Monocular image depth estimation method based on pyramid pooling module
A technology of pyramid pooling and image depth, applied in the field of image depth estimation, which can solve the problems of difficulty in estimating depth, blurring, and no matching allowed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
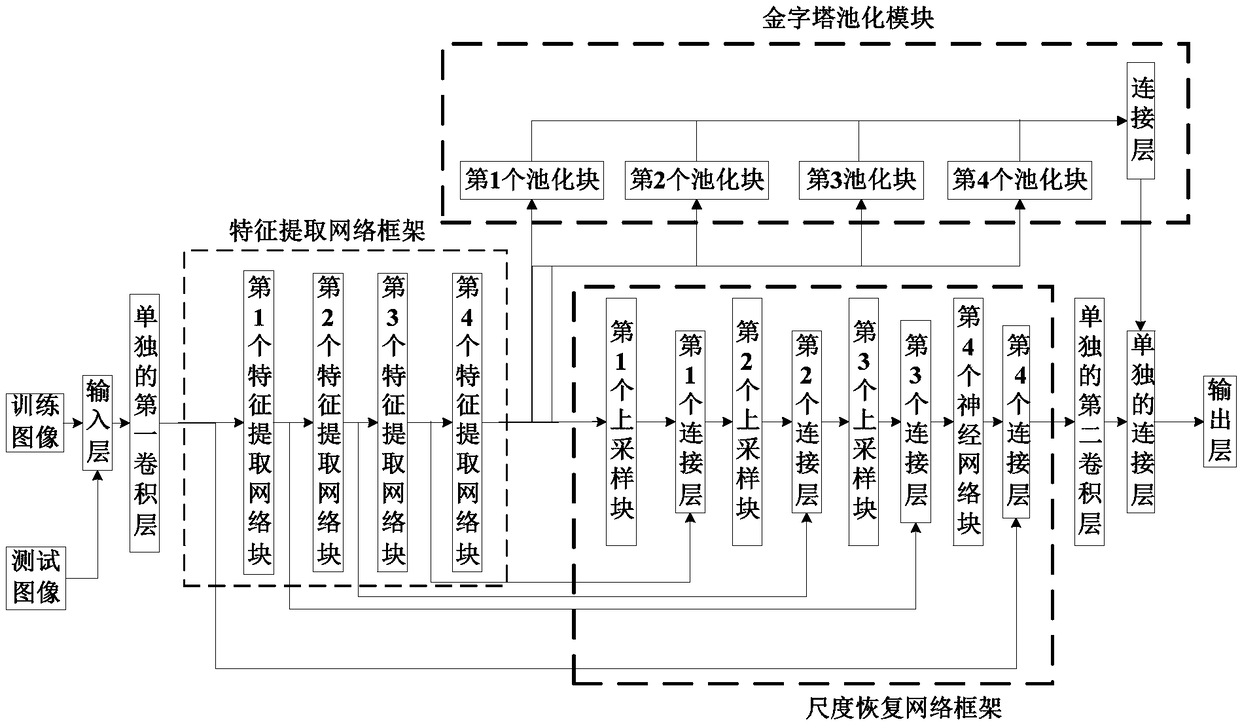
[0033] A monocular image depth estimation method based on the pyramid pooling module proposed by the present invention, its overall realization block diagram is as follows figure 1 As shown, it includes two processes of training phase and testing phase;
[0034] The specific steps of the described training phase process are:
[0035] Step 1_1: Select Q original monocular images and the real depth images corresponding to each original monocular image, and form a training set, record the qth original monocular image in the training set as {I q (i,j)}, combine the training set with {I q (i,j)} corresponds to the real depth image is denoted as Among them, Q is a positive integer, Q≥200, such as taking Q=4000, q is a positive integer, 1≤q≤Q, 1≤i≤W, 1≤j≤H, W means {I q (i,j)} and The width of H means {I q (i,j)} and the height of I q (i,j...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com