Electronic identity database and detection method of pesticide compounds in edible agricultural products based on GC-Q-Orbitrap
An electronic identity and electronic identity card technology, applied in the field of electronic identity database and detection of pesticide compounds in edible agricultural products based on GC-Q-Orbitrap, to save resources, improve accuracy and operability, and increase accuracy and reliability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
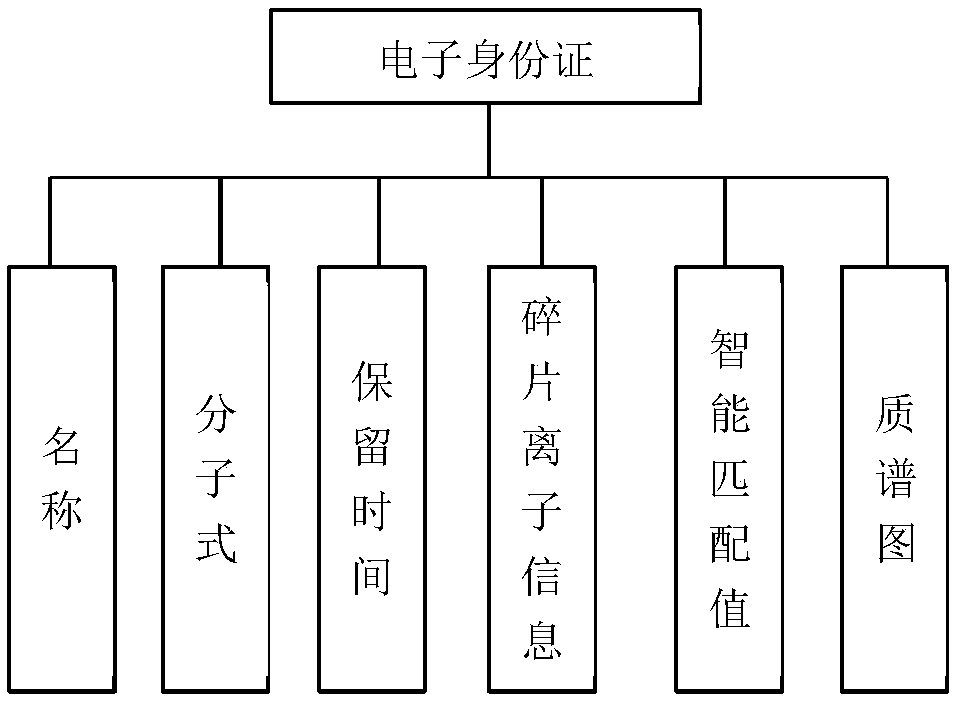
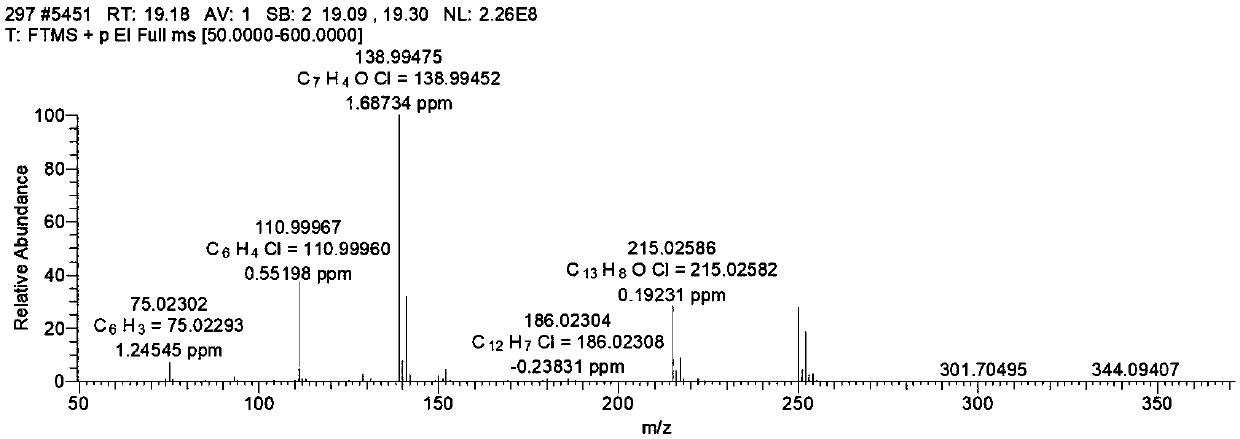
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] Implementation examples of GC-Q-Orbitrap screening and confirmation technology for more than 600 pesticides in cabbage, including the following steps;
[0093] 1. Specific steps of sample pretreatment technology:
[0094] 1.1 Take the edible part of the head cabbage sample, chop it up, mix it evenly, seal it, and mark it;
[0095] 1.2 Weigh 10g of cabbage sample (accurate to 0.01g), add 40mL of 1% acetic acid acetonitrile into a 100mL centrifuge tube, use a high-speed homogenizer at 10000r / min, homogenize and extract for 1min, add 1g of sodium chloride, 4g of no Magnesium sulfate in water, shaken for 10 min, centrifuged at 4200 r / min for 5 min, took 20 mL of the supernatant, concentrated it to about 1 mL by rotary evaporation in a water bath at 40 °C, and waited for purification.
[0096] 1.3 Use CarbonNH2 column, add about 2cm high anhydrous sodium sulfate to Carbon / NH2 column. Rinse the SPE column with 5mL acetonitrile + toluene (3+1, v / v) first, and discard the eff...
Embodiment 2
[0108] An implementation example of GC-Q-Orbitrap screening and confirmation technology for more than 600 pesticides (such as those described above) in tomato.
[0109] The sample pretreatment steps, GC-Q-Orbitrap operating conditions and the screening process of pesticide residues in the samples all refer to Example 1.
[0110] GC-Q-Orbitrap screening results in tomato samples from a provincial capital city: 16 commercially available tomato samples from a provincial capital city were collected, more than 600 pesticide residues were screened using GC-Q-Orbitrap technology, and GC-Q-Orbitrap technology detected There are 16 kinds of pesticide residues, with a total of 45 frequencies, involving 15 samples. The specific results are shown in Table 4.
[0111] Table 4 GC-Q-Orbitrap screening results in tomato samples from a certain area
[0112]
Embodiment 3
[0114] Implementation example of GC-Q-Orbitrap screening and confirmation technology for more than 600 pesticides in grapes (such as the pesticides described above).
[0115] The sample pretreatment steps, GC-Q-Orbitrap operating conditions and the screening process of pesticide residues in the samples all refer to
[0116] According to Example 1.
[0117] GC-Q-Orbitrap screening results of grape samples in a provincial capital city: Collected 16 commercially available grape samples in a provincial capital city, applied GC-Q-Orbitrap technology to screen more than 600 pesticide residues, and GC-Q-Orbitrap technology detected 21 kinds of pesticide residues, a total of 73 frequencies, involving 16 samples, the specific results are shown in Table 5.
[0118] Table 5 GC-Q-Orbitrap screening results in grape samples in a certain area
[0119]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com