Adsorbent for efficiently adsorbing sulfate ions in water, and preparation method thereof
A sulfate ion and adsorbent technology, which is applied in the direction of adsorption of water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problem of low sulfate ion removal efficiency, achieve high sulfate removal efficiency, and optimize the removal efficiency. The effect of removal efficiency and excellent adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
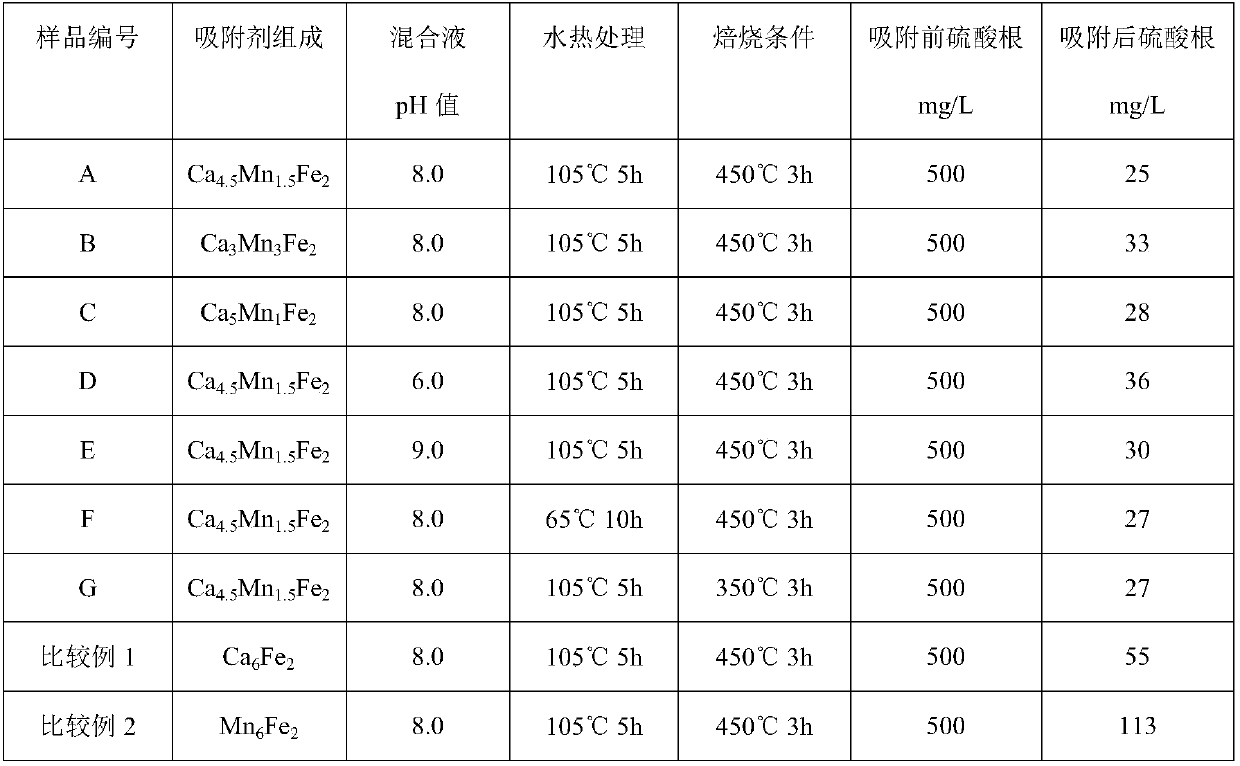
[0037]Dissolve calcium nitrate, manganese nitrate and ferric nitrate in deionized water at a molar ratio of 4.5:1.5:2, stir at room temperature until clear, and record it as solution A; dissolve sodium hydroxide in deionized water, stir at room temperature until clear , recorded as solution B; quickly drop solution B into solution A, stop when the pH value of the solution reaches 8.0, continue to stir for 2 hours, pour the solution into a crystallization kettle and treat it with hydrothermal treatment at 105°C for 5 hours, filter, wash, and dry at 100 ℃ dry 10h. The adsorbent product A was obtained by roasting the dried powder at 450°C for 3 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere.
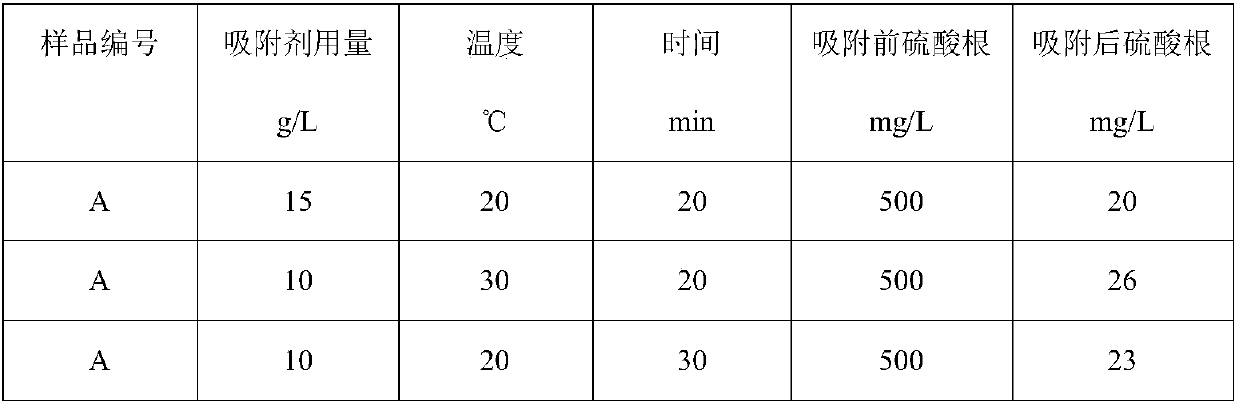
[0038] Add 10 g of adsorbent A to 1 L of aqueous solution containing 500 mg of sulfate ions at 20°C, stir for 20 min, and then detect the content of sulfate ions in the water. The results are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Dissolve calcium nitrate, manganese nitrate and ferric nitrate in deionized water at a molar ratio of 3:3:2, stir at room temperature until clear, and record it as solution A; dissolve sodium hydroxide in deionized water, stir at room temperature until clear , recorded as solution B; quickly drop solution B into solution A, stop when the pH value of the solution reaches 8.0, continue to stir for 2 hours, pour the solution into a crystallization kettle and treat it with hydrothermal treatment at 105°C for 5 hours, filter, wash, and dry at 100 ℃ dry 10h. The dried powder was calcined at 450°C for 3 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain the adsorbent product B.
[0041] Add 10 g of adsorbent B to 1 L of aqueous solution containing 500 mg of sulfate ions at 20°C, stir for 20 min, and then detect the sulfate ion content in the water. The results are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Dissolve calcium nitrate, manganese nitrate and ferric nitrate in deionized water at a molar ratio of 5:1:2, stir at room temperature until clear, and record it as solution A; dissolve sodium hydroxide in deionized water, stir at room temperature until clear , recorded as solution B; quickly drop solution B into solution A, stop when the pH value of the solution reaches 8.0, continue to stir for 2 hours, pour the solution into a crystallization kettle and treat it with hydrothermal treatment at 105°C for 5 hours, filter, wash, and dry at 100 ℃ dry 10h. The adsorbent product C was obtained by roasting the dried powder at 450°C for 3 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere.
[0044] Add 10 g of adsorbent C to 1 L of aqueous solution containing 500 mg of sulfate ions at 20°C, stir for 20 minutes, and then detect the content of sulfate ions in the water. The results are listed in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com