A light emit diode
A technology of light-emitting diodes and metal electrodes, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., and can solve the problem that the surface of the metal electrode of the LED core is easily corroded.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
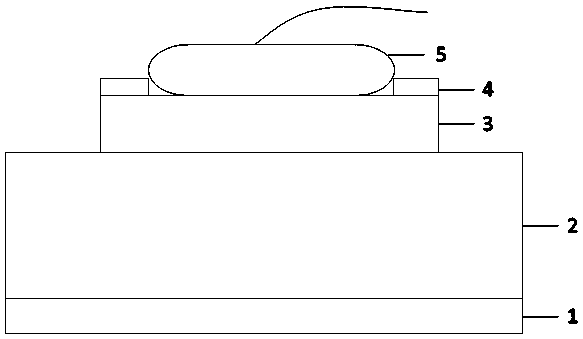
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, the light-emitting diode is a flip-chip red light-emitting diode, including from bottom to top: a back metal electrode and a conductive substrate 1, and the front side of the conductive substrate includes a multi-layer metal layer: a metal bonding layer, a metal reflective layer and a transparent Insulating layer (metal bonding layer, metal reflective layer and transparent insulating layer are not shown in the figure), wherein the transparent insulating layer is located on the metal reflective layer and is in front contact with the light-emitting epitaxial structure 2, and the transparent insulating layer includes through holes and fills them The metal conductive material is used for the metal reflective layer to form electrical contact with one side of the light-emitting epitaxial structure. The upper side of the light-emitting epitaxial structure includes a front electrode, and the surface of the front electrode is provided with a low-potent...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The difference from Example 1 is that the electrode pads at least include an ohmic contact layer, an anti-diffusion layer and a wire metal layer, the material of the ohmic contact layer is Cr, and the material of the anti-diffusion layer is Ti / Pt / Ni / W / TiW One of the metals that can block the diffusion between the solder layer and the ohmic contact layer; the ohmic contact layer is gold. The low-potential metal is one of Al, Zn, Cr, Ti, Fe, Co, and the low-potential metal layer is a compression-resistant metal material layer to improve the compressive strength of the electrode pad and slow down the welding line. For the pressure damage to the electrode pad during gold ball bonding, the Mohs hardness of the low-potential metal is preferably higher than 6, and more preferably the metal material is a metal material with high Mohs hardness such as Ti and Cr.
Embodiment 3
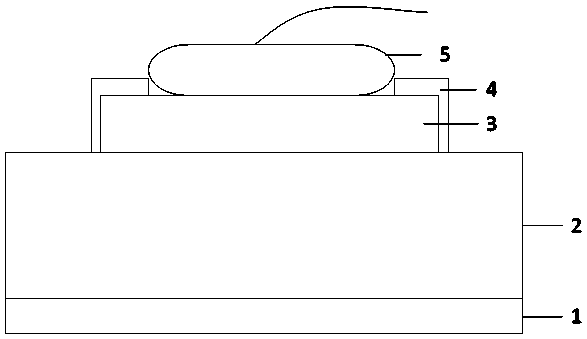
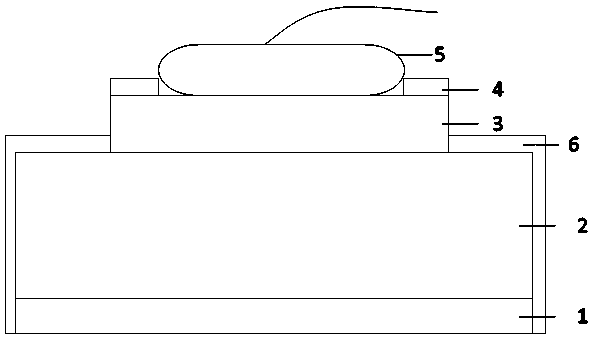
[0051] Different from embodiment 1 or 2, such as Figure 4 As shown, the insulating protection layer preferably further extends to the side surface and the outermost peripheral area of the electrode pad, and at least partially covers the low-potential metal layer, and forms the middle of the pad electrode together with the low-potential metal layer and the insulating protection layer. Leave the area blank for wire bonding to gold balls for soldering, or if Figure 5 As shown, the insulating protection layer preferably exposes a part of the low-potential metal layer, so as to increase the protective effect of the low-potential metal on the surface of the metal layer of the electrode pad and wire. or as Image 6 As shown, the low-potential metal layer is located in the non-edge area, and the edge area is left blank for making an insulating protective layer covering.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mohs hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com