Method of treatment on vitamin production wastewater
A technology for the production of wastewater and vitamins, applied in multi-stage water treatment, water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as excessive sludge, non-degradable organic matter, and increased treatment costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The following are specific examples of the present invention to further describe the technical solutions of the present invention, but the present invention is not limited to these examples.
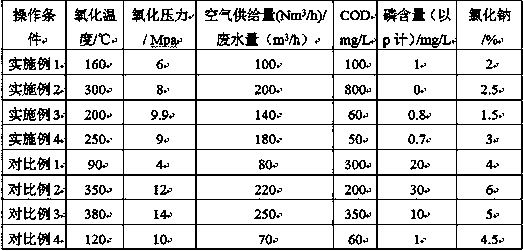
[0022] A factory produces multivitamins. After purification and concentration, waste water is produced. The total phosphorus of this waste water exceeds 20000mg / L, COD50000mg / L, and sodium chloride 18%.
[0023] The waste water is pre-oxidized to oxidize and degrade the refractory organic matter into small molecular organic matter, and some of them are directly oxidized into CO 2 , water, which is convenient for salt extraction; the catalytic wet oxidation reaction temperature is set at 160°C, the reaction pressure is 6.0Mpa, and the air supply rate (Nm 3 / h) / Wastewater volume (m 3 / h) 100 times.
[0024] Crystallization is carried out by freezing and crystallization technology, and qualified industrial phosphate is obtained after filtration and cleaning. The total phosphorus f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com