Intestinal simulation model-based lactic acid bacteria intestinal probiotic effect measuring method
A technique of simulating models and measuring methods, which is applied in the field of detection, can solve problems such as difficulty in sampling intestinal bacteria, achieve high accuracy, exclude host factors, and overcome sampling difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1: Activation of Lactobacillus sake LZ217
[0053] Take out the preserved strain (Lactobacillus sake LZ217) from the refrigerator at -80°C, place it in a refrigerator at 4°C to thaw for 30 minutes, streak on the flat plate MRS solid medium, put it in a 30°C incubator for 36 hours, and pick a single colony to Activated twice in MRS liquid medium to obtain activated Lactobacillus sake LZ217.
[0054] Plate MRS solid medium, made from the following raw materials:
[0055]
[0056]
[0057] First mix the above raw materials, dilute to 1L with water, then adjust the pH to 7.0, then add 15g of agar and sterilize at 121°C for 15min.
[0058] MRS liquid medium, made from the following raw materials:
[0059]
[0060] First mix the above raw materials, dilute to 1 L with water, adjust the pH to 7.0, and then sterilize at 121°C for 15 minutes.
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2: In vitro simulation culture of human intestinal flora
[0062] Formulated intestinal simulation medium, made from the following raw materials:
[0063]
[0064]
[0065] First mix the above components, add water to make the volume to 1000mL, and sterilize at 121°C for 15min to obtain intestinal simulated medium.
[0066] (1) Add the activated Lactobacillus sakei LZ217 obtained in Example 1 to the intestinal simulation medium, and add L. sakei LZ217 cells to the experimental group, so that the number of viable L. sakei LZ217 bacteria reaches 1×10 8 CFU / mL (that is, the number of live bacteria of Lactobacillus sake LZ217 in the intestinal simulation medium reaches 1×10 8 CFU / mL), the mixed solution was blown evenly with a pipette gun to obtain an intestinal simulated medium added with Lactobacillus sake LZ217, and without adding Lactobacillus sake LZ217 as a blank control, to obtain an intestinal simulated medium without added Lactobacillus sake LZ217; ...
Embodiment 3
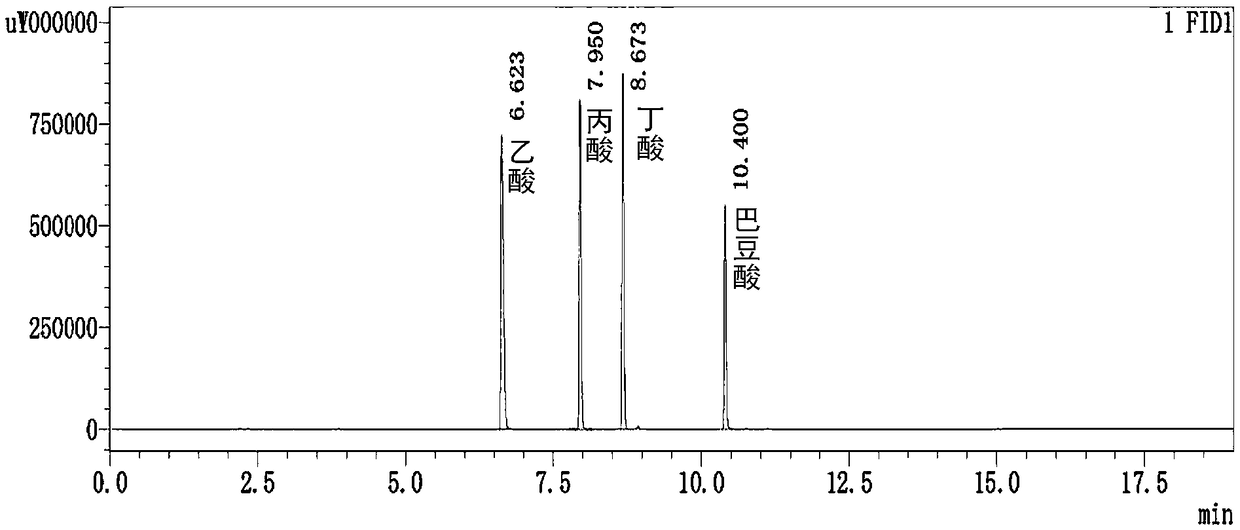
[0070] Embodiment 3: Detection of short-chain fatty acids in fermentation broth by gas chromatography
[0071] (1) Processing of samples. Take out the supernatant obtained in Example 2, filter it with a 0.22 μm filter membrane, take 500 μL of the filtered supernatant and add 100 μL of crotonic acid, shake and mix to obtain a mixed solution, take 20 μL of the mixed solution and inject it into a sample injection bottle detection. All samples to be tested were continuously injected three times on GC (GC series gas chromatograph).
[0072] (2) Column temperature rise program. Column temperature: keep at 70°C for 1min, raise to 180°C at 15°C / min, hold for 2min, raise to 240°C at 40°C / min and hold for 3min; inlet parameters: temperature 250°C, injection volume: 1μL; spectrum Column flow: 2.93mL / min, FID (Flame Ionization Detector) detector parameters: temperature 250°C; gasification chamber: 250°C. Carrier gas: nitrogen, makeup gas flow: 30mL / min, hydrogen flow: 40mL / min, air fl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com