Injectable high-strength thermosensitive modified chitin-based hydrogel and its preparation method and application
A temperature-sensitive, high-strength technology, applied in the field of biomedical materials and tissue engineering, can solve the problems of weak material strength and achieve good biocompatibility, good biocompatibility, and easy industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of hydrophilic macromolecular cross-linking agent
[0038] 1. Synthesis of benzaldehyde-modified polyethylene glycol (PEG) macromolecular cross-linking agent
[0039] (1) Synthesis of linear bisbenzaldehyde-terminated PEG (DF-PEG)
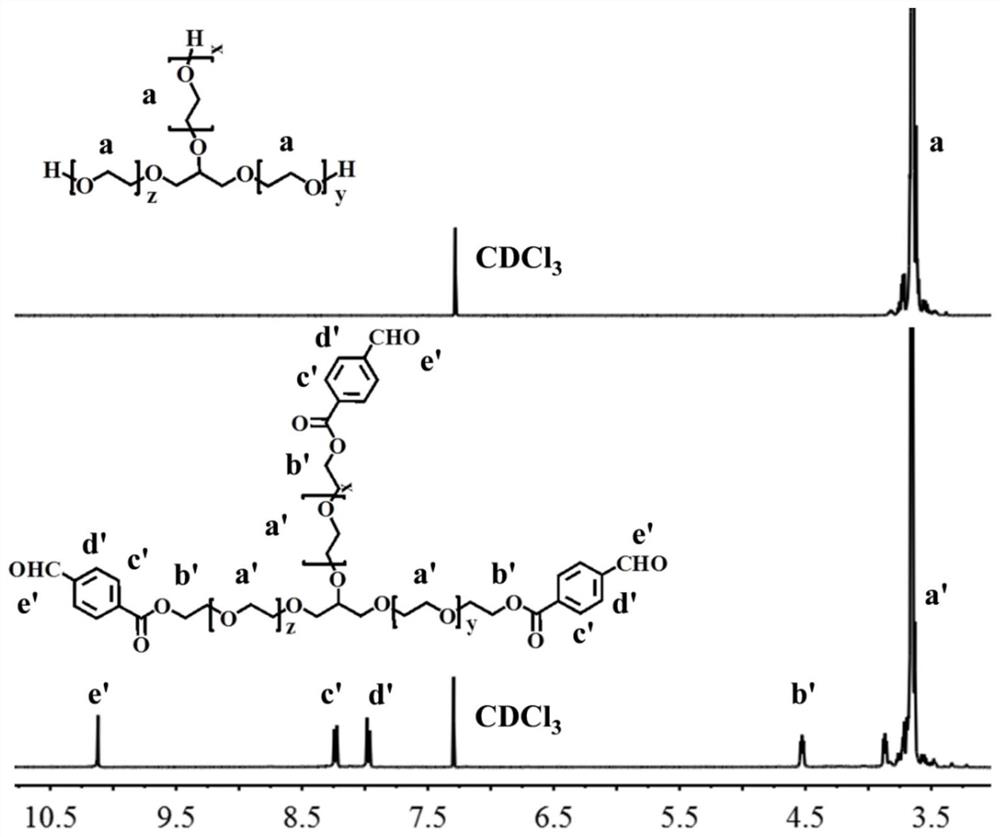
[0040] Benzaldehyde with linear PEG end group Linear bisbenzaldehyde end group PEG
[0041] Weigh 1.5 gram of PEG 6k and 0.19 gram of 4-carboxybenzaldehyde and place in a 100mL round bottom flask, add 30mL of dried methylene chloride to dissolve, then add 0.15 gram of 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) and 0.31 gram of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC), stirred and reacted at room temperature for 24 hours, filtered and collected the filtrate and precipitated in a large amount of ether, and the collected crude product was dissolved, recrystallized and dried in isopropanol to obtain bifunctional benzaldehyde PEG, 79% yield. 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 ,δ): 10.1 (hydrogen on the aldehyde functional group), 8.2, 7.9 (hydroge...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment 2: Preparation of thermosensitive chitin derivative A
[0053] Preparation of thermosensitive hydroxypropyl chitin (HPCH)
[0054] According to our previous research work [Chinese invention patent application publication specification CN201410170871.8], a homogeneous method was used to prepare hydroxypropyl chitin with a low degree of deacetylation in a sodium hydroxide-urea system. Weigh 2 grams of purified chitin (viscosity-average molecular weight is 756,000) and stir and disperse it in 100 grams of aqueous solution containing 11wt% sodium hydroxide and 4wt% urea in advance, freeze overnight at -25°C, take it out at room temperature Under mechanical stirring to thaw it, and then repeat the freezing and thawing twice to obtain the dissolved chitin aqueous solution. Add 11.5 grams of propylene oxide to the obtained chitin solution (100 grams, 2 wt%), and the system is mechanically stirred at 2°C for 2 hours to mix the reactants evenly, then the temperature ...
Embodiment 3
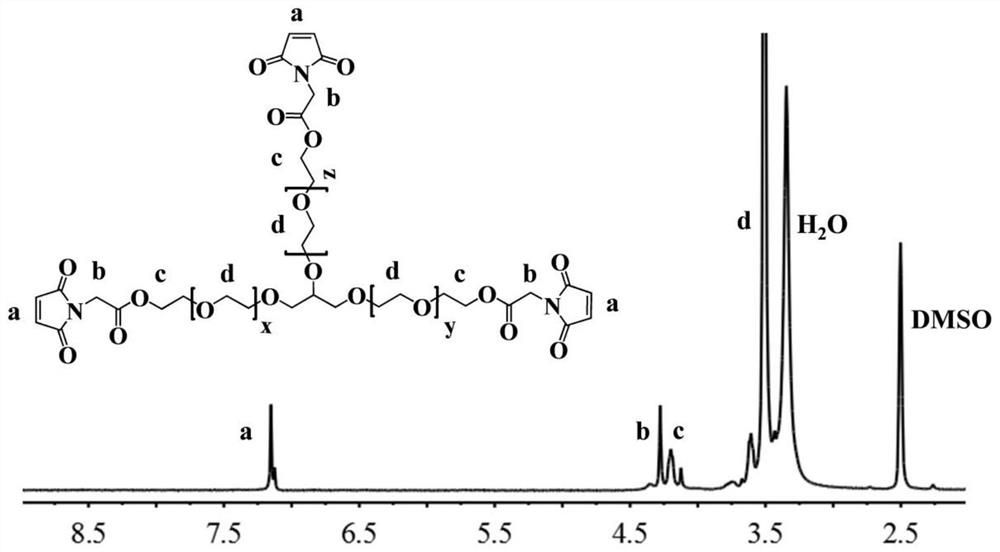
[0060] Example 3: Preparation of thermosensitive ammonia aldehyde in situ reaction modified hydroxypropyl chitin HPCH hydrogel
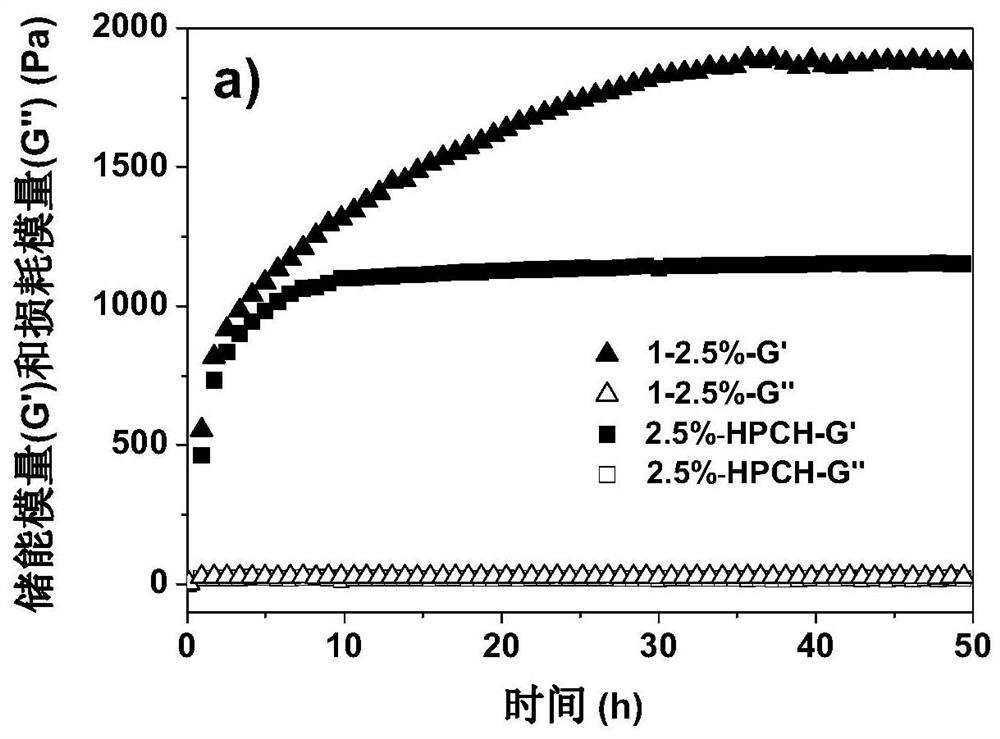
[0061] The DF-PEG prepared in Example 1 (the molecular weight of PEG is 2000) and the thermosensitive hydroxypropyl chitin HPCH-T1 prepared in Example 2 were respectively dissolved in 0.15M PBS buffer at pH 7.4, and the concentration of A solution of 20 wt% DF-PEG and 3 wt% HPCH-T1. Take 0.047g of DF-PEG solution, 1g of HPCH-T1 solution and 0.14g of PBS buffer solution and mix them uniformly at 2-15°C for half a minute at low temperature (it is liquid for a long time after mixing at low temperature, and has good injectability properties) It was placed in a constant temperature water bath at 37°C and quickly formed a gel, which illustrated its in-situ rapid gelation characteristics in vivo. Because the chemical crosslinking of ammonia aldehyde proceeds slowly in the body, in a constant temperature water bath at 37°C for 6-24 hours, a hydrogel with a ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com