Ensemble empirical mode decomposition current diagnosis method for motor broken bar faults
A technology that integrates empirical modes and decomposes currents. It is applied in the field of detection and can solve problems such as lack of spatial locality, limited adaptability of wavelet analysis, and ineffective mutation signals.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
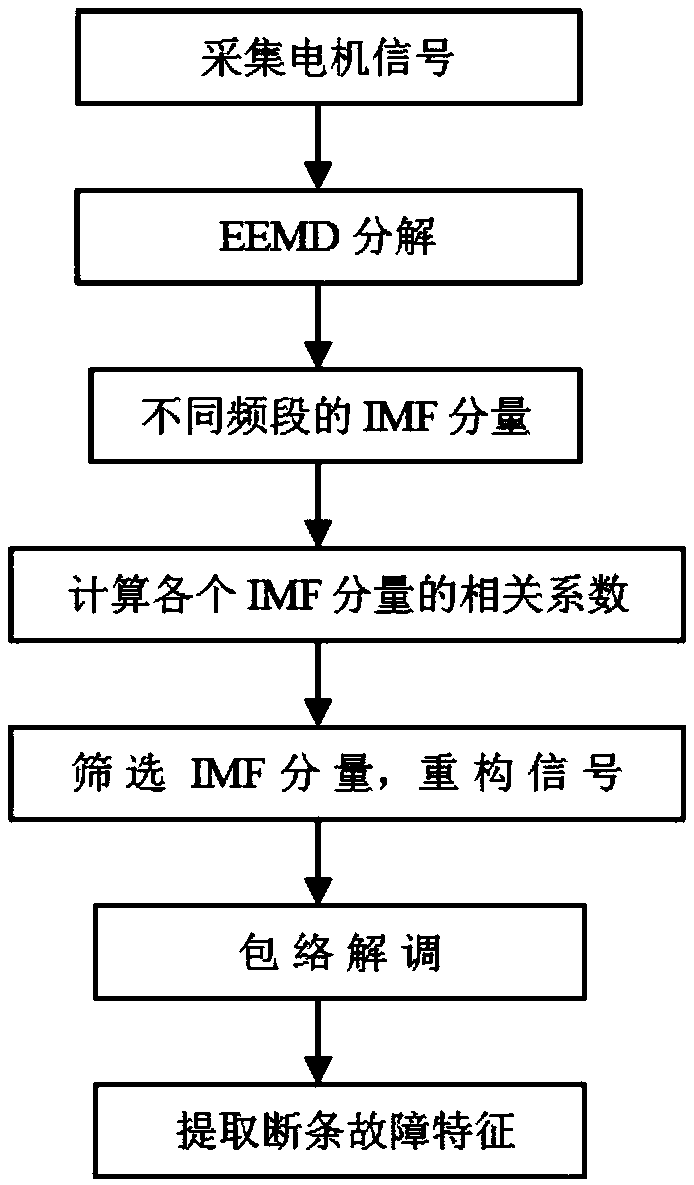
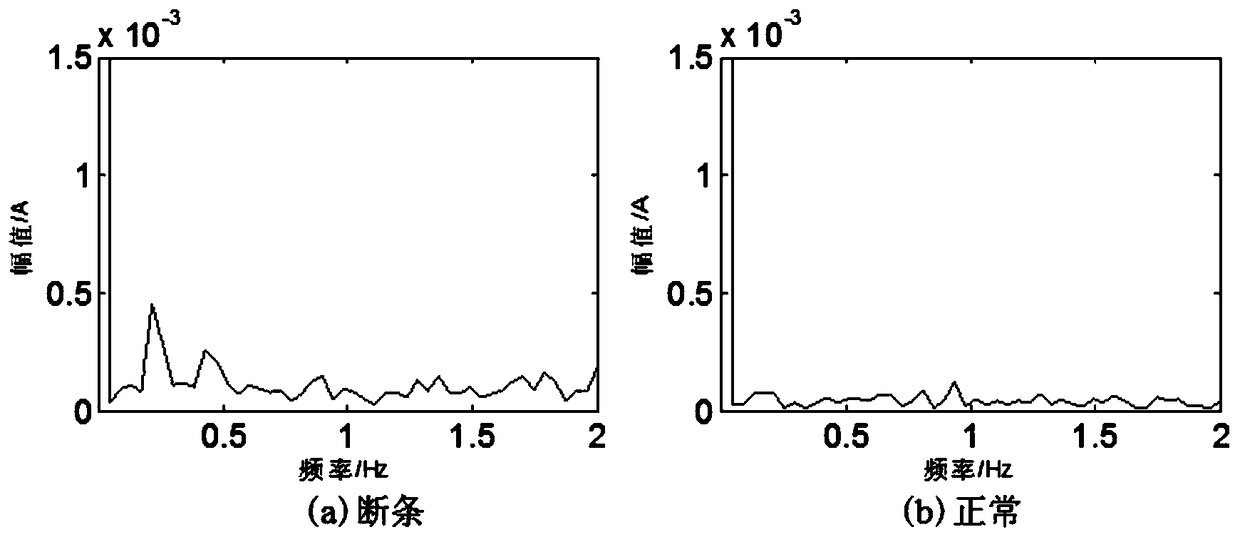
[0044] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, an ensemble empirical mode decomposition current diagnosis method for motor broken bar fault, the steps are as follows:
[0045] S1, collecting the stator current of the motor at a certain constant speed;
[0046] The stator current during the operation of the motor is obtained through a current sensor (current clamp) and a data acquisition system.
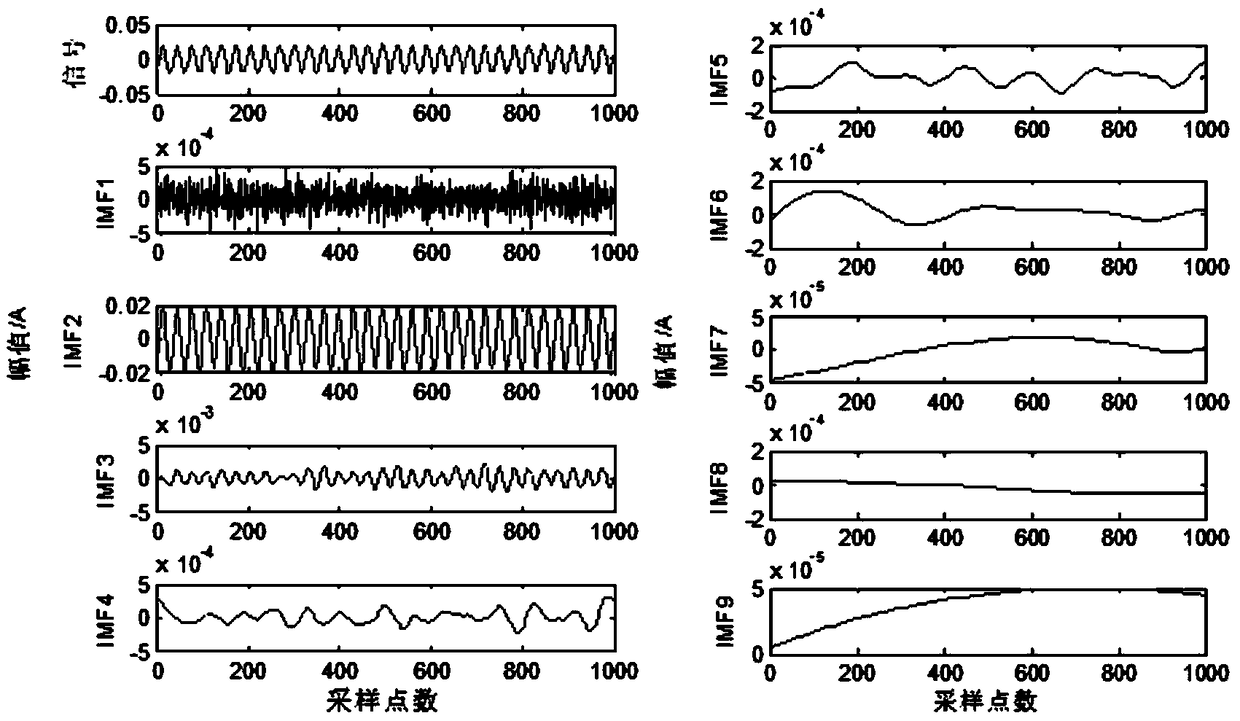
[0047] S2, performing EEMD decomposition on the obtained stator current to obtain IMF components.
[0048] S2.1, add a group of random Gaussian white noise signals with zero mean and equal variance to the original signal of the stator current, so that the original signal of the stator current is a mixed signal with Gaussian white noise added.
[0049] S2.2. Obtain an upper envelope and a lower envelope of the mixed signal.
[0050] S2.2.1, Determine the local maxima of the mixed signal.
[0051] S2.2.2, using the cubic spline interpolation method to obtain the local maximum point to o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com