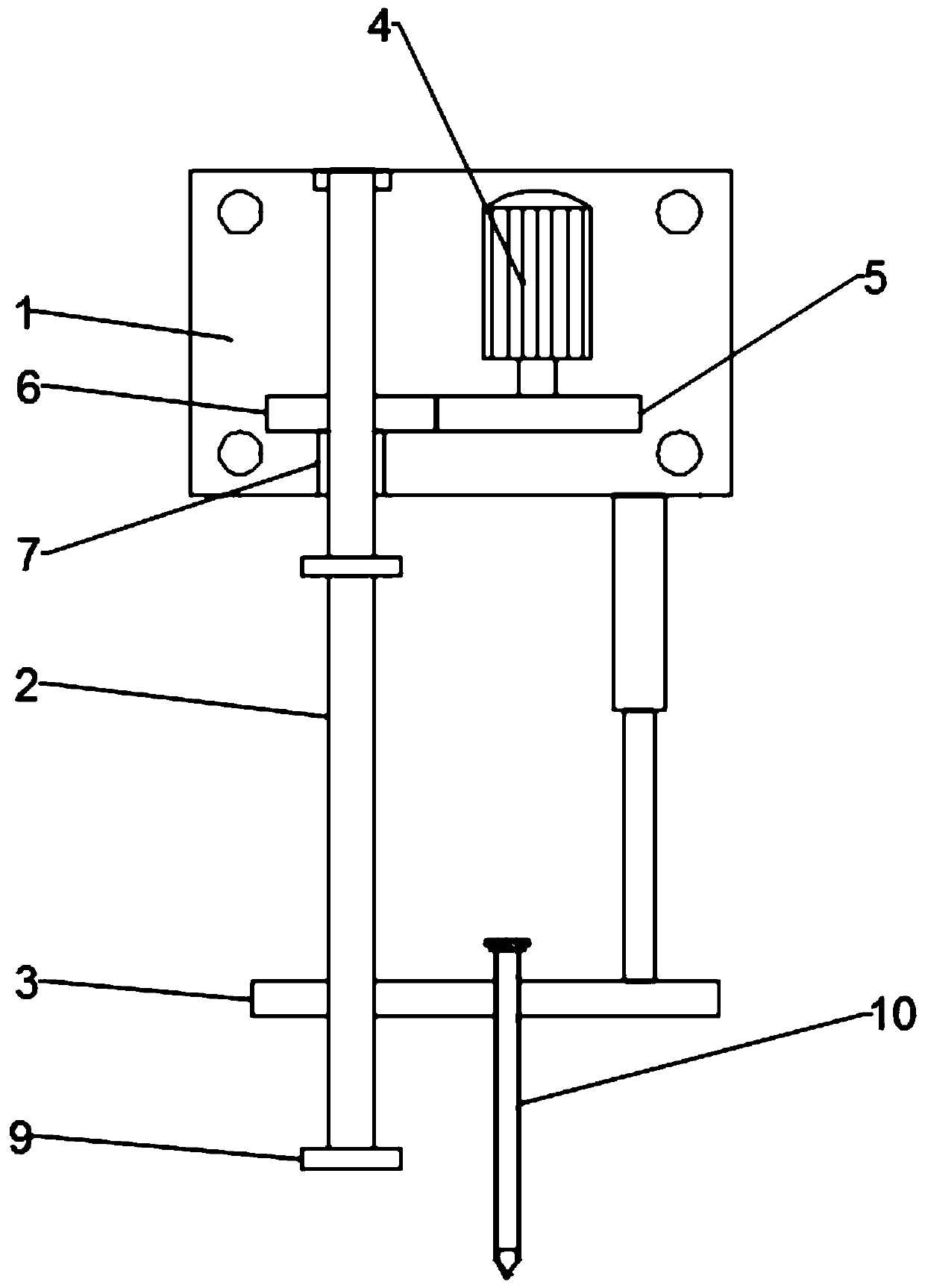
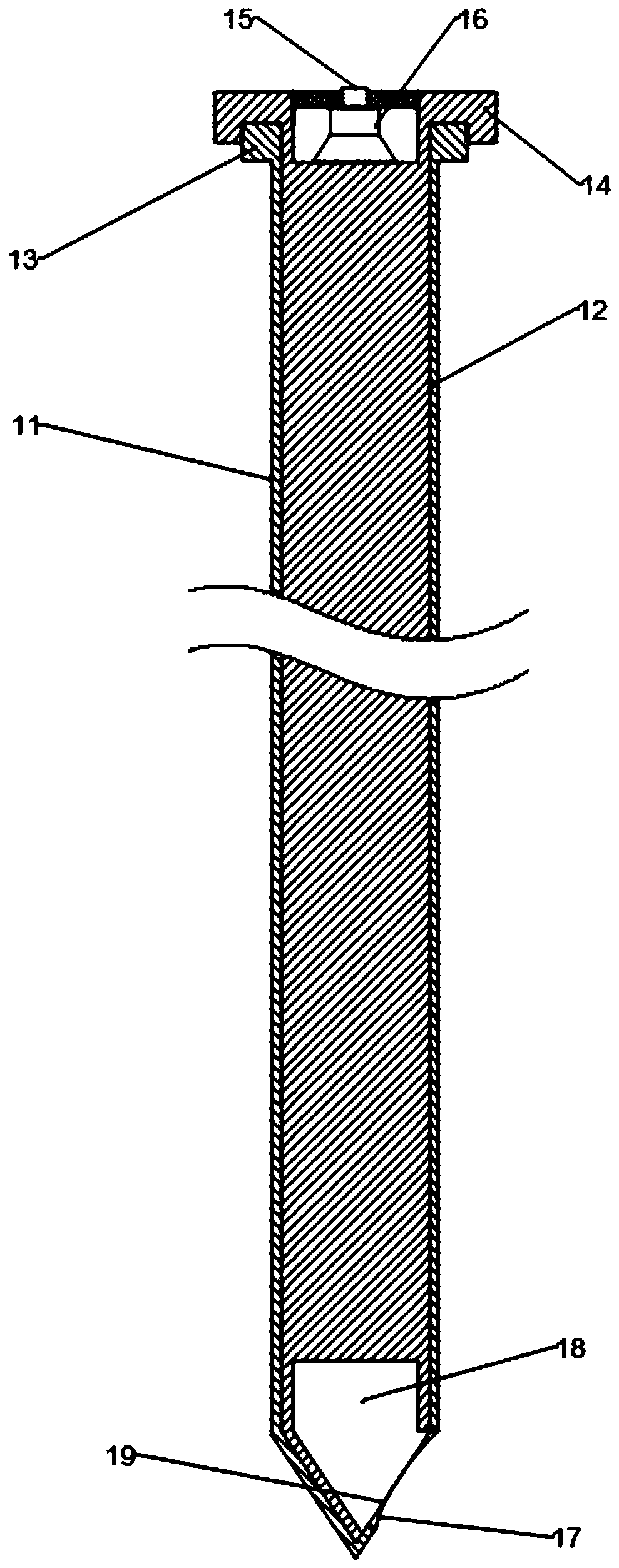
Method for performing single-needle or multi-needle puncture biopsy through laser guide
A puncture biopsy and laser-guided technology, applied in the direction of puncture needles, trocars, surgical navigation systems, etc., can solve the problems of inability to accurately guide puncture biopsy equipment, impossibility of puncture biopsy needle puncture, high experience requirements, etc., to achieve suitable promotion , avoid errors, and achieve high surgical accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] A method for single-needle or multiple-needle biopsy guided by laser, the specific steps are as follows:
[0058] S1. Fix the patient's body position, and obtain the image of the patient's pathological tissue through scanning;
[0059] S2. Determine the information of the pathological tissue according to the scanned image information, and determine the target sampling area;
[0060] S3. Import the confirmed target sampling area image into the processing system for modeling to obtain a target area model with a three-dimensional coordinate system;
[0061] S4. Import the target area model into the computer 3D treatment planning system for dimensional development, determine the biopsy route and puncture depth, and export the developed 3D data;
[0062] S5. Import the developed three-dimensional data into the laser emitting device, and adjust the laser emitting device to emit laser rays along the biopsy route;
[0063] S6. Adjust the puncture biopsy needle on the puncture...
Embodiment 2
[0066] As a preferred technical solution of the present invention, on the basis of embodiment 1, the specific steps of the step S2 are:
[0067] S201. Firstly, according to the scanned image of the patient's pathological tissue, confirm the volume, shape and position information data of the pathological tissue;
[0068] S202. Then confirm the important organs, bones, nerve vessels and adhesion with surrounding tissues around the pathological tissue, and determine the target sampling area according to the above information and the specific information of the pathological tissue;
[0069] S203. Then determine the model data of the target sampling area, and output the data for subsequent processing.
[0070] Through the scanned images, the basic information of pathological tissues can be determined, including the volume, shape and position information data of pathological tissues. Since important organs have a great influence on the vital signs of the human body, and the distribu...
Embodiment 3
[0072] As a preferred technical solution of the present invention, on the basis of Example 2, in the step S3, the modeling step is,
[0073] Step S301. Make a body surface marker point A0 on the target area of the patient;
[0074] Step S302. Establish a three-dimensional coordinate system for the regional model. The three-dimensional coordinate system takes the body surface marker point A0 as the coordinate origin, takes the vertical line passing through the body surface marker point A0 as the z-axis, and determines x according to the coordinate origin and the z-axis axis and y-axis;
[0075] Step S303. Perform three-dimensional coordinate editing on the body surface contour, internal organ contour and pathological tissue in the patient's target area in the three-dimensional coordinate system;
[0076] Since the biopsy needle needs to enter the body through the body surface of the human body, it is necessary to determine a positioning point on the patient's body surface to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com