Loudspeaker plastic cone body
a technology of loudspeaker and plastic cone body, which is applied in the field of loudspeaker, can solve the problems of paper cone body moisture problems, paper cone body manufacturing tolerances that are undetectable, and cone body stiffness to weight ratio is still relatively low
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
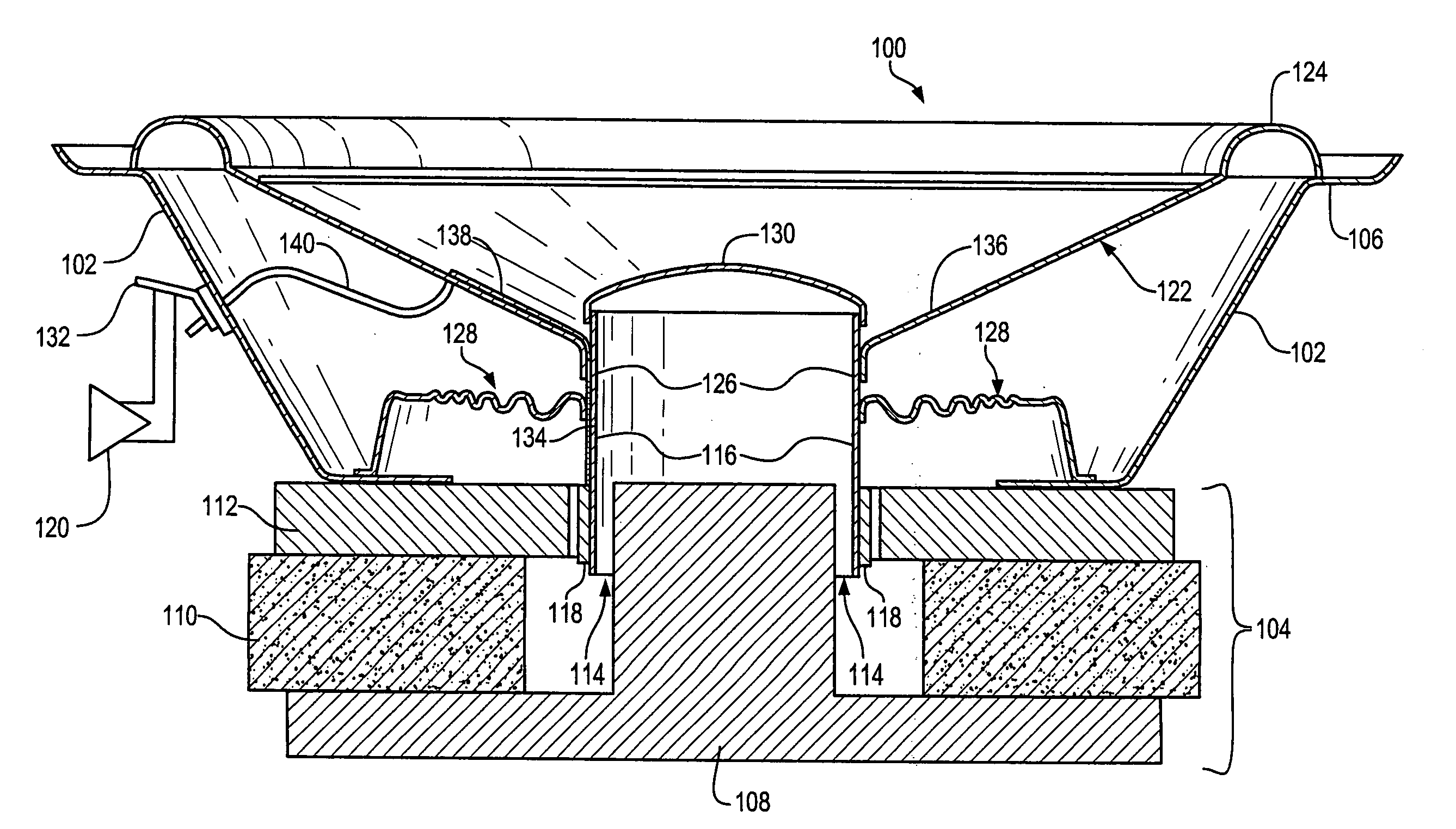
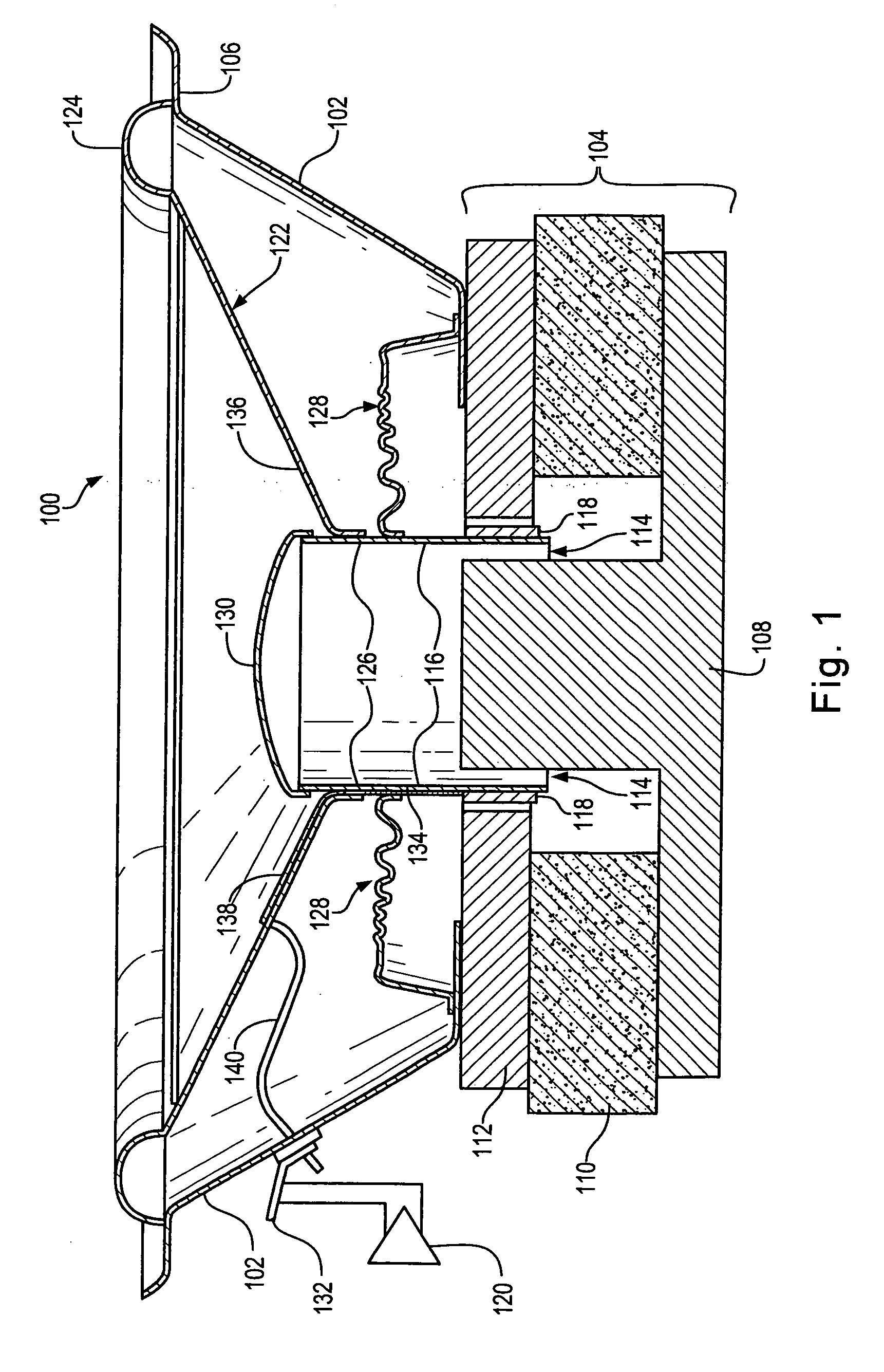
[0028] The present invention provides a loudspeaker cone made of plastic and plastic compatible materials which improves loudspeaker performance through improved stiffness to weight ratio and higher material damping at equivalent material stiffness. In addition, the loudspeaker cone manufacturing process described later may extend the range of practical cone geometries and cone sizes that may be produced. Specifically, the loudspeaker cone may be formed by injection molding and / or thermoforming from a predetermined mixture of materials that maximize the stiffness to weight ratio. In addition, the cone may have relatively thin wall sections. Since the cone bodies are made of plastic and other plastic compatible materials, raw materials may be more economical, manufacturing may be streamlined and repeatability may be improved. In addition, significant improvements in acoustical performance may be achieved.
[0029] The following examples employ certain combinations of material and proce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com