Preparation method and application of gelatin microspheres
A technology of gelatin and microspheres, which is applied in the field of regenerative medicine, can solve the problems of aggravated microsphere adhesion, easy adhesion, and low sphericity, and achieve the effect of simple operation, low cost, and reduced adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
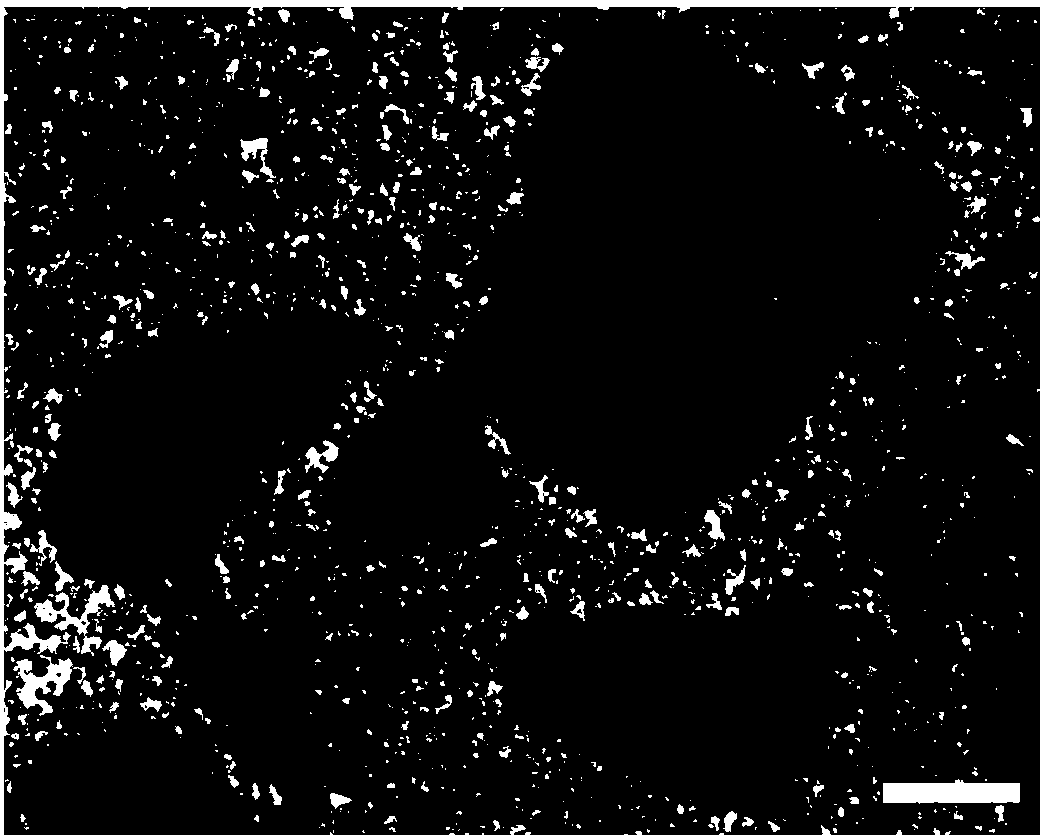
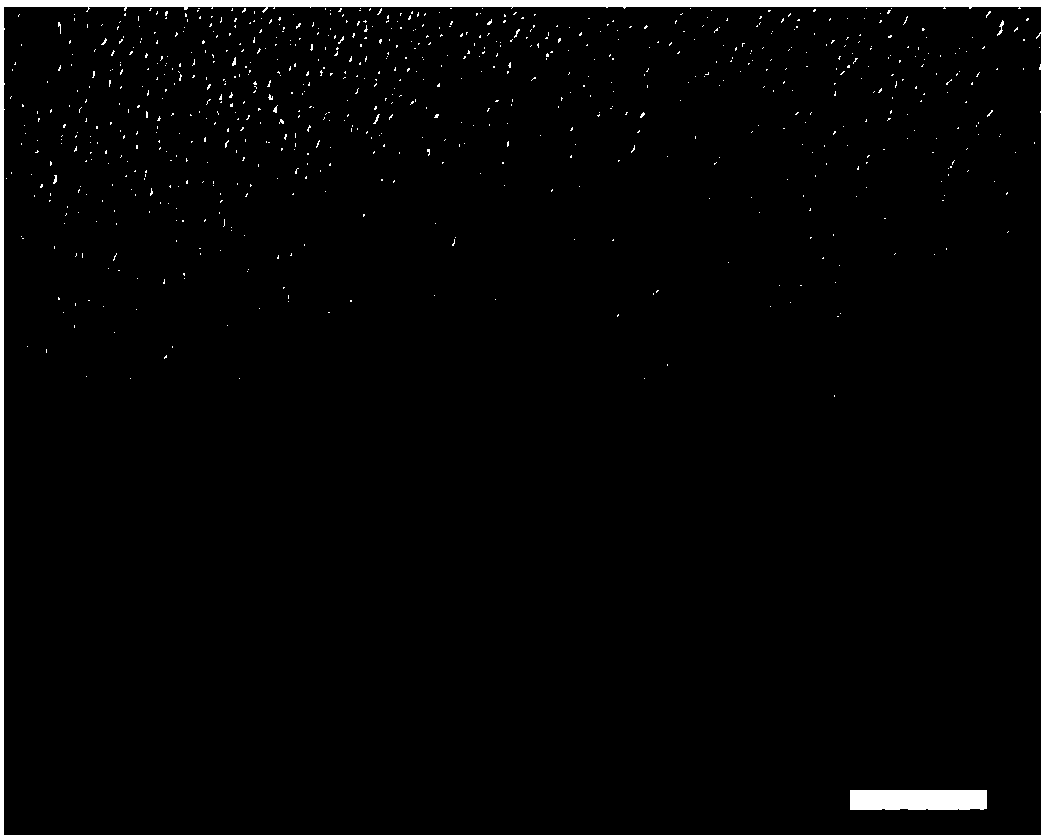
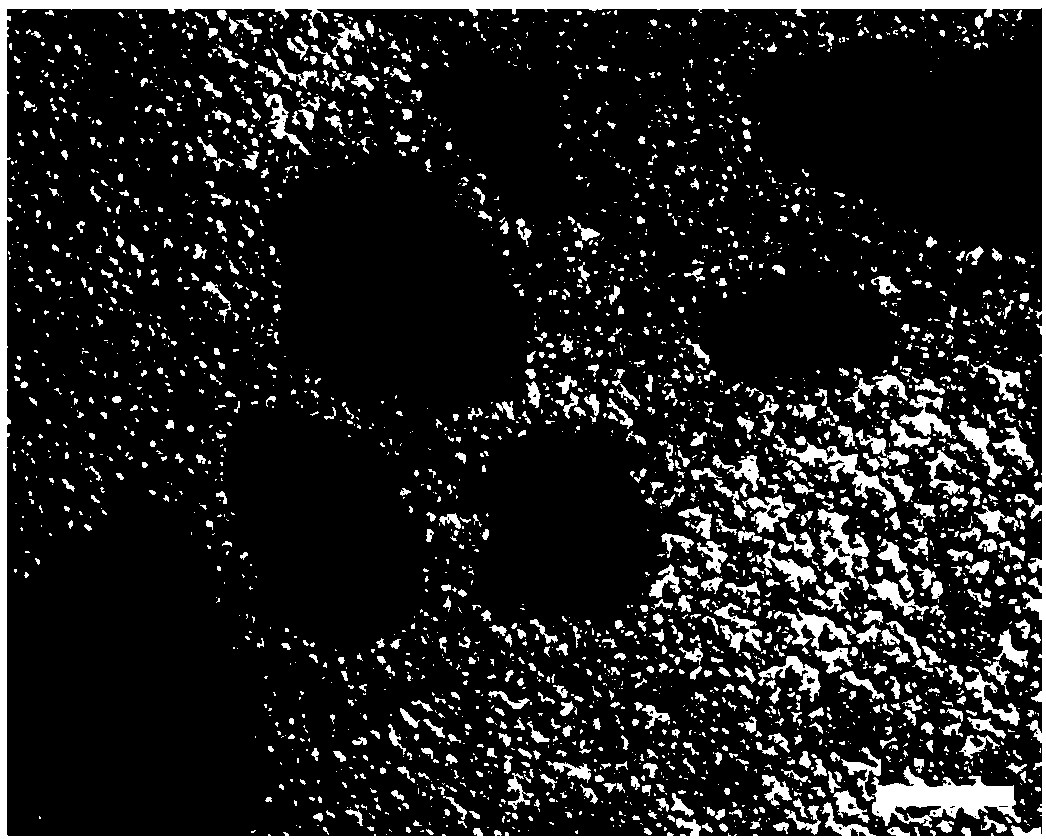
[0037] Prepare 20 g of 25% (w / v, g / ml) alkaline gelatin (120 Bloom g) aqueous solution and preheat it in a water bath at 53° C. for 1.5 h. In addition, prepare liquid paraffin containing span80 (the density of liquid paraffin is 0.9, and the volume ratio of liquid paraffin to span80 is 50:1), mix well, and preheat in a water bath at 53°C for 1.5h. After that, the gelatin solution was slowly added dropwise to the liquid paraffin under the stirring condition of 1200rpm, the volume ratio of the aqueous gelatin solution to the liquid paraffin containing span80 was 1:10, and the stirring time was 15min to prepare stable water-in-oil droplets. Then, under the condition of constant stirring speed, add an ice bath to cool down, and stir for 30 minutes to form solidified microspheres. Afterwards, 5% (w / v, g / ml) genipin solution was added, the final concentration of which was 0.3% (w / v, g / ml) when cross-linked, and the reaction was stirred for 72 hours. Then, slowly add isopropanol wit...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Prepare 20 g of an aqueous solution of 10% (w / v, g / ml) acid gelatin (180 Bloom g), and preheat it in a water bath at 53° C. for 2 h. In addition, prepare liquid paraffin containing span80 (density specific gravity of liquid paraffin is 0.89, volume ratio of liquid paraffin and span80 is 30:1), mix well, and preheat in 53°C water bath for 2h. After that, the gelatin solution was slowly added dropwise to the liquid paraffin under the stirring condition of 700rpm, the volume ratio of the aqueous gelatin solution to the liquid paraffin containing span80 was 1:10, and the stirring time was 9min to prepare stable water-in-oil droplets. Then, under the condition of constant stirring speed, add an ice bath to cool down, and stir for 15 minutes to form solidified microspheres. Afterwards, 2% (w / v, g / ml) genipin solution was added, the final concentration of which was 0.03% (w / v, g / ml) when cross-linked, and the reaction was stirred for 12 hours. Then, slowly add isopropanol wit...
Embodiment 3
[0041]Prepare 30 g of an aqueous solution of 18% (w / v, g / ml) alkaline gelatin (200 Bloom g), and preheat it in a water bath at 53° C. for 2.5 h. In addition, prepare the liquid paraffin containing span80 (the density of liquid paraffin is 0.9, the volume ratio of liquid paraffin and span80 is 40:1), mix well, the volume ratio of gelatin aqueous solution and the liquid paraffin containing span80 is 1:10, and in Preheat in a water bath at 53°C for 2.5h. After that, the gelatin solution was slowly added dropwise into the liquid paraffin under the stirring condition of 1000rpm, and the stirring time was 12min to prepare stable water-in-oil droplets. Then, under the condition of constant stirring speed, add an ice bath to cool down, and stir for 20 minutes to form solidified microspheres. Afterwards, add 5% (w / v, g / ml) genipin solution, its final concentration is respectively 0.02% (w / v, g / ml), 0.03% (w / v, g / ml) when cross-linking , 0.3% (w / v, g / ml) and 0.4% (w / v, g / ml), stirred ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com