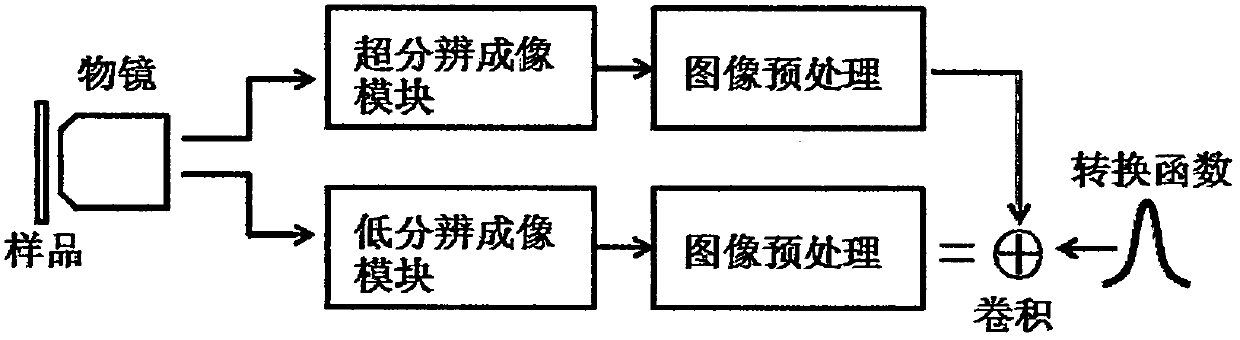
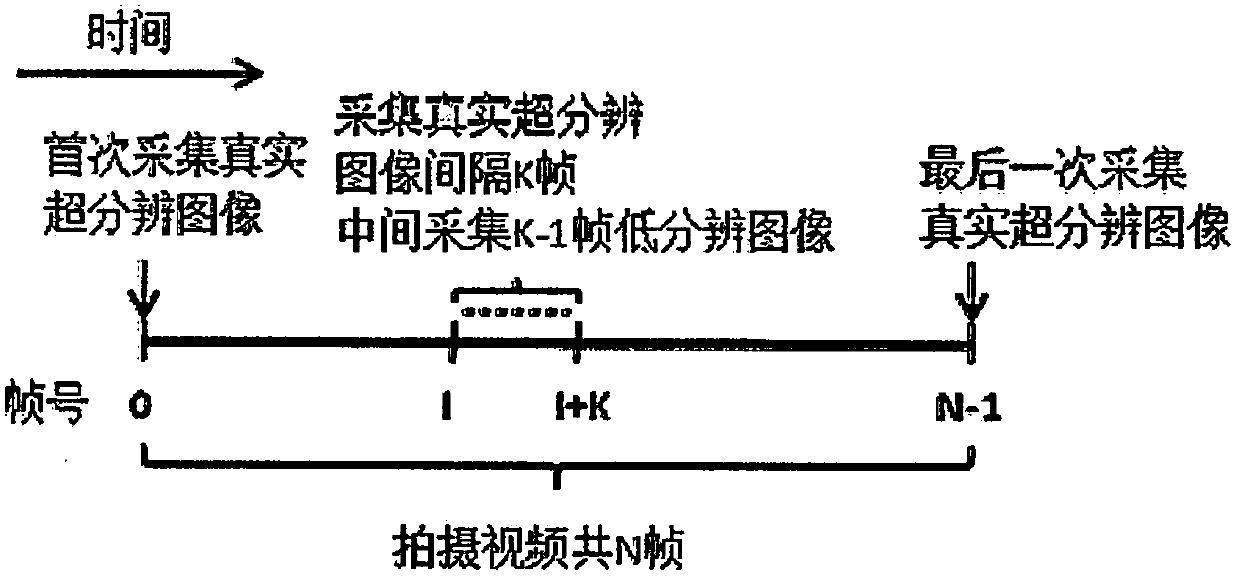
Dynamic super-resolution fluorescence imaging technology
A super-resolution imaging and super-resolution imaging technology, applied in the field of super-resolution fluorescence imaging, can solve the problems of aggravating the fluorescence bleaching and phototoxicity of the sample, and taking a long time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0094] The general structure of the optical path of embodiment one is as follows Figure 6 As shown, in this embodiment, STED is used for super-resolution imaging, and common scanning confocal method is used for low-resolution imaging. The super-resolution imaging module and the low-resolution imaging module share multiple components in the optical path, including: objective lens, lens group, spot scanning module, mirror, dichromatic mirror 1 / 2, band-pass filter, optical fiber, detector, The excitation light; the loss light belongs to the super-resolution imaging module. Although the super-resolution imaging module and the low-resolution imaging module share most of the optical path components, functionally speaking, the control module can turn off or turn on the lost light to switch between super-resolution imaging and low-resolution imaging, so it meets the figure 1 The structural block diagram shown; and, because the imaging optical path is shared, the field of view of the...
Embodiment 2
[0095] The general structure of the light path of embodiment two is as Figure 7 As shown, in this embodiment, STED is used for super-resolution imaging and total internal reflection illumination is used for low-resolution imaging. The components included in the super-resolution imaging module are: lens group, spot scanning module, mirror, dichromatic mirror 1 / 2, band-pass filter, optical fiber, detector, phase plate, excitation light, lost light; low-resolution imaging module The components included are: prism, bandpass filter, CCD camera, and TIRF excitation light; the components shared by the two modules are: objective lens and beam splitter. The super-resolution imaging module and the low-resolution imaging module are separated by a beam splitter. The control module controls the opening and closing of excitation light, depletion light, and TIRF excitation light, and can switch between super-resolution imaging and low-resolution imaging. In low-resolution imaging, the TIR...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com