Marker for identifying benign and malignant pulmonary nodules by using exosome protein and application of marker
A technology of pulmonary nodules and exosomes, which is applied in the field of exosomal proteins as markers for distinguishing benign and malignant pulmonary nodules, and can solve the problems of unreported FGB expression in benign and malignant pulmonary nodules, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
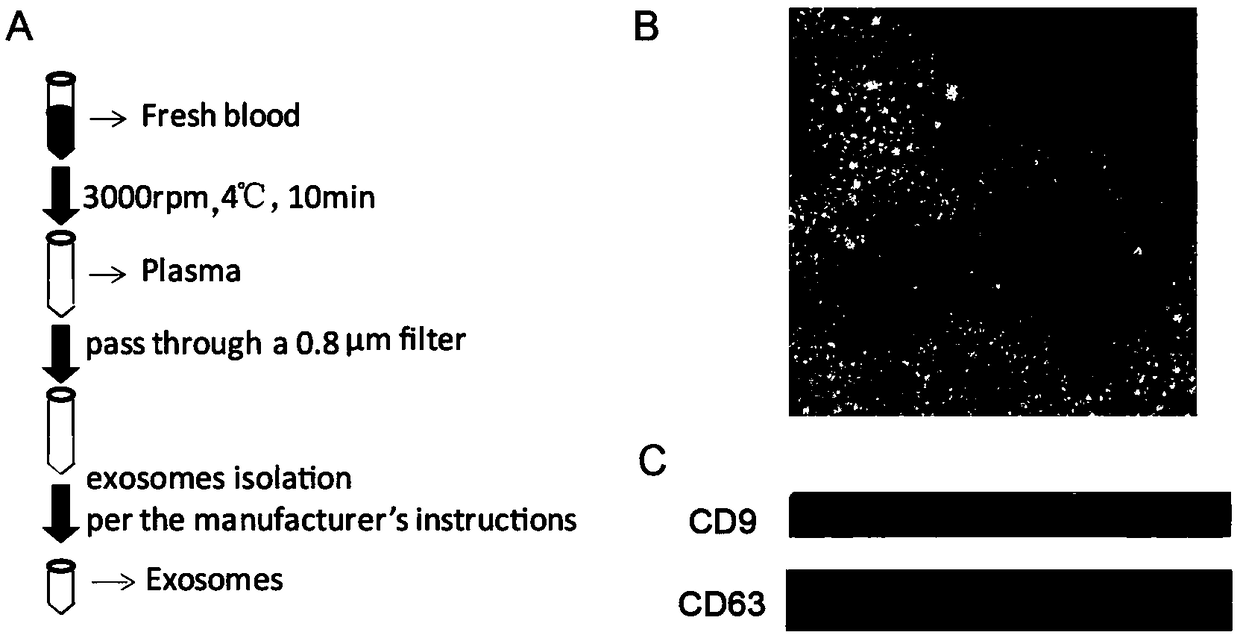
[0026] see Figure 1-3 , the present invention provides the following technical scheme: an exosomal protein as a marker for differentiating benign and malignant pulmonary nodules and its application, comprising the following steps:
[0027] S1. Search for proteins differentially expressed in plasma exosomes of patients with benign and malignant pulmonary nodules;
[0028] S2, screening differential proteins;
[0029] S3. To verify the role of FGB in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant pulmonary nodules;
[0030] S4. Analysis of relative expression
[0031] In the present invention, non-invasive liquid biopsy methods are used to find molecular markers for distinguishing benign and malignant pulmonary nodules, and through mass spectrometry detection and subsequent bioinformatics analysis, it is shown that the molecular marker FGB of the present invention is the diagnosis and clinical efficacy of pulmonary nodules The observation provides a new molecular target....
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2: Screening of target markers of the present invention
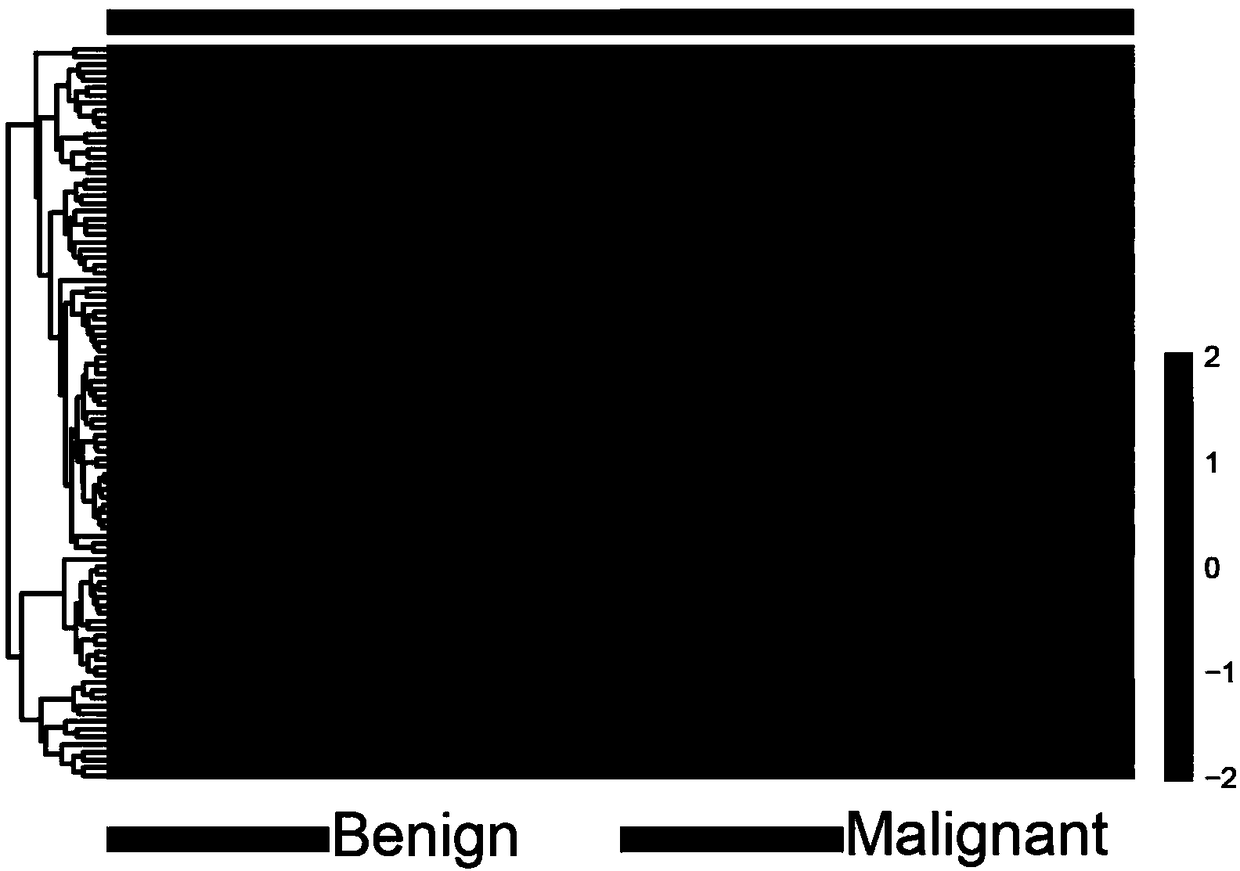
[0055] In order to screen the differences of exosomal proteins in patients with benign and malignant pulmonary nodules, a protein profile study was carried out to screen out a series of differential proteins ( figure 2 ).
[0056] The experimental steps are as follows:
[0057] (1) Cleavage and quantification of protein:
[0058] Label the collected exosomes, add 100 μL of SDT lysate, boil water bath for 10 min, and sonicate (100 W, work for 10 s, pause for 10 s, cycle 10 times). Centrifuge at 13400rpm for 30min, and take the supernatant. BCA method for protein quantification.
[0059] (2) SDS-PAGE experiment of protein protein
[0060] Take 20 μg of protein samples from each group and add 5X loading buffer at 5:1 (v / v), put in boiling water bath for 5 minutes, centrifuge at 14000 g for 10 minutes to get the supernatant, and perform 12.5% SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. Conditions: constant current 15m...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3: Verification of screening markers
[0082] In the stage of screening differential proteins, plasma exosome samples from 30 patients with malignant pulmonary nodules and 10 patients with benign pulmonary nodules were included.
[0083] The inclusion criteria for patients are:
[0084] 1. Patients diagnosed with pulmonary nodules by imaging from April to July 2016;
[0085] 2. The patient agrees to receive surgical treatment and resect the lesion;
[0086] Exclusion criteria:
[0087] 1. Exclude patients with other tissue system tumors;
[0088] 2. Exclude other lung disease patients with non-substantial pulmonary lesions.
[0089] Blood samples were collected from patients who met the above criteria, and 5-8mL of peripheral blood was drawn, placed in an EDTA anticoagulant tube, centrifuged twice, and the supernatant was taken for exosome extraction.
[0090] The inventors analyzed the protein profiles of the two groups of samples, and screened out a serie...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com