Application of Indole-3-Carboxaldehyde and Its Derivatives in Controlling Plant Diseases Caused by Phytopathogenic Fungi
A technology for phytopathogenic fungi and plant diseases, applied in the direction of chemicals, applications, biocides for biological control, etc., to ensure high quality, broad research and market application prospects, and growth inhibition effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
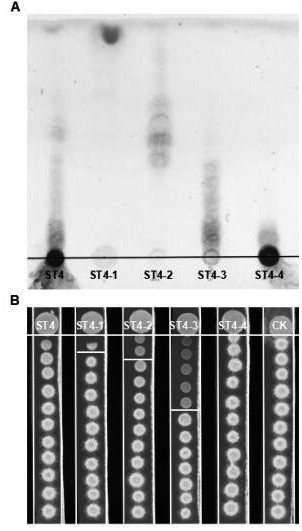
[0064] Example 1 Extraction of Pseudomonas ST4 metabolites and detection of its biological activity
[0065] 1. Extraction of strain ST4 metabolites
[0066] (1) Inoculate the overnight cultured ST4 bacterial solution on a PDA plate (13×13 cm), culture at 28°C for 48 hours, and wipe off the colonies with sterile gauze to obtain a fermentation medium;
[0067] (2) Cut the fermentation medium into small pieces and soak in 3 times the volume of a mixed solution composed of ethyl acetate:methanol:glacial acetic acid at a volume ratio of 80:15:5, shake for 2 hours, and filter to collect the supernatant; Use a rotary evaporator to remove organic solvents such as ethyl acetate and methanol in the supernatant, leaving the aqueous phase solution;
[0068] (3) Extract the aqueous phase solution 3 times with 3 times the volume of ethyl acetate, collect the aqueous phase and the organic phase respectively, evaporate the organic phase to dryness using a rotary evaporator, and concentrate ...
Embodiment 2
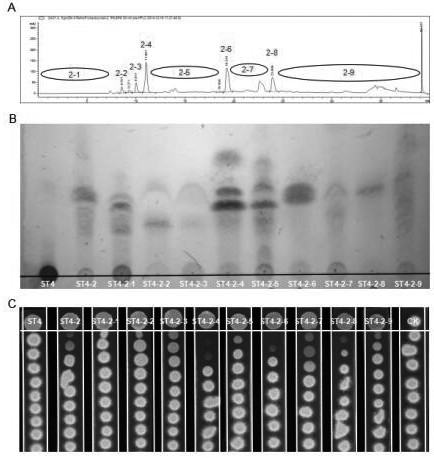
[0075] The separation and purification of the effective active substance of embodiment 2 Pseudomonas ST4
[0076] 1. Separation and purification method
[0077] The ethyl acetate extract obtained in Example 1 was sequentially separated by Claricep FlashSilica (CS) standard silica gel column chromatography, Butch medium pressure separator, high performance liquid chromatography and HPLC semi-preparative separation, the specific methods are as follows:
[0078] (1) Standard silica gel column chromatography separation:
[0079]1) Sample loading: Accurately weigh 5-6 g of the ethyl acetate extract of Pseudomonas ST4 each time, dissolve it with an appropriate amount of methanol, add twice the amount of 60-100 mesh silica gel, stir well, and air-dry the methanol. The silica gel containing the sample is added to the sample column, connected with the Claricep FlashSilica (CS) standard silica gel column, and connected with the Butch medium pressure separator and analytical grade metha...
Embodiment 3
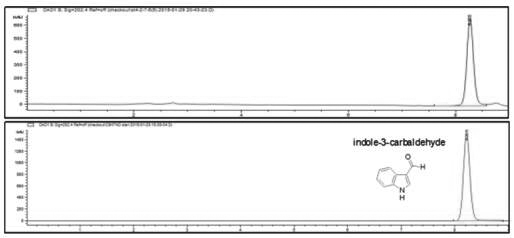
[0098] Molecular formula and structure identification of embodiment 3 compound ST4-2-8
[0099] 1. Structural identification: ST4-2-8 obtained in Example 2 was analyzed by NMR and LC-MS to identify its chemical structure.
[0100] 2. Identification results:
[0101] The NMR analysis of ST4-2-8 shows that the compound contains 9 carbons, 7 Hs, 1 N and 1 O atom, and contains a parallel structure of a benzene ring and a pyrrole ring, at the 3rd position of benzopyrrole Containing an aldehyde group, the possible structure is indole-3-carbaldehyde; LC-MS analyzes the molecular weight of this substance to be 146.15, consistent with indole-3-carbaldehyde; Shown by HPLC analysis with finished product ( image 3 ), the retention time of ST4-2-8 and indole-3-carbaldehyde is 8.255min, and the peak shape and three-dimensional structure are completely consistent. Therefore, ST4-2-8 is identified as indole-3-carbaldehyde.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com