Forced pressure-in-draw-out type turbogenerator ventilation cooling system with multi-wind path interleaving
A turbogenerator, ventilation and cooling technology, applied in the direction of cooling/ventilation device, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, electric components, etc., can solve the problem of increasing fluid flow, reducing thermal stress of turbogenerator, high temperature, etc. problem, achieve the effect of increasing the total fluid flow, speeding up the flow rate and reducing thermal stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
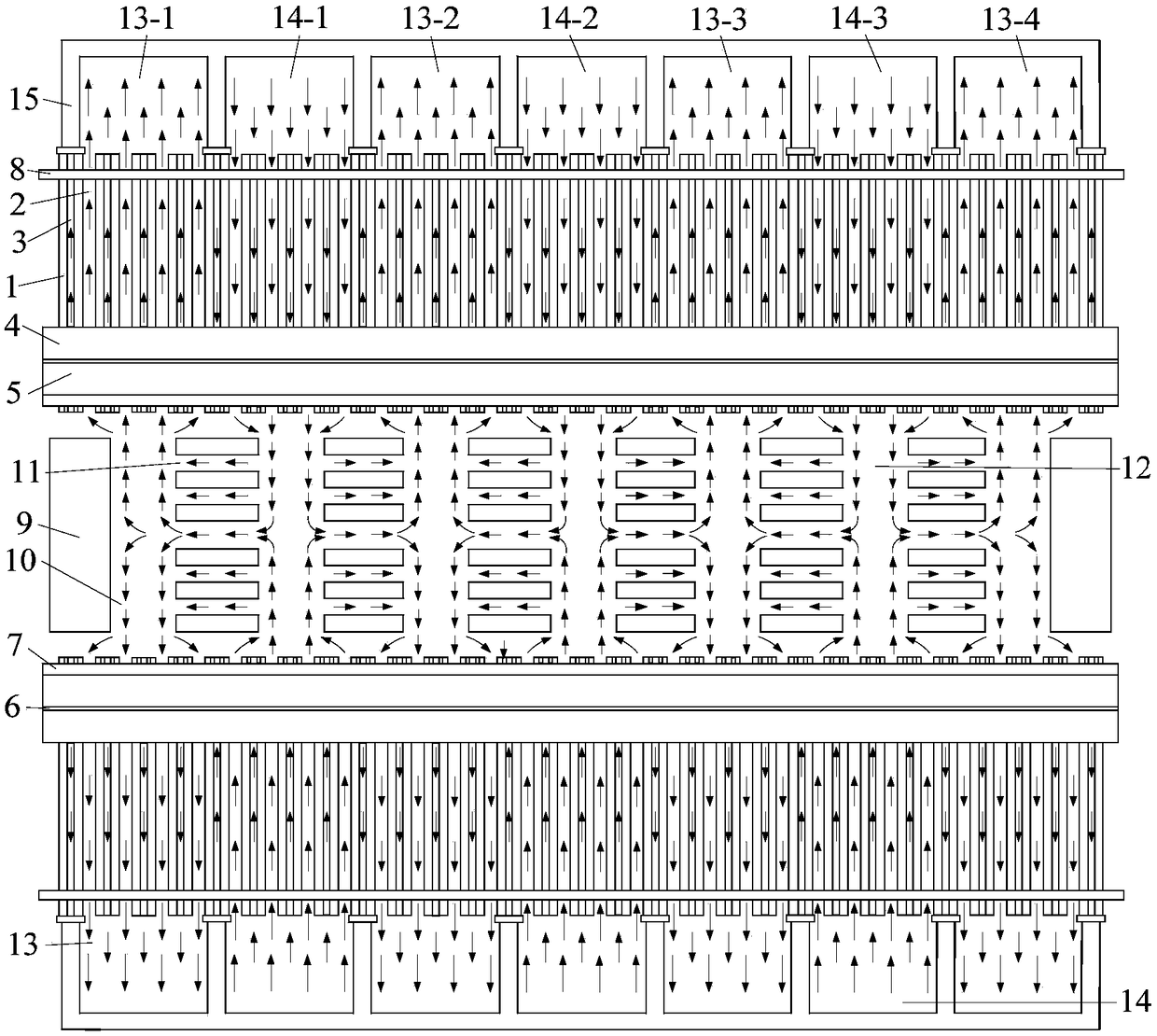
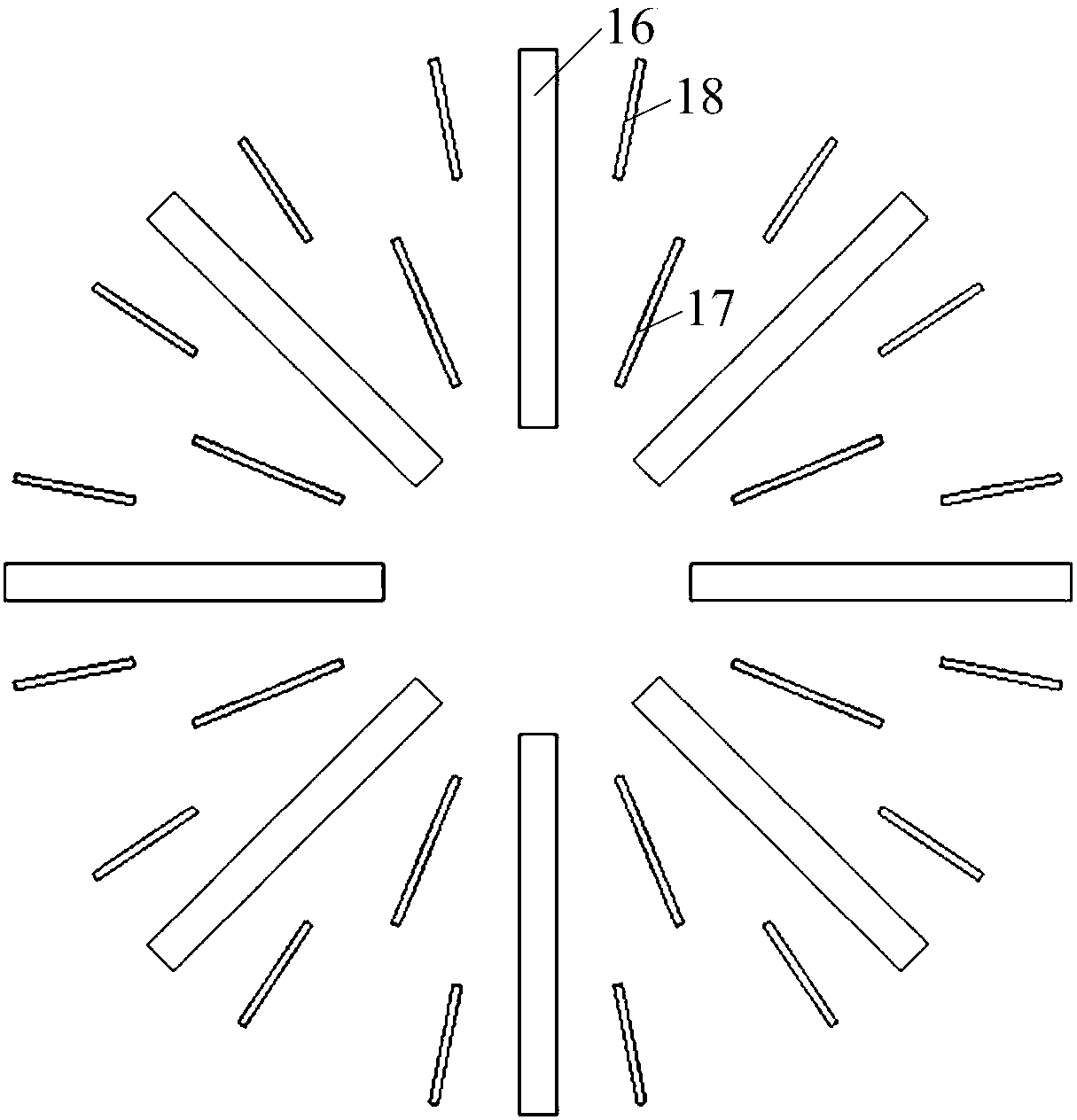
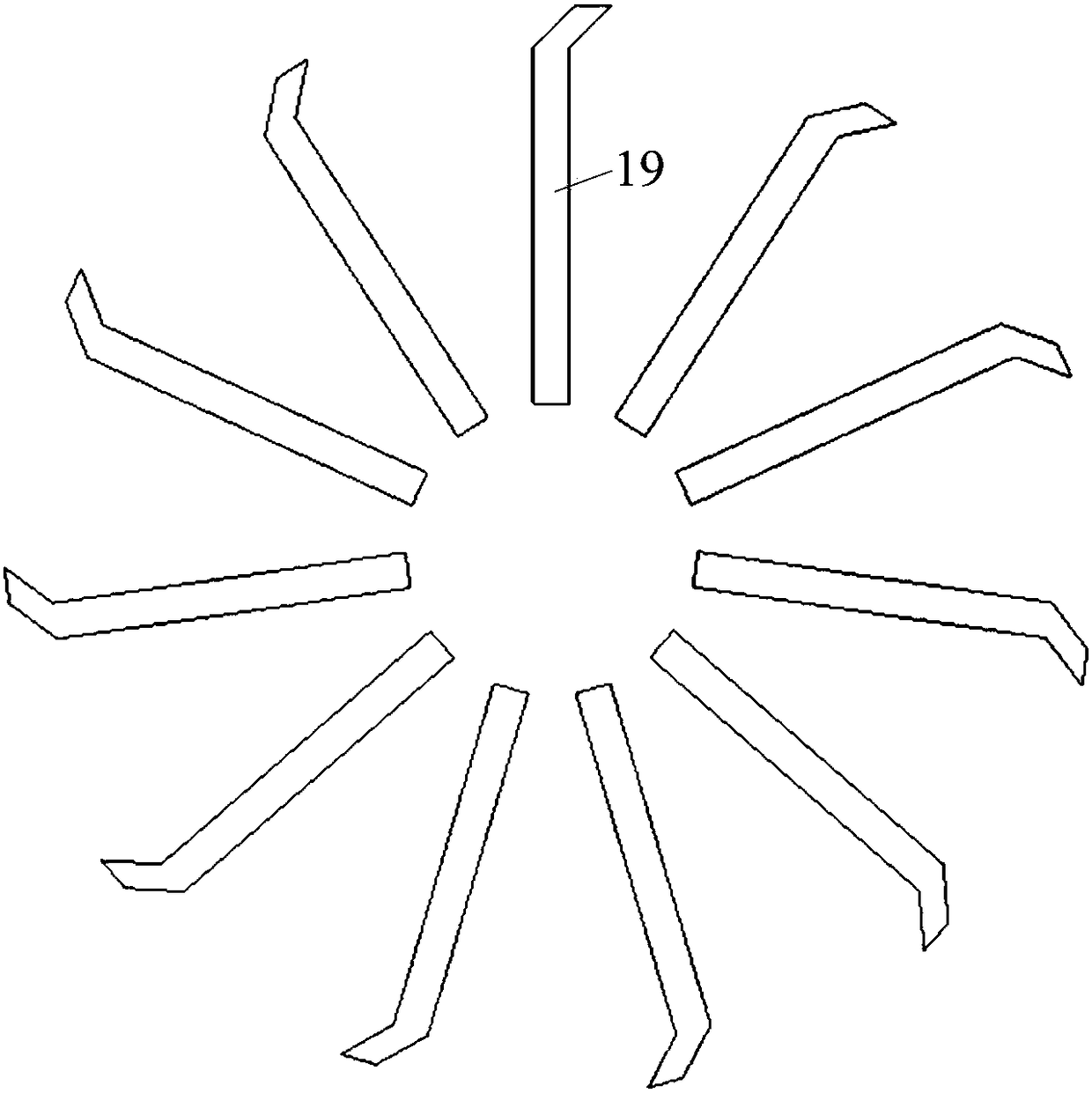
[0027] Embodiment 1: Combining figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 and Figure 5Illustrating this embodiment, a forced press-in-extraction type turbo-generator ventilation and cooling system with interlaced multi-air paths described in this embodiment includes a stator iron core 1, a stator radial ventilation ditch 2, and a "Y"-shaped stator. Internal ventilation channel 3, stator lower winding 4, stator upper winding 5, interlayer insulation 6, slot wedge 7, positioning ribs 8, rotor core 9, rotor hot air area 10, rotor axial ventilation hole 11, rotor cold air area 12, stator Hot air area 13, stator cold air area 14, stator frame 15, rotor throw-out fan blades 16, rotor first-stage pressurized fan blades 17, rotor second-stage pressurized fan blades 18, rotor suction fan blades 19 and stator groove 20. "Y"-shaped stator internal ventilation channel 3 includes stator I-type inner cooling ventilation channel 3-1 and stator V-shaped inner cooling ventilation channe...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0030] Specific implementation mode 2: Combining Image 6 and Figure 7 Describing this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the inlet area of the stator radial ventilation groove 2 in the stator hot air area 13 and the stator cold air area 14 is increased, and the entry into the stator radial ventilation groove 2 is increased. The flow rate of the cooling gas improves the ability of the cooling gas to take away the heat of the stator core 1 , and further reduces the temperature of the stator core 1 . Other components and connection relationships are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0031] Specific implementation three: combination Figure 8 Describing this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the number of the rotor second stage pressurizing fan blades 18 is increased, which further increases the pressure of the cooling gas, accelerates the flow rate of the cooling gas, and effectively improves the The utilization rate of the cooling gas further reduces the temperature of the stator core 1 and the rotor core 9 . Other components and connection relationships are the same as those in the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com