Method for preparing Y-type molecular sieve from FCC waste catalyst by microwave heating
A waste catalyst and microwave heating technology, which is applied in the field of comprehensive recycling of secondary resources, can solve the problems of large quantities of emissions, and achieve the effects of reducing the content of poisoned metals, convenient operation, and short crystal formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] This microwave heating prepares the method for Y-type molecular sieve from FCC waste catalyst, and its concrete steps are as follows:
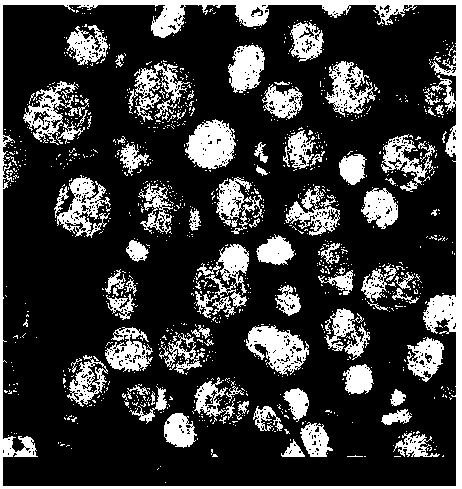
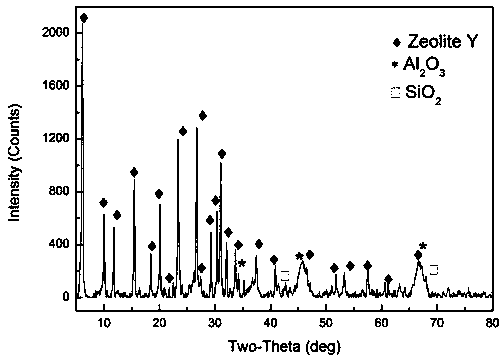
[0026] Step 1. First, mix the spent FCC catalyst with the leaching mother liquor (5wt% HCl solution) at a liquid-solid ratio of 6:1mL / g, and then leaching for 30 minutes at a temperature of 80°C to obtain vanadium, nickel, and iron poisoning metals. The leaching solution (the leaching rates of Fe, V, and Ni are 44%, 46%, and 33%, respectively, and the Al loss rate is 10%) and the spent FCC catalyst with basically complete molecular sieve structure after demetallization and revival; the molecular sieve structure after demetallization and revival The basically complete SEM image of FCC spent catalyst is shown in Fig. figure 1 shown;
[0027] Step 2. Use the spent FCC catalyst with basically complete molecular sieve structure obtained in step 1 as the aluminum source, and add 6.5 kilograms of silicon source (silica sol) and 2.1 kilograms ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] This microwave heating prepares the method for Y-type molecular sieve from FCC waste catalyst, and its concrete steps are as follows:
[0031]Step 1. First, mix the spent FCC catalyst with the leaching mother liquor (3wt% HCl solution) at a liquid-solid ratio of 10:1mL / g, and then leaching for 30 minutes at a temperature of 80°C to obtain vanadium, nickel, and iron poisoning metals. Leaching solution (the leaching rates of Fe, V, and Ni are 42%, 40%, and 28%, respectively, and the loss rate of Al is 12%) and the spent FCC catalyst with basically complete molecular sieve structure after demetallization and resurrection;
[0032] Step 2. Use the spent FCC catalyst with basically complete molecular sieve structure obtained in step 1 as the aluminum source, and add 6.8 kilograms of silicon source (silica sol) and 2.0 kilograms of sodium source (sodium source is sodium hydroxide), 12.0 kg of water and 2.8 kg of directing agent (the molecular formula of the directing agent is...
Embodiment 3
[0035] This microwave heating prepares the method for Y-type molecular sieve from FCC waste catalyst, and its concrete steps are as follows:
[0036] Step 1. First, mix the spent FCC catalyst with the leaching mother liquor (concentration: 1wt% oxalic acid solution) at a liquid-solid ratio of 15:1mL / g, and then leaching for 50 minutes at a temperature of 50°C to obtain vanadium, nickel, and iron poisoning metals. The leaching solution (the leaching rates of Fe, V, and Ni are 63%, 58%, and 32%, respectively, and the loss rate of Al is 3%) and the spent FCC catalyst with basically complete molecular sieve structure after demetallization and resurrection;
[0037] Step 2. Use the spent FCC catalyst with basically complete molecular sieve structure obtained in step 1 as the aluminum source, and add 6.7 kilograms of silicon source (silica sol) and 1.9 kilograms of sodium source (sodium source is sodium hydroxide), 11.9 kg of water and 3.0 kg of directing agent (the molecular formul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com