Automatic splicing method of ferritic stainless steel for explosive welding
An explosive welding and automatic splicing technology, applied in welding/welding/cutting items, welding equipment, non-electric welding equipment, etc., can solve problems such as low production efficiency, achieve good surface quality, reduce repair steps, and save labor.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Step 1. Manufacturing of large-area 0Cr13 composite boards. Place the two 06Cr13AL boards to be spliced, with sizes 3*1500*6800 and 3*1300*6800mm, on the tailor welding machine, and remove the oil within 50mm on both sides of the welding boards. , water, rust, oxide layer and other dirt;
[0018] Step 2. Press the test plate to be welded tightly with a piano-type pressing plate, and the gap is controlled between 0 and 0.5mm;
[0019] Step 3. When assembling tack welding, the weld joints should be flush, without misalignment, the length of tack welding should be 7~12mm, and the spacing should be 100~200mm;
[0020] Step 4. Set the plasma welding current to 120~170A, voltage to 20~26V, and welding speed to 200~400mm / min. During the welding process, feed ER321 welding wire continuously, and the diameter of the welding wire is φ0.8mm to ensure that the weld seam is filled. The height is controlled within 0.5~1mm;
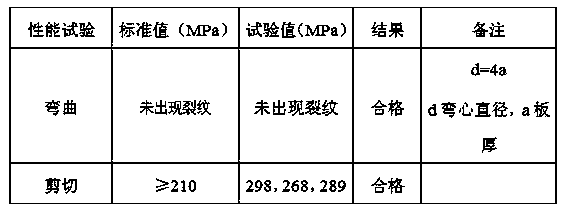
[0021] Step 5. After the welding is completed, the weld r...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Step 1. Manufacturing of large-area 0Cr13 composite boards. Place the two 06Cr13 boards to be spliced, with dimensions of 4*1400*5800 and 4*1200*5800mm, on the tailor welding machine, and remove the oil within 50mm on both sides of the welding board. , water, rust, oxide layer and other dirt;
[0027] Step 2. Press the test plate to be welded tightly with a piano-type pressing plate, and the gap is controlled between 0 and 1mm;
[0028] Step 3. When assembling tack welding, the weld joints should be flush, without misalignment, the length of tack welding should be 7~12mm, and the spacing should be 100~200mm;
[0029] Step 4. Set the plasma welding current to 120~170A, voltage to 20~26V, and welding speed to 200~400mm / min. During the welding process, feed ER321 welding wire continuously. The diameter of the welding wire is φ1.2mm to ensure that the weld seam is filled. The height is controlled within 0.5~1mm;
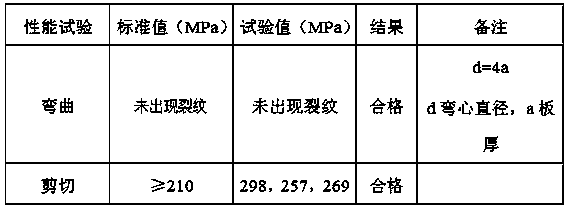
[0030] Step 5. After the welding is completed, the weld re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com