Preparation method for 4-thiophenyl-thiophenol
A technology of phenylthio and benzene thiol, applied in the field of preparation of 4-phenylthio-benzene thiol, can solve problems such as difficulty in meeting industrialized mass production, cost control, environmental friendliness improvement cannot be said to be sufficient, etc. Production environment, lower synthesis costs, wide-ranging effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
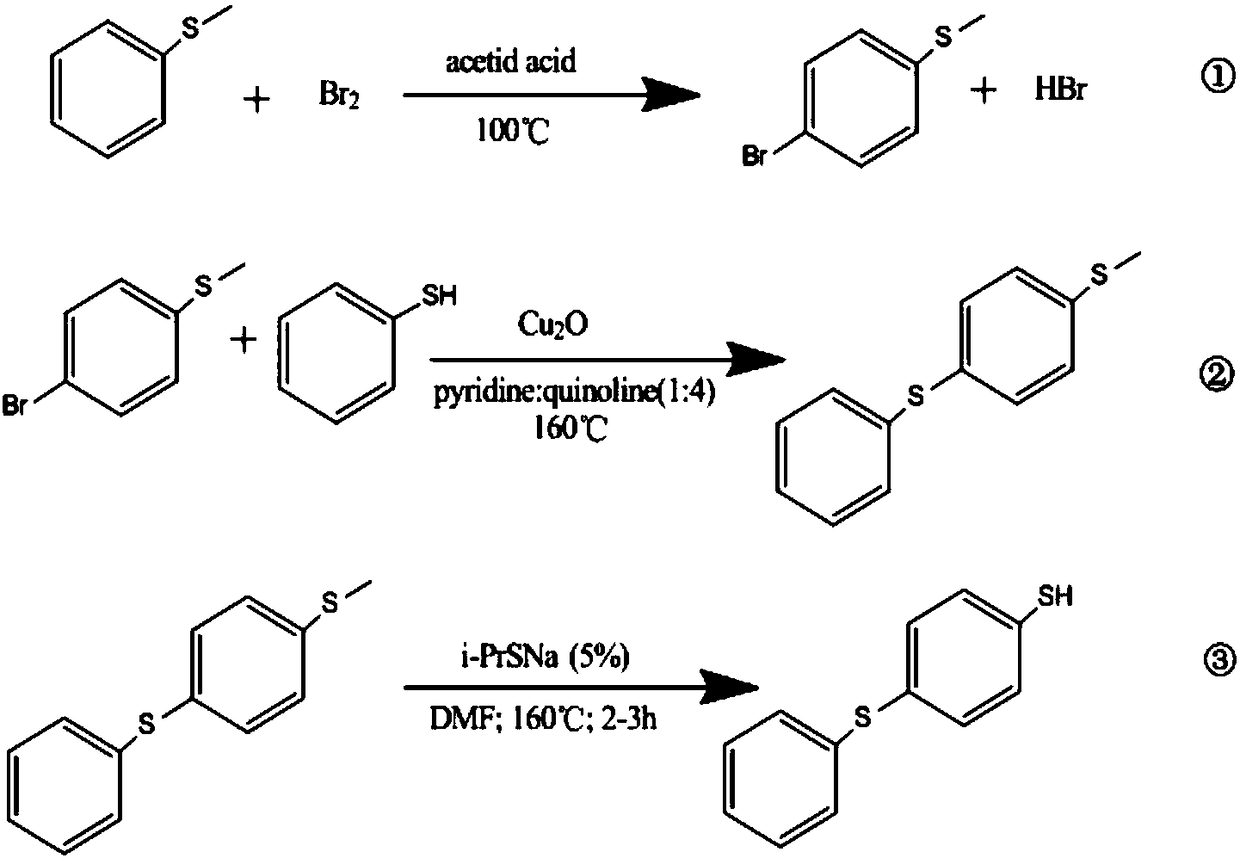
[0050]In the first embodiment, the present invention provides a method for preparing 4-phenylthio-benzenethiol, which includes: using phenylene sulfide as a raw material to perform a halogenation reaction to obtain halogenated phenylene sulfide. In the embodiment of the present invention wherein, the halogenated phenylene sulfide is 4-halogenated phenylene sulfide; the 4-halogenated phenylene sulfide is reacted with a sulfhydrylating reagent to obtain 4-phenylthio-phenylthiolate; Said 4-phenylthio-benzenethiol is hydrochloridized to obtain 4-phenylthio-benzenethiol.
[0051] Specifically, the preparation method includes the following steps:
[0052] 1) Halogenation reaction: add peroxide into a mixed solution containing phenylene sulfide, organic solvent, halogenating agent, and inorganic acid to carry out bromination reaction; after the reaction is completed, separate layers, and remove the organic solvent in the organic layer to obtain 4-halogenated Phenyl sulfide;
[0053...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0092] The second embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing 4-phenylthio-benzenethiol. The raw materials, solvents and water used in the preparation process are recovered and reused. That is to say, in this embodiment, except that the raw materials required for the initial reaction are all unused new products, in the subsequent continuous production, the aqueous phase produced in the middle of step 1)-step 3) of the present invention is , organic solvents for application. Wherein the total recycling rate of the aqueous phase and the organic phase is 80%, preferably more than 90%, more preferably more than 95%, most preferably close to 100%.
[0093] In this embodiment, in step 1), the halogenation reaction adopts a two-phase system. The halogenation reaction takes place in the organic phase, and the inorganic salts produced during the reaction remain in the aqueous phase.
[0094] Considering the recycling of the water layer in step 1), the inorgani...
Embodiment 1
[0102] 1) Halogenation reaction
[0103] In the glass-lined reaction kettle, add 34.0kg (400mol) of dichloromethane, 18.6kg (100mol) of phenylene sulfide, 9.27kg (90mol) of sodium bromide, 44.1kg (90mol) of 20% sulfuric acid, protect it with nitrogen, and stir The temperature of the mixed solution was raised to 40° C., and then 5.1 kg (45 mol) of 30% concentration hydrogen peroxide was added dropwise to the reactor, and the time for adding was controlled to be 2 hours. After the addition was completed, the reaction was continued for 2 hours. After the reaction is completed, the obtained reaction solution is left to stand for stratification, and the water layer is used for the acidification reaction of step 3); 2) The extraction process in.
[0104] 2) Sulfhydryl reaction
[0105] In the stainless steel reaction kettle, add N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (hereinafter referred to as NMP) 39.6kg (400mol), 50% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution 7.2kg (90mol), under the condition of stirr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com