a vena cava filter
A vena cava and filter technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problem of no recognized filter, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing blood vessel tearing, improving fishing efficiency, and prolonging service life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
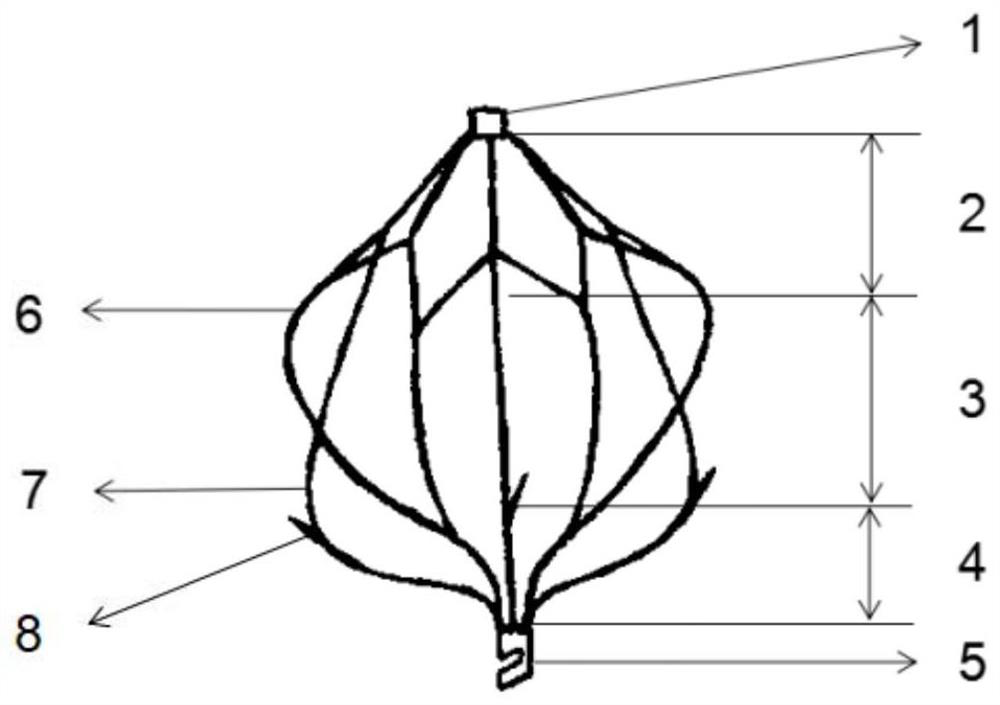
[0030] figure 1 with figure 2 The structural diagram of the vena cava filter provided in this embodiment is composed of a head end 1, an upper filter 2, a support section 3, a lower filter 4, and a recovery part 5 connected in sequence. The head end 1, the upper filter screen 2, the support section 3, the lower filter screen 4, and the recovery part 5 are all woven or cut from nickel-titanium and other shape memory alloy materials.
[0031] The head end 1 is a nickel-titanium tube, and the upper filter screen 2 is folded to facilitate recovery into the sheath; the head end 1 contains a nut for connecting with the delivery rod.
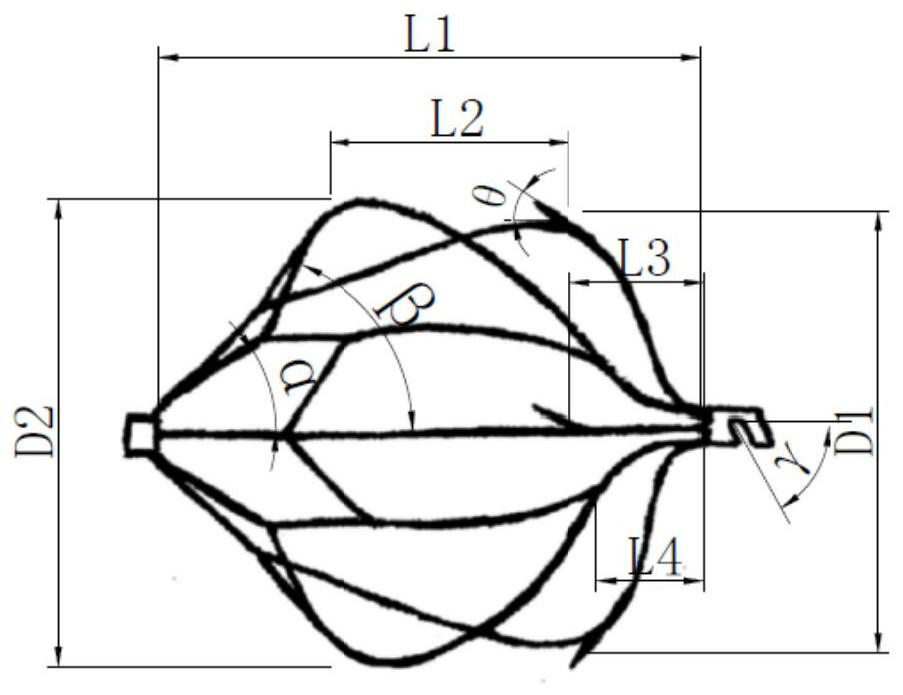
[0032] The upper filter net 2 is a petal shape formed by splicing a plurality of rhombic grids in a ring shape, and the rings are evenly distributed (central symmetry). From the upper end to the lower end, there are first-level grids and second-level grids. The vertex angles of each cell of the first-level grid and the second-level grid are α and β ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 lies in the design of the upper filter screen 2 .
[0047] In embodiment 1, such as figure 1 , the upper filter screen 2 is designed to contain a primary grid and a secondary grid, the rhombus tip of the upper filter screen 2 is connected at one end of the connecting rod 6, and the diamond-shaped concave end of the upper filter screen 2 is connected at one end of the support rod 7.
[0048] In this example, if Figure 4 The design of the upper filter screen 2 contains a primary grid, a secondary grid and a tertiary grid. One end of the connecting rod 6 is connected to the rhombus tip of the secondary grid of the upper filter screen 2, and one end of the support rod 7 is connected to the third end of the upper filter screen 2. level grid tip. In particular, the angle of the third-level grid is smaller than that of the second-level grid, which is the design of the transition part between the support rod 7 and the u...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 lies in the design of the connecting rod 6 .
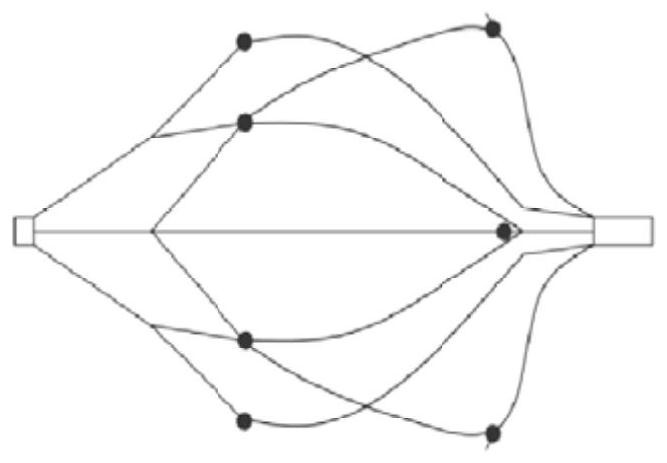
[0051] In embodiment 1, such as figure 1 with figure 2 , the connecting rod 6 is merged into a single strand at the distance L4 from the recovery part 7, and the merged position is designed to be located at the lower filter screen 4. At this time, there are 6 evenly distributed wires near the axis of the filter to filter and catch thrombus, and the position away from the axis of the filter is 3 evenly distributed wires are used to filter and catch thrombus.
[0052] In this example, if Figure 5 , it is designed that the merging position is located in the area of the support section 3, at this time, the lower filter screen 4 contains 6 evenly distributed wires to filter and catch thrombus.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com