Inactivation of highly resistant infectious microbes and proteins with unbuffered hypohalous acid compositions
A composition and hypohalous acid technology, applied in hypochlorous acid, bromine oxy compounds, plant growth regulators, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-5
[0118] Characteristics of Representative Hypohalous Acid Formulations
[0119] The following examples are set forth in order to provide those skilled in the art with a complete description of the characteristics of hypohalous acid solutions (for the most important new and useful properties of hypohalous acid solutions). These include the lack of contaminating aqueous halogen species or foreign stable entities during production and after storage, their stability of hypohalous acid solutions under various storage conditions and temperatures, the efficacy of hypohalous acid solutions in inactivating resistant infectious agents , and the safety of hypohalous acid solutions during human exposure. These examples are not intended to limit the scope of what the inventors regard as the invention, nor do they represent all of the experiments that have been performed to demonstrate the use of the methods disclosed herein.
Embodiment 1
[0121] Representative HOCl solution (BrioHOCl TM ) purity and storage effect
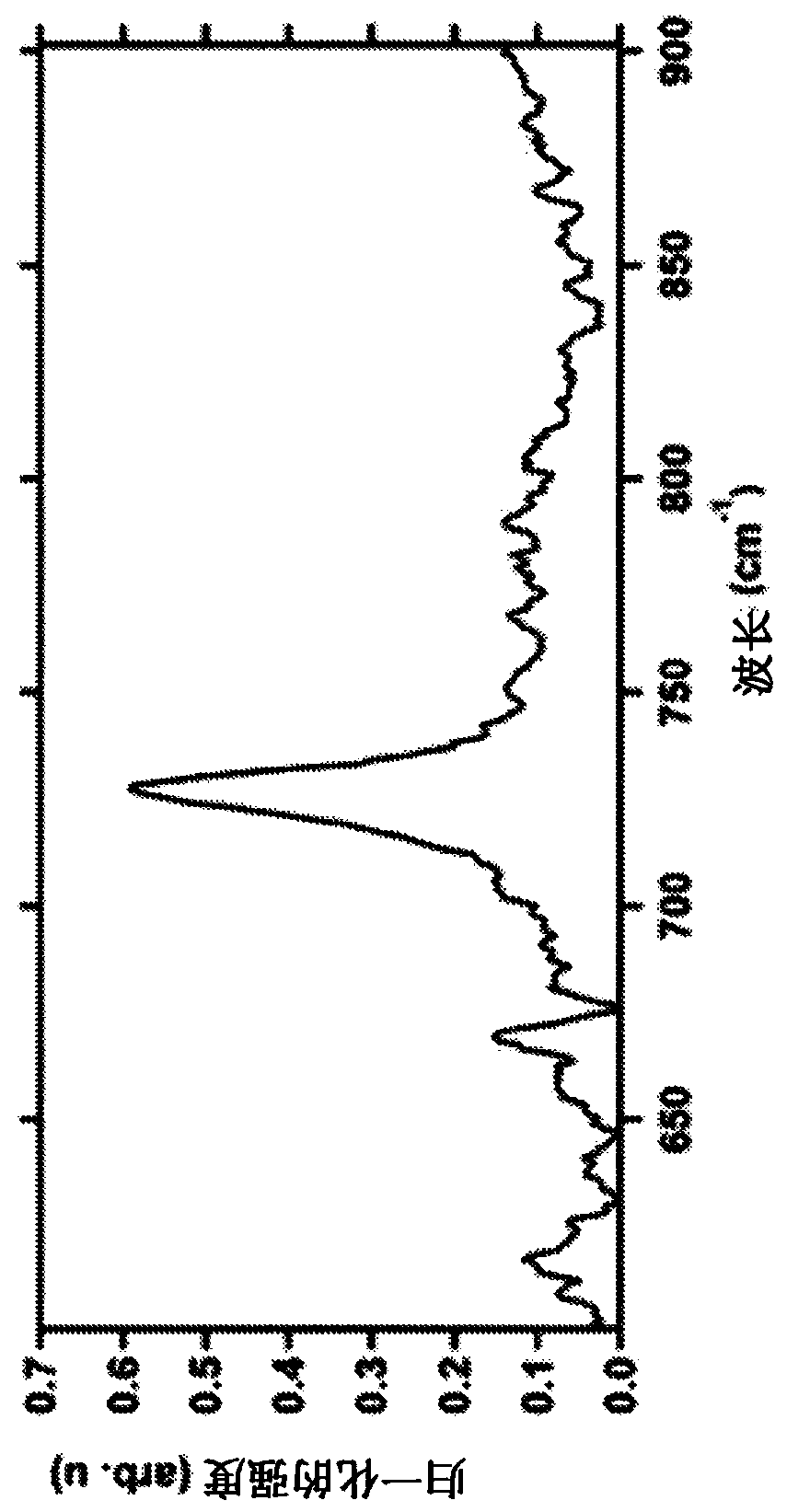
[0122] Unbuffered electrolytically produced BrioHOCL collected over a period of two years from freshly prepared samples TM As aliquots of approximately 100 mL and detected by Raman spectroscopy. These samples consistently showed a peak shift at wavelength 728 / cm, which was only equivalent to HOCl (Nakagawara S, Goto T, Nara M, Ozawa Y, Hotta K, Arata Y (1998)( figure 1 ). Spectral characteristics of aqueous chlorine solutions and pH dependence of bactericidal activity. Analytical Sciences, 14(4):691-8). In samples stored at room temperature for 14 months, the profile of the samples was indicated by Raman spectroscopy.
[0123] These results indicated that the preparation contained only HOCl. Absence of other chlorine species (e.g. Cl 2 ,ClO 2 ,OCl - or OCl 3 ) peak sign. Under spectroscopic conditions, other aqueous chlorine species were evident with peaks between 640 and 870 at >0.3 in...
Embodiment 2
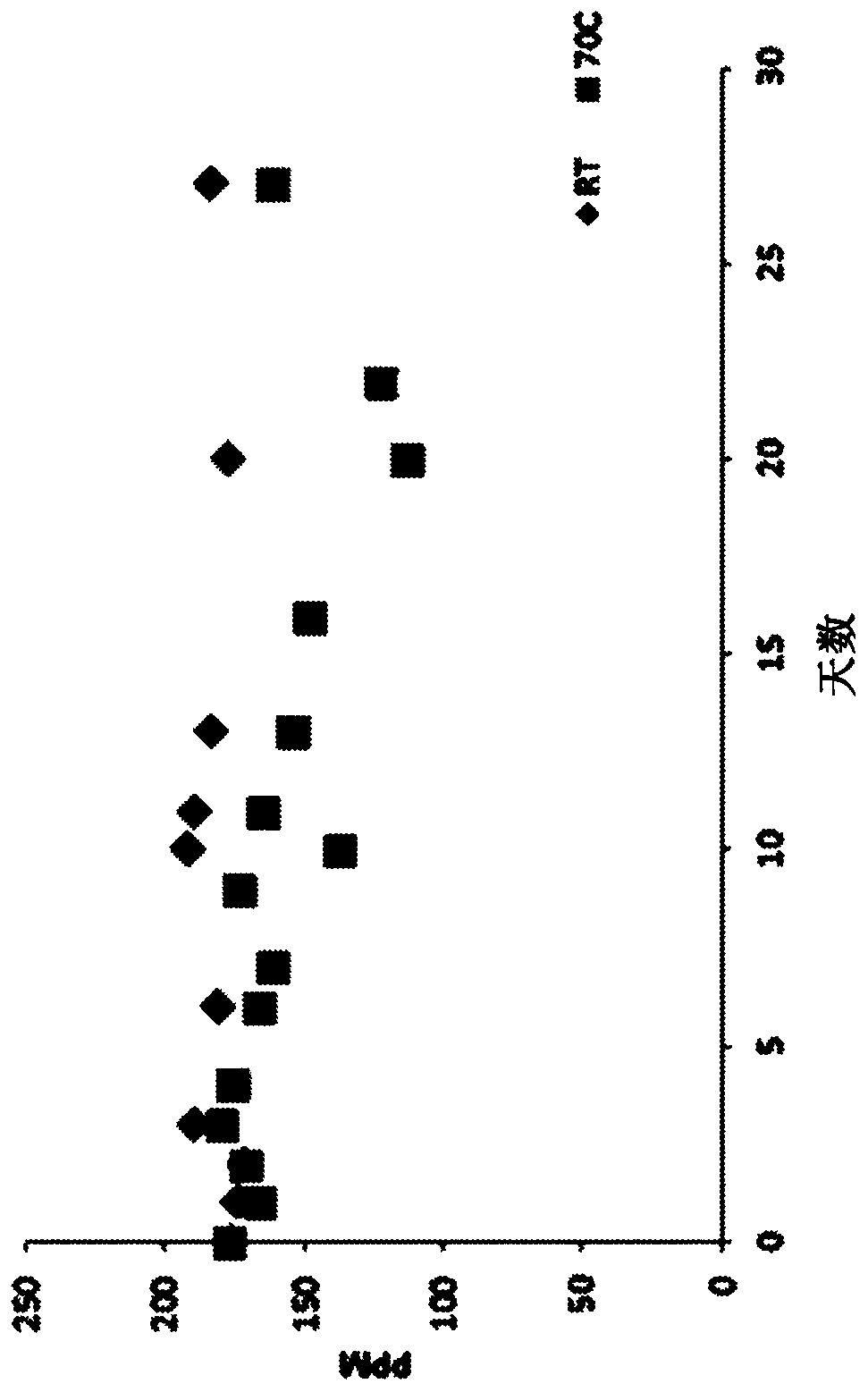
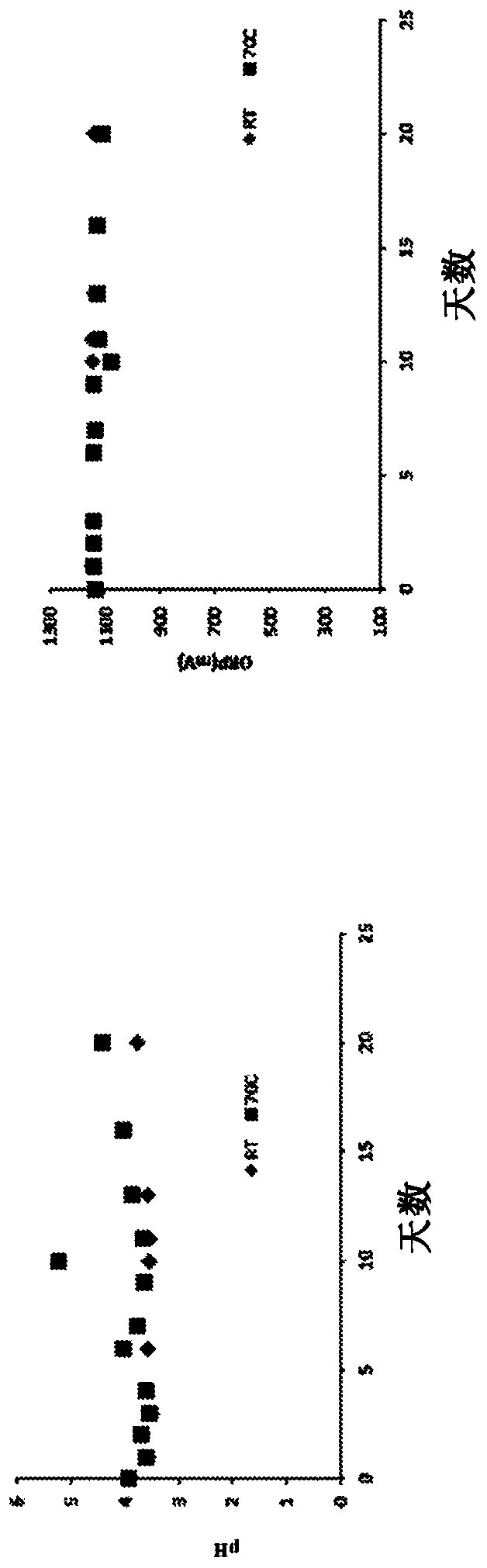
[0125] Stability and storage effects of representative HOCl solutions
[0126] The purpose of the first experiment was to determine measurable changes in HOCl samples exposed to high temperatures that would be expected to degrade conventional preparations. From several batches of BrioHOCL prepared 3-9 months ago and warehoused at uncontrolled temperatures TM The six samples obtained (unbuffered) were exposed for 24 hours at an oven temperature of approximately 80°C. The ORP mv potentials of the samples are before and after heating, respectively: sample 1, 1029mv and 1020mv; sample 2, 1044mv and 1030mv; sample 3, 1060mv and 1040mv; sample 4, 1057mv and 1030mv; sample 5, 1040mv and 1040mv; 6, 1030mv and 1020mv. In these heated samples, the free chlorine content decreased by an average of only 18.5%. The results indicate that electrolytically produced unbuffered HOCl has unpredictable high temperature tolerance that would be expected to cause rapid degradation of conventiona...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com