Db) were inoculated 10 6 After one Cryptosporidium parvum oocyst, the infected state remained throughout the experimental period, indicating that this strain of mice is related to the resistance and susceptibility of Cryptosporidium parvum. And the H-2Kb restricted epitope has similar anchor residues with the epitope of HLA-A*0201 molecule widely expressed in the human population. Therefore, using C57BL / 6N mice as hosts to screen avian influenza virus CTL epitopes will provide a reliable basis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com