A kind of multifunctional carbon nanotube plant-derived fiber and preparation method thereof
A carbon nanotube and plant-sourced technology, applied in the field of cellulose fibers, can solve the problems of easy oxidative browning of active ingredients, ineffective use of cellulose, and destruction of active ingredients.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
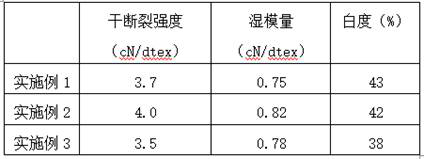
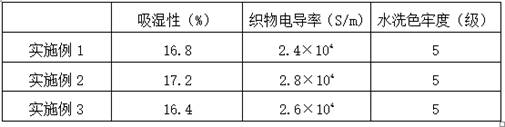
[0057] Example 1 A method for preparing multifunctional carbon nanotube plant-derived fibers, comprising the following preparation steps:
[0058] 1. Preparation of viscose spinning solution
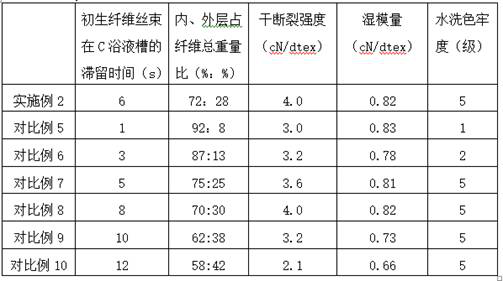
[0059] 1. The pulp is soaked, squeezed, crushed, aged, and yellowed, and then the modified auxiliary slurry is added in the dissolution process, and then filtered, defoamed, and matured to make conventional sulfonate method viscose spinning Liquid; viscose spinning liquid indicators: alkali: 2.5 ± 0.2%, methyl fiber: 6.6 ± 0.2%, maturity: 12ml (15% ammonium chloride), viscosity 50S;
[0060] The configuration method of the modified additive slurry: mix sodium bicarbonate: sodium carbonate: carbon nanotubes according to the ratio, add 6 times the weight of water, add the dispersant and stir at 60±3°C for 2 hours; sodium bicarbonate: The mass ratio of sodium carbonate: carbon nanotubes is 2:1:3; the amount of modified additive slurry added is 5.5% of the weight of methyl fiber in the visc...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Example 2 A method for preparing multifunctional carbon nanotube plant-derived fibers, comprising the following preparation steps:
[0074] 1. Preparation of viscose spinning solution
[0075] 1. The pulp is soaked, squeezed, crushed, aged, and yellowed, and then the modified auxiliary slurry is added in the dissolution process, and then filtered, defoamed, and matured to make conventional sulfonate method viscose spinning liquid; the indicators of the viscose spinning solution are: alkali: 2.5 ± 0.2%, methyl fiber: 6.6 ± 0.2%, maturity: 14ml (15% ammonium chloride), viscosity 55S;
[0076]The configuration method of the modified additive slurry: mix sodium bicarbonate: sodium carbonate: carbon nanotubes according to the ratio, add 6 times the weight of water, add the dispersant and stir at 60±3°C for 2 hours; sodium bicarbonate: The mass ratio of sodium carbonate: carbon nanotubes is 2:1:3; the amount of modified additive slurry added is 6.5% of the weight of methyl f...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3 A method for preparing multifunctional carbon nanotube plant-derived fibers, comprising the following preparation steps:
[0090] 1. Preparation of viscose spinning solution
[0091] 1. The pulp is soaked, squeezed, crushed, aged, and yellowed, and then the modified auxiliary slurry is added in the dissolution process, and then filtered, defoamed, and matured to make conventional sulfonate method viscose spinning Liquid; viscose spinning liquid indicators: alkali: 2.5 ± 0.2%, methyl fiber: 6.6 ± 0.2%, maturity: 16ml (15% ammonium chloride), viscosity 60S;
[0092] The configuration method of the modified additive slurry: mix sodium bicarbonate: sodium carbonate: carbon nanotubes according to the ratio, add 6 times the weight of water, add the dispersant and stir at 60±3°C for 2 hours; sodium bicarbonate: The mass ratio of sodium carbonate: carbon nanotubes is 2:1:3; the amount of modified additive slurry added is 7.5% of the weight of methyl fiber in the visc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com