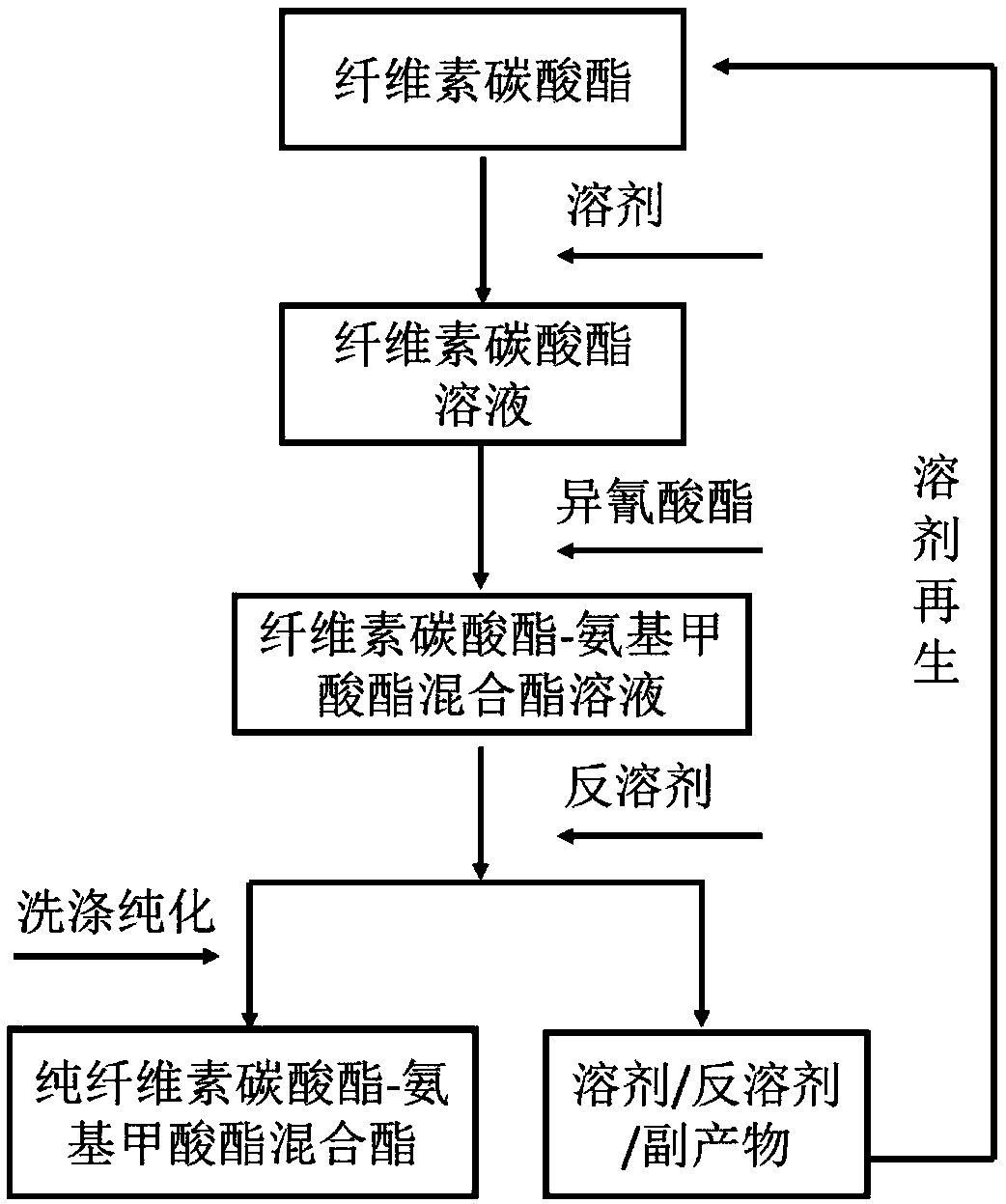
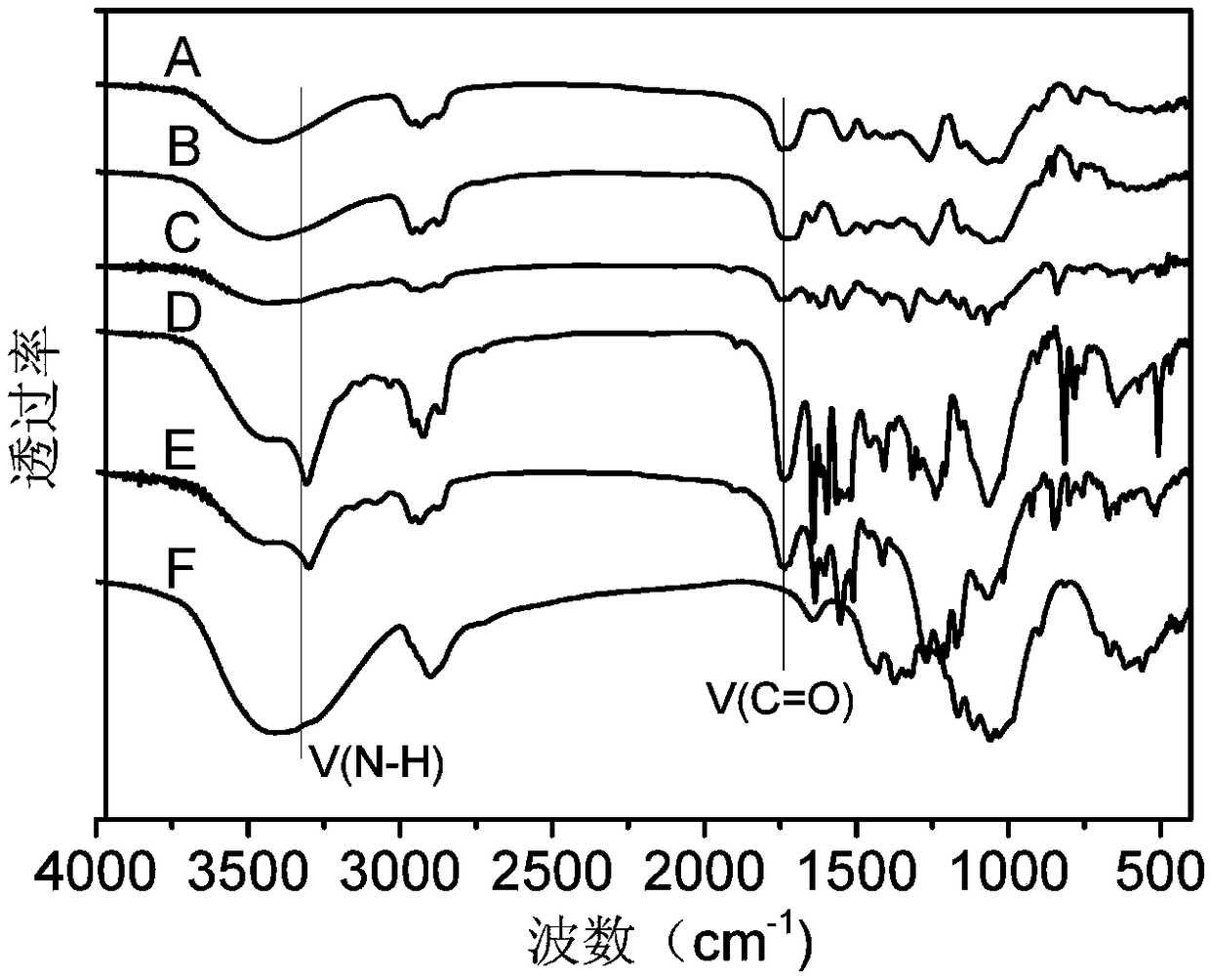
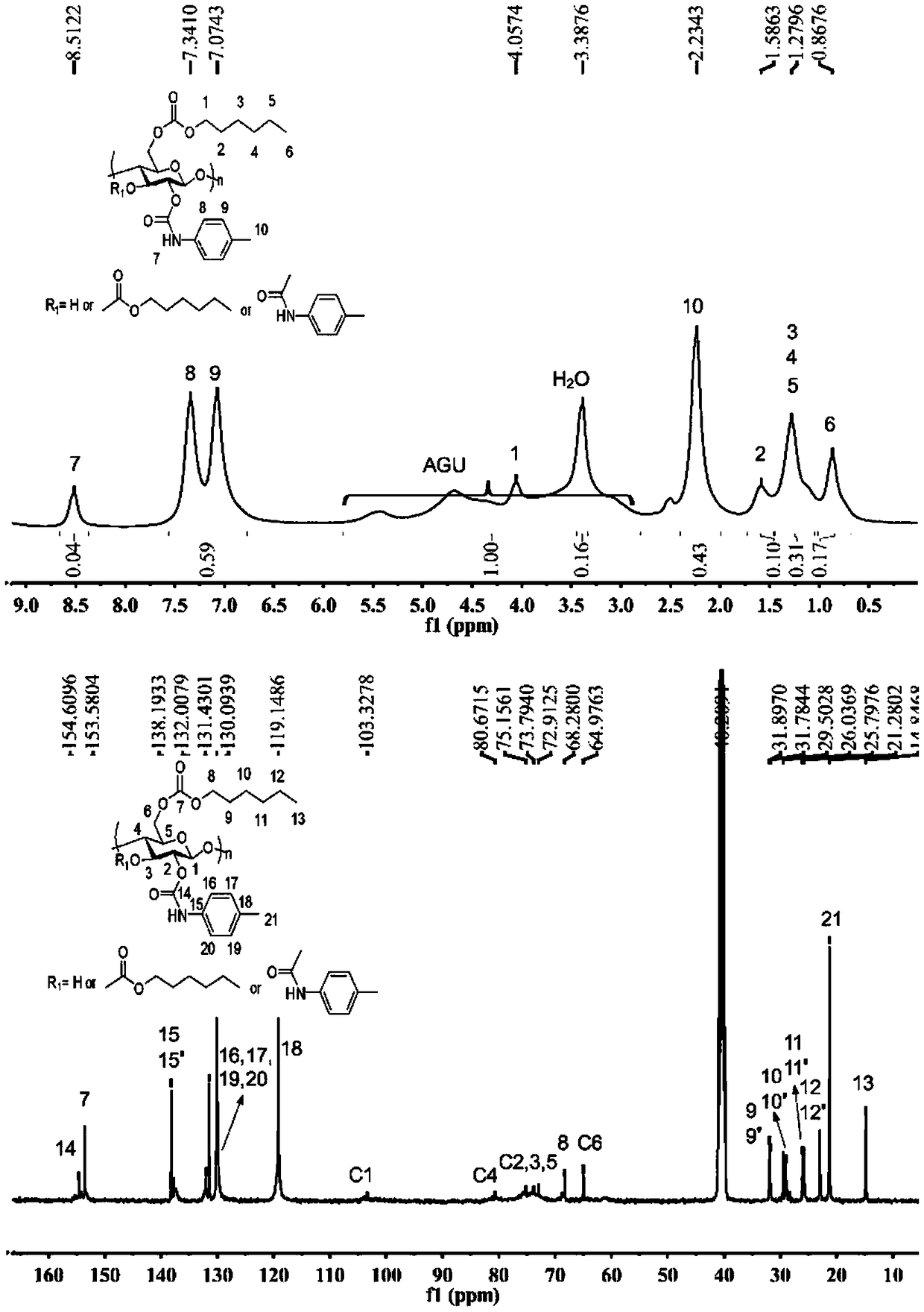
Method for preparing carbonic ester-carbamate mixed ester based on cellulose carbonic ester
A technology of carbamate and carbonate, applied in the field of preparation of mixed ester materials, can solve the problems of cellulose carbonate derivative literature and patent reports, type restrictions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0107] Weigh 1.00 g of cellulose carbonates with different substitution structures in a flask, take 5 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and heat to dissolve at 50° C. Add 1.165 mL of p-toluene isocyanate and 10 wt % DBU relative to cellulose carbonate as a catalyst, and react at 50° C. for 3 h. After the end, use 100 mL of water for precipitation, wash with suction and filter 3 times, and freeze-dry to obtain the product. The relevant results are shown in the table below:
[0108] Table 1 Reaction of cellulose carbonates with different structures
[0109]
[0110] where DS C1 and DS C2 Respectively represent the degree of substitution of carbonate groups of pure cellulose carbonate and the reacted cellulose carbonate-urethane mixed ester. discover DS C2 The value is generally higher than the DS C1 Large, due to NMR calculation errors.
[0111] This example fully demonstrates that for cellulose carbonates of different structures, cellulose carbonate-urethane mixed este...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Weigh 1.00 g of cellulose hexyl carbonate into a flask, take different volumes of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and heat to dissolve at different temperatures. Add 1.165mL of p-toluene isocyanate, and catalysts of different types and different mass fractions, and react at 50°C for 3h. After the end, use 100 mL of water for precipitation, wash with suction and filter 3 times, and freeze-dry to obtain the product. The relevant results are shown in the table below:
[0114] Table 2 Study of different cellulose carbonate concentrations, temperatures and organic solvents
[0115]
[0116] a: ratio content of cellulose carbonate to solvent (W / V); b: dissolution temperature of cellulose carbonate; c: dissolution reagent used.
[0117] This example fully demonstrates that for different cellulose carbonate concentrations, as well as dissolution temperature and dissolution reagents, the reaction with isocyanate reagents can be realized, and finally a carbonate-urethane mixed ce...
Embodiment 3
[0119] Based on the fact that ionic liquid is a good solvent with good stability and wide adaptability, it is also a good catalyst for organic reactions. Ionic liquid has both the functions of solvent and catalyst, and a series of researches are carried out on this.
[0120] Weigh 1.00 g of cellulose hexyl carbonate into a flask, take different ionic liquids (Ionic Liquid), and heat to dissolve at different temperatures. Add 1.165mL of p-toluene isocyanate and react at 50°C for 3h. After the end, use 100 mL of water for precipitation, wash with suction and filter 3 times, and freeze-dry to obtain the product. The relevant results are shown in the table below:
[0121] Table 3 Ionic Liquids as Solvents
[0122]
[0123] a: ratio of cellulose carbonate to ionic liquid (W / W); b: dissolution temperature of cellulose carbonate; c: ionic liquids with different structures.
[0124] In conjunction with Example 2, examples fully demonstrate that ionic liquids have good solubility...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com