Method and application for inducing direct somatic embryogenesis
A technology of somatic embryos and cell embryos, which is applied in the field of direct induction of somatic embryos, to achieve the effect of simple culture procedures, simple operation, and high occurrence frequency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
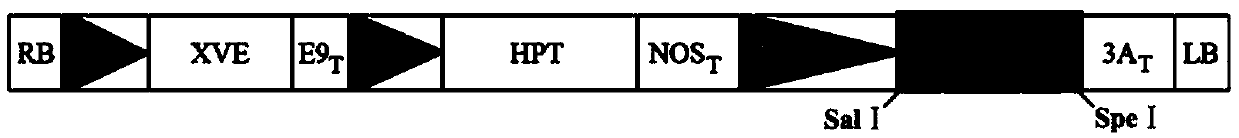
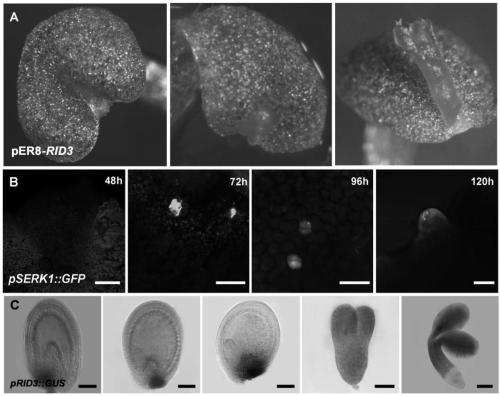
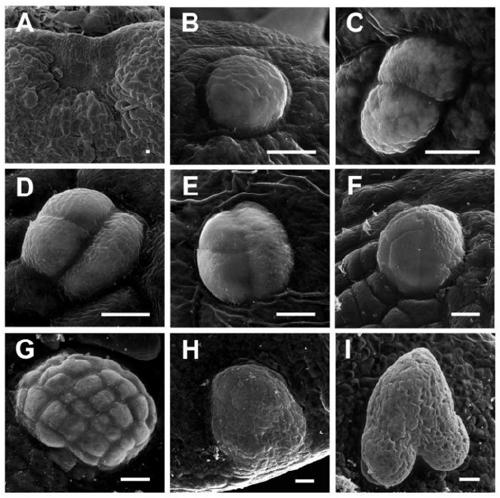
[0098] Embodiment 1: RID3 and YUC10 gene cloning and plant expression vector construction
[0099] 1.1 Extraction of total RNA from Arabidopsis tissue
[0100] The total RNA of the plant material was extracted using the Trizol kit, and the operation steps were as follows:
[0101] (1) Add 1 mL of Trizol reagent to the centrifuge tube;
[0102] (2) Removal of cell wall residues, proteins, polysaccharides, and fats: Grind about 0.1 g of plant material in liquid nitrogen, transfer the powder to a centrifuge tube, mix with a shaker, and let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes, then 12,000 rpm, 4 Centrifuge for 10 minutes;
[0103] (3) Phase separation: transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube, add 200 μL of chloroform, shake vigorously for 15 seconds, then let stand at room temperature for 2-3 minutes, centrifuge at 12000 rpm, 4 °C for 15 minutes;
[0104] (4) Precipitation and removal of polysaccharides: Transfer the colorless aqueous phase (about 600 μL) into a n...
Embodiment 2
[0128] Embodiment 2: the cloning of SERK1, RID3 and YUC10 promoter and the construction of plant expression vector
[0129] 2.1 Extraction of plant genomic DNA
[0130] The genomic DNA of Arabidopsis thaliana was extracted by the small amount method. The extraction method is as follows:
[0131] (1) Take fresh plant leaves and grind them into powder in liquid nitrogen;
[0132] (2) Add 500 μL of DNA extraction solution, shake and mix well, and place in a water bath at 60°C for 2 minutes;
[0133] (3) After taking it out, add 500 μL of phenol to the centrifuge tube, shake and mix well, centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 5 min;
[0134] (4) Take the supernatant, transfer it to a new 1.5mL centrifuge tube, add 500μL phenol / chloroform (1:1), shake and mix, and centrifuge at 12000rpm for 5min;
[0135] (5) Take the supernatant, transfer it to a new centrifuge tube, add 500 μL of chloroform, shake and mix, and centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 5 minutes;
[0136] (6) Transfer the supernatan...
Embodiment 3
[0169] Example 3: Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis inflorescences and acquisition of resistant plants
[0170] The transformation steps of Arabidopsis thaliana are as follows:
[0171] (1) The preparation of Agrobacterium should be carried out one day before the transformation, and the Agrobacterium should be activated with 100mL of culture solution added with corresponding antibiotics. Arabidopsis can be transformed the next morning;
[0172](2) Configure liquid: 5% sucrose dissolved in ddH 2 O, add 0.03-0.05% Silwet L-77;
[0173] (3) Centrifuge at 5000-6000rpm for 5-8min, discard the supernatant, and collect the bacteria;
[0174] (4) Suspend the bacteria with the infection liquid;
[0175] (5) Soak the inflorescences of Arabidopsis thaliana in the infection solution and shake gently for about 30 seconds;
[0176] (6) Then Arabidopsis is placed horizontally in a cardboard box, covered with a film, and placed in the dark for one day;
[0177] (7) Pu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com