A multi-layer fast multi-pole parallel mesh refinement method based on auxiliary tree
A multi-pole and grid technology, applied in the field of computational electromagnetic computing research, can solve problems such as unavailable, discrete initial grid, and difficult reading, achieving high parallel efficiency, improving reading efficiency, and reducing additional communication.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
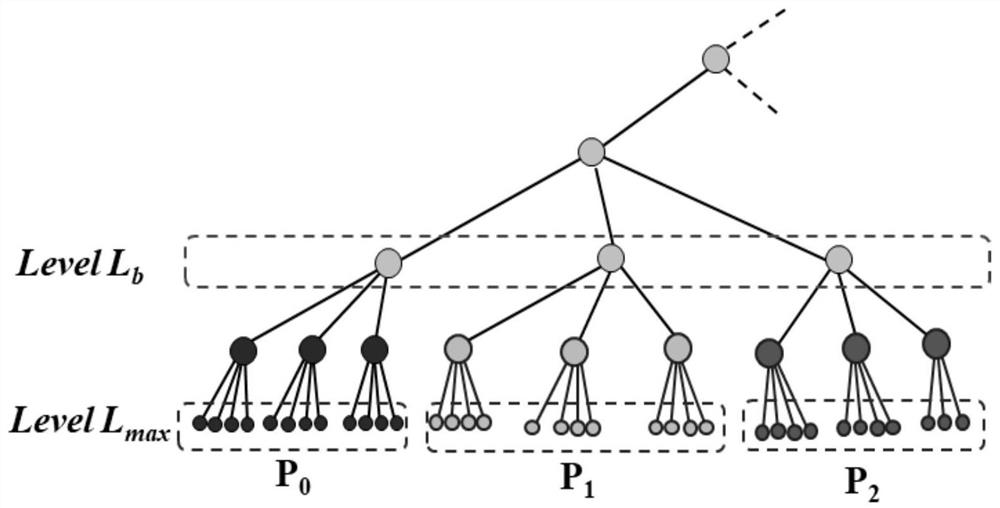
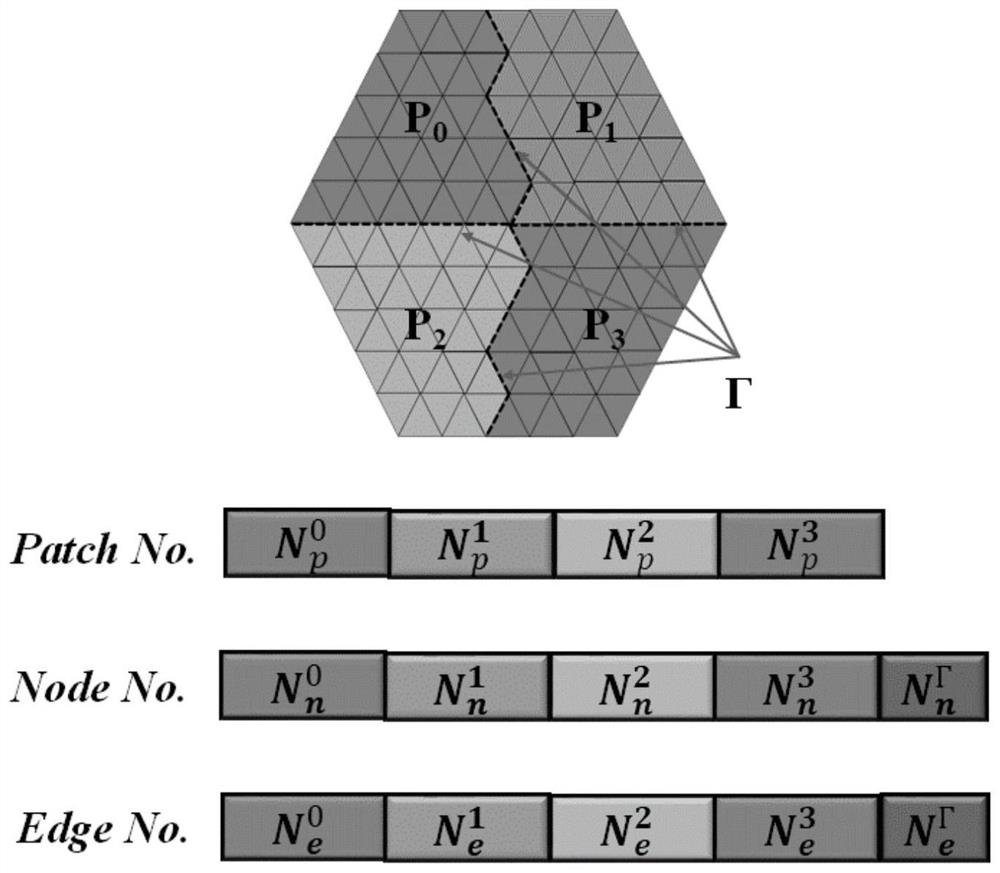
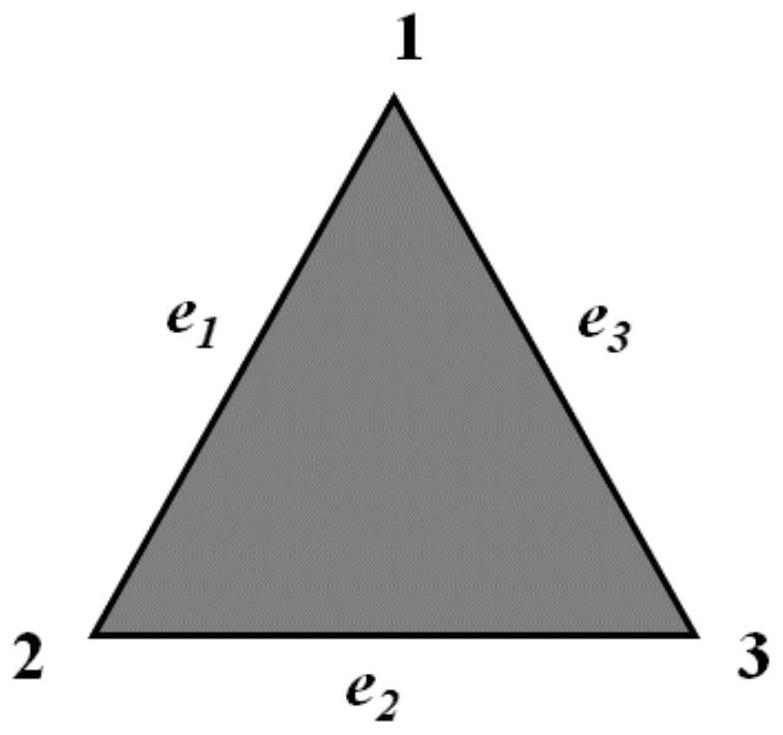
[0096] In this embodiment, a metal ball with a diameter of 2400 wavelength and such as Picture 9 The ship target model with a length of about 6000 wavelengths is shown as the target. The parallel mesh fine meshing method proposed by the present invention is used to call 960 MPI processes for fine meshing and then call the ternary parallel multi-layer fast multi-pole subroutine calculation to test The correctness of the generated mesh. The computing platform is the "Yuan" supercomputing platform of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Network Center, with 256G memory per node, 2 Intel-E5-2680V3 processors, and 24 CPU cores.
[0097] The mesh information generated for the two target fine sections is shown in Table 1. The initial grid is generated by CATIA subdivision, the coarse grid is used to construct the auxiliary tree from the initial grid after three fine divisions, and the final grid is the grid division that meets the required scale of calculation. It can be seen that the time...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com