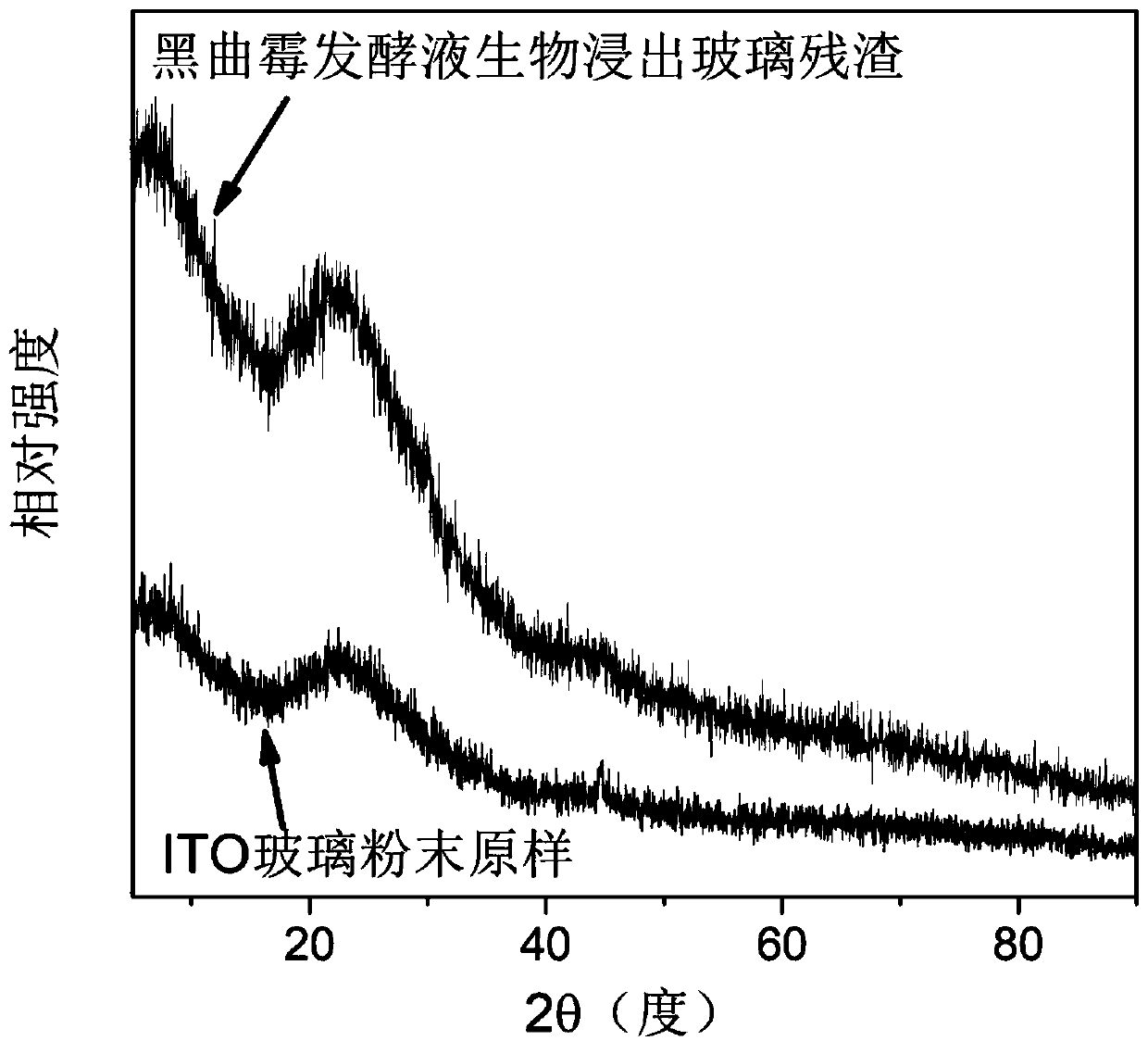
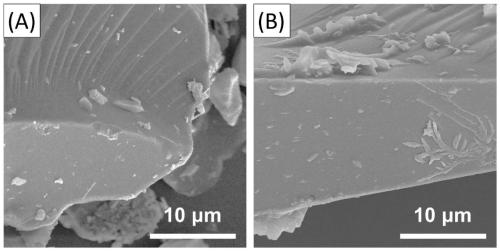
A kind of method utilizing aspergillus niger bioleaching indium in waste liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display and biological leaching technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of leaching that have not yet been solved, and achieve the effects of reducing recycling costs, small secondary pollution, and mild treatment conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 One-step bioleaching
[0041] A method for biologically leaching indium from waste liquid crystal displays by Aspergillus niger:
[0042] 1. Disassemble the waste liquid crystal display, take out the liquid crystal screen, remove the polarizer and liquid crystal with acetone, and separate the ITO glass substrate.
[0043] 2. Then mechanically crush the ITO glass substrate to make a powder sample with an average particle size of 75μm;
[0044] 3. Configure 5 groups of 100mL sucrose fermentation medium, the medium components include: sucrose (50g / L), NaNO 3 (1.5g / L), KH 2 PO 4 (0.5g / L), MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O (0.025g / L), KCl (0.025g / L), yeast extract (1.6g / L);
[0045] 4. Adjust the initial pH of the sucrose fermentation medium configured in step 3 to 4.0 with 1M hydrochloric acid;
[0046] 5. Set the inoculation amount to 1% (v / v) concentration to 3×10 7 A / mL Aspergillus niger spore suspension is added to the 5 groups of sucrose fermentation medium configured in step (4), immedia...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 Two-step biological leaching
[0050] A method for biologically leaching indium from waste liquid crystal displays by Aspergillus niger:
[0051] 1. Disassemble the waste LCD, take out the LCD screen, remove the polarizer and liquid crystal with acetone, and separate the ITO glass substrate;
[0052] 2. Mechanically crush the ITO glass substrate to prepare a powder sample with an average particle size of 75μm;
[0053] 3. Configure 5 groups of 100mL sucrose fermentation medium, the medium components include: sucrose (50g / L), NaNO 3 (1.5g / L), KH 2 PO 4 (0.5g / L), MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O (0.025g / L), KCl (0.025g / L), yeast extract (1.6g / L);
[0054] 4. Adjust the initial pH of the sucrose fermentation medium configured in step 3 to 4.0 with 1M hydrochloric acid;
[0055] 5. Set the inoculation amount to 1% (v / v) concentration to 3×10 7 A / mL Aspergillus niger spore suspension was added to the 5 groups of sucrose fermentation medium in step (4), cultured for 3 days at a temperature of 3...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3 Bioleaching of fermentation broth
[0059] A method for biologically leaching indium from waste liquid crystal displays by Aspergillus niger:
[0060] 1. Disassemble the waste LCD, take out the LCD screen, remove the polarizer and liquid crystal with acetone, and separate the ITO glass substrate.
[0061] 2. Mechanically crush the ITO glass substrate to prepare a powder sample with an average particle size of 75μm.
[0062] 3. Configure 5 groups of 100mL sucrose fermentation medium, the medium components include: sucrose (50g / L), NaNO 3 (1.5g / L), KH 2 PO 4 (0.5g / L), MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O (0.025g / L), KCl (0.025g / L), yeast extract (1.6g / L).
[0063] 4. Adjust the initial pH of the sucrose fermentation medium to 4.0 with 1M hydrochloric acid.
[0064] 5. Set the inoculation amount to 1% (v / v) concentration to 3×10 7 A / mL Aspergillus niger spore suspension was added to the 5 groups of sucrose fermentation medium in step (4), and the temperature was 30°C and the shaking speed was 12...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com