Doping modified sodium vanadium fluorophosphates positive electrode material and preparation method thereof
The technology of sodium vanadium fluorophosphate and positive electrode material is applied in the field of doping and modified sodium vanadium fluorophosphate positive electrode material and its preparation, and can solve the problems of high synthesis temperature of sodium vanadium fluorophosphate, long sintering time at high temperature, material agglomeration and the like, Achieve the effect of improving charge-discharge specific capacitance and rate performance, low synthesis cost, and improving ionic conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
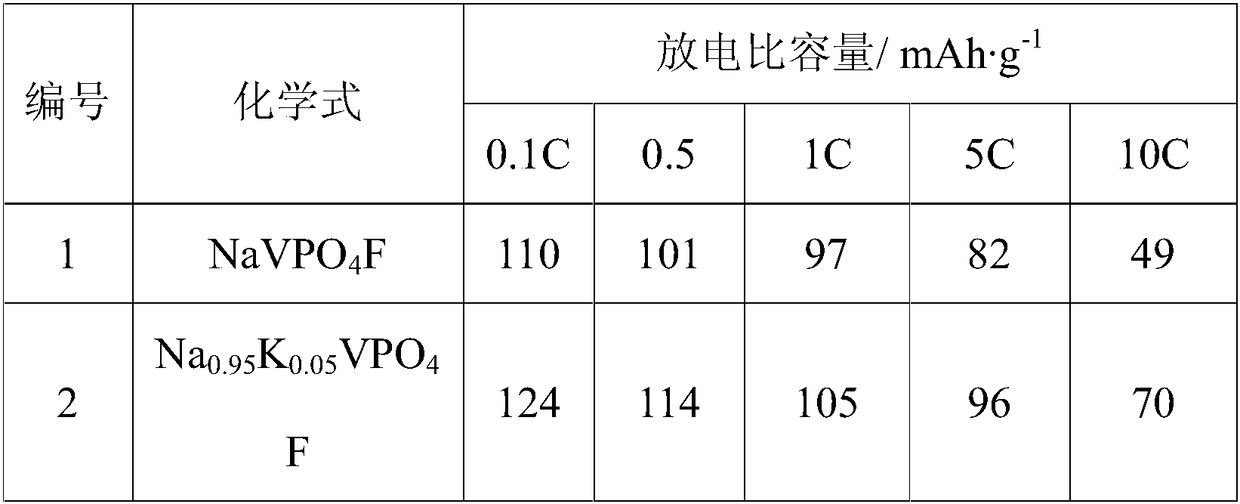
[0031] 1) Sodium fluoride, potassium fluoride, ammonium metavanadate and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate are mixed and dissolved in the desulfurized adding oxalic acid with a molar ratio of 2:1 to vanadium in ammonium metavanadate in ionized water, and mixing at room temperature to prepare a uniformly mixed precursor solution;
[0032] 2) Transfer the precursor solution to a -40°C refrigerator for 12 hours, and then freeze-dry it for 24 hours to prepare the precursor powder; place it in a non-oxidizing atmosphere tube furnace for 2 hours at 300°C and 4 hours at 600°C to obtain Sodium vanadium fluorophosphate modified by potassium ion doping. The blank sample is sodium vanadium fluorophosphate without adding potassium fluoride, and other conditions remain unchanged.
[0033] The resulting product was packed into a button battery to measure its charge and discharge specific capacity, and its discharge specific capacity data is shown in Table 1.
[0034] Experimental condition an...
Embodiment 2
[0038] 1) Sodium fluoride, potassium fluoride, ammonium metavanadate and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate are mixed and dissolved according to the molar ratio of sodium, potassium, vanadium, phosphorus and fluorine elements in a molar ratio of 0.95:0.05:1:1:1 In deionized water, add oxalic acid with a molar ratio of 2:1 to ammonium metavanadate, and mix under normal temperature conditions to prepare a uniformly mixed precursor solution;
[0039] 2) Transfer the precursor solution to a -40°C refrigerator to freeze for 12h, then freeze-dry for 24h to prepare the precursor powder; place it in a non-oxidizing atmosphere tube furnace at 300°C for 2h, 500, 550, 600, 650 , 700°C for 4 hours to prepare potassium ion-doped sodium vanadium phosphate. The resulting product was assembled into a button cell to measure its charge and discharge specific capacity, and the discharge specific capacity data is shown in Table 2.
[0040] Experimental condition and result of table 2 embodiment 2
...
Embodiment 3
[0044] 1) Sodium fluoride, potassium fluoride, ammonium metavanadate and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate are mixed and dissolved according to the molar ratio of sodium, potassium, vanadium, phosphorus and fluorine in a ratio of 0.9:0.1:1:1:1 In deionized water, add oxalic acid with a molar ratio of 2:1 to ammonium metavanadate, and mix under normal temperature conditions to prepare a uniformly mixed precursor solution;
[0045]2) Transfer the precursor solution to a -40°C refrigerator for 12 hours, and then freeze-dry it for 24 hours to prepare the precursor powder; place it in a non-oxidizing atmosphere tube furnace for 2 hours at 300°C and 4 hours at 650°C to obtain Sodium Vanadium Phosphate Modified by Potassium Ion Doping 0.9 K 0.1 VPO 4 F. Pack the obtained product into a button battery to measure its charge and discharge specific capacity, and the discharge specific capacity at 0.1C, 0.5C, 1C, 5C, and 10C rates is 130mAh·g respectively -1 , 121mAh·g -1 , 117mAh·g -1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com